Figures

Figure 1. Age distribution of patients with elevated CAVI. CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index.

Figure 2. Correlation matrix between vascular stiffness markers, risk factors, clinical and biochemical measurements in patients < 50 years of age. HTN: hypertension; IGT: impaired glucose tolerance; BMI: body mass index; WC: waist circumference; HC: hip circumference; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; TC: total cholesterol; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; TG: triglycerides; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; LAP: lipid accumulation product; VAI: visceral adiposity index; BFP: body fat percentage.

Figure 3. Correlation matrix between vascular stiffness markers, risk factors, clinical and biochemical measurements in patients ≥ 50 years. HTN: hypertension; IGT: impaired glucose tolerance; BMI: body mass index; WC: waist circumference; HC: hip circumference; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; TC: total cholesterol; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; TG: triglycerides; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; LAP: lipid accumulation product; VAI: visceral adiposity index; BFP: body fat percentage.

Figure 4. Significance of CAVIAge model components for detecting high arterial stiffness (Random Forest estimation) in the < 50 years group. DBP: diastolic blood pressure; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; GFR (EPI): glomerular filtration rate (calculated by Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation); LAP: lipid accumulation product index; VAI: visceral adiposity index.

Figure 5. Significance of the CAVI≥ 9 model components for detecting high arterial stiffness (Random Forest estimation) in the < 50 years group. DBP: diastolic blood pressure; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; GFR (EPI): glomerular filtration rate (calculated by Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation); LAP: lipid accumulation product index; VAI: visceral adiposity index.
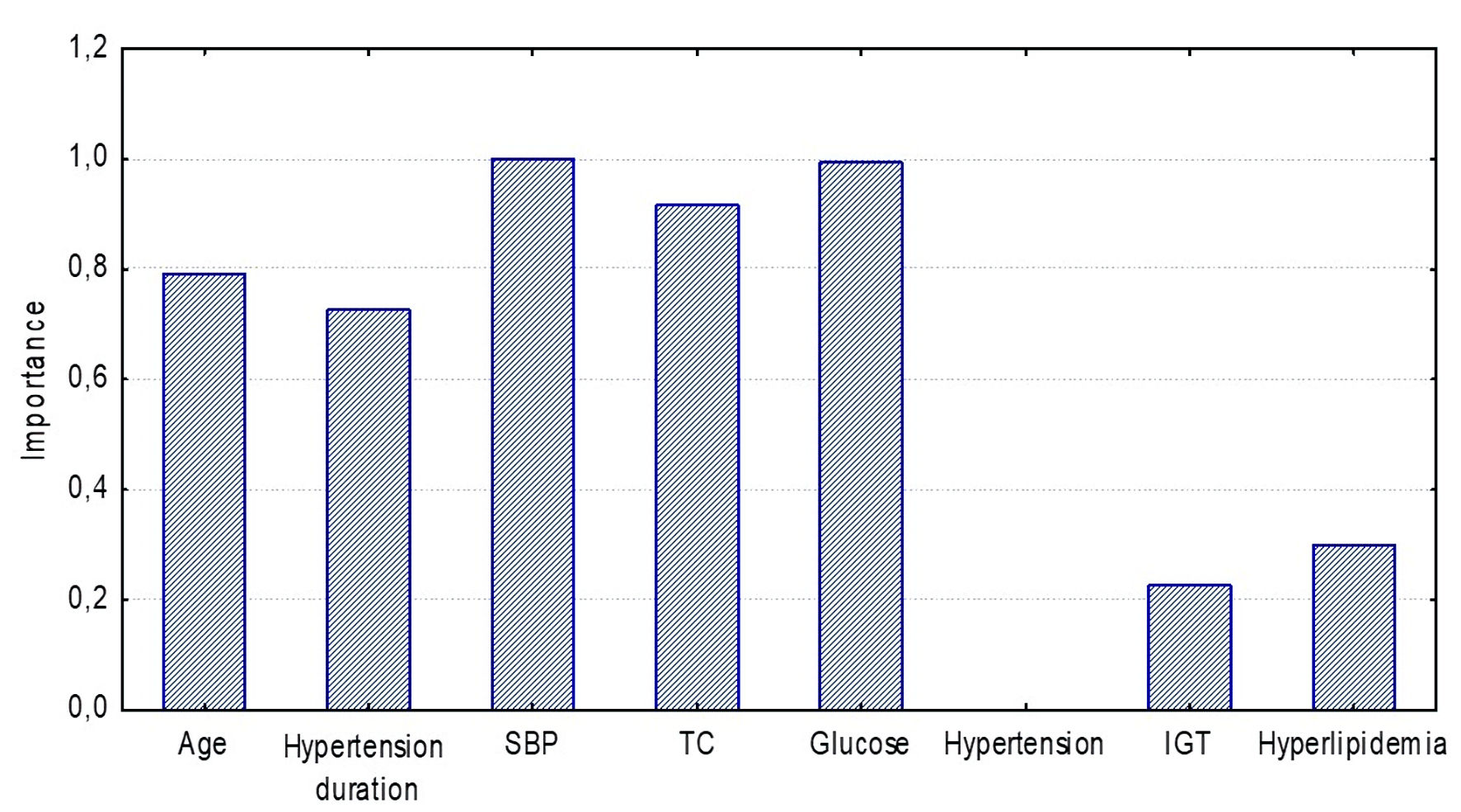
Figure 6. Significance of CAVIAge model components for detecting high arterial stiffness (Random Forest estimation) in the ≥ 50 years group. SBP: systolic blood pressure; TC: total cholesterol; IGT: impaired glucose tolerance.
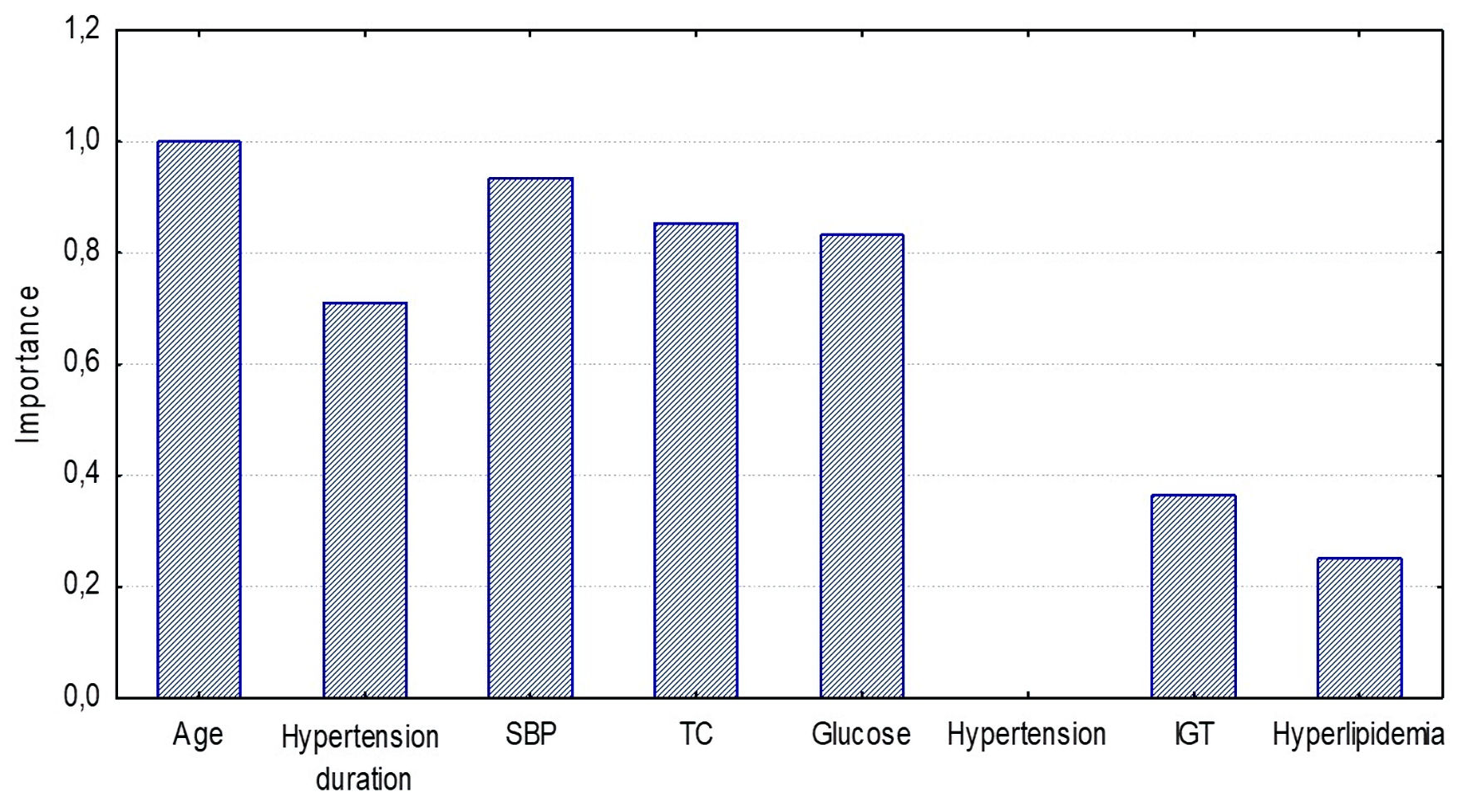
Figure 7. Significance of CAVI≥ 9 model components for detecting high arterial stiffness (Random Forest estimation) in the ≥ 50 years group. SBP: systolic blood pressure; TC: total cholesterol; IGT: impaired glucose tolerance.

