| Age (year) | 67.5 ± 13.0 | | | | |
| Male (%) | 43.8 | | | | |
| Height (cm) | 159.1 ± 10.1 | | | | |
| Weight