Figure 8. ROC curves for the logistic regression model determining arterial stiffness using CAVIAge in the < 50 years group. ROC: receiver operating characteristic.

Figure 9. ROC curves for the logistic regression model determining arterial stiffness using CAVI≥ 9 in the < 50 years group. ROC: receiver operating characteristic.

Figure 10. ROC curves for the logistic regression model determining arterial stiffness using CAVIAge in the ≥ 50 years group. ROC: receiver operating characteristic.

Figure 11. ROC curves for the logistic regression model determining arterial stiffness using CAVI≥ 9 in the ≥ 50 years group. ROC: receiver operating characteristic.

Figure 12. Algorithm for choosing CAVI reference values in apparently healthy adults. CAVIAge: age-specific cardio-ankle vascular index reference values; CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index.
Table
Table 1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of Participants
| Parameter | All (n = 600) | Age < 50 (n = 378) | Age ≥ 50 (n = 222) | P value for age, < 50 vs. ≥ 50 |
|---|
| BMI: body mass index; WC: waist circumference; HC: hip circumference; SBP: systolic blood pressure; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; TC: total cholesterol; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; TG: triglycerides; GFR: glomerular filtration rate; LAP: lipid accumulation product; VAI: visceral adiposity index; BFP: body fat percentage; CAVIAge: patients with high arterial stiffness formed according to age-specific cardio-ankle vascular index reference values; CAVI≥ 9: patients with high arterial stiffness formed according to universal cardio-ankle vascular index reference values. |
| Age, years | 39.8 ± 18.3 | 28.78 ± 10.4 | 60.9 ± 7.5 | < 0.001 |
| Men, % | 43.17 | 42.28 | 40.09 | 0.88 |
| Weight, kg | 77.09 ± 19.14 | 72.9 ± 19.2 | 85.4 ± 16.4 | 0.02 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29.29 ± 7.3 | 28.87 ± 8.7 | 29.98 ± 5.2 | 0.85 |
| WC, cm | 80.79 ± 15.51 | 78.55 ± 14.01 | 91.9 ± 17.2 | 0.022 |
| Hypertension, % | 32.67 | 11.94 | 66.67 | 0.001 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 128.4 ± 15.33 | 125.8 ± 12.87 | 132.9 ± 17.6 | < 0.001 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 79.19 ± 9.32 | 78.08 ± 8.58 | 81.5 ± 10.2 | 0.032 |
| TC, mmol/L | 4.8 ± 1.20 | 4.49 ± 0.89 | 5.47 ± 1.45 | < 0.001 |
| LDL, mmol/L | 2.85 ± 1.26 | 2.46 ± 1.01 | 3.64 ± 1.28 | <0.001 |
| HDL, mmol/L | 1.37 ± 0.4 | 1.4 ± 0.45 | 1.29 ± 0.42 | 0.08 |
| TG, mmol/L | 1.82 ± 1.18 | 1.8 ± 1.15 | 1.9 ± 1.16 | 0.28 |
| Glucose, mmol/L | 5.30 ± 1.89 | 4.85 ± 1.1 | 6.2 ± 2.78 | < 0.001 |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 84.13 ± 18.06 | 79.86 ± 14.95 | 92.03 ± 20.45 | < 0.001 |
| GFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 97.5 ± 22.87 | 97.6 ± 18.56 | 68.1 ± 16.5 | < 0.001 |
| LAP | 41.28 ± 34.2 | 34.87 ± 34.1 | 54.1 ± 31.2 | < 0.001 |
| VAI | 1.99 ± 1.13 | 1.8 ± 1.05 | 2.3 ± 1.16 | 0.002 |
| BFP | 34.38 ± 8.6 | 31.3 ± 10.4 | 40.3 ± 8.3 | < 0.001 |
| High CAVIAge, % | 29.7 | 19.04 | 47.7 | < 0.001 |
| High CAVI≥ 9, % | 16.3 | 3.97 | 37.4 | < 0.001 |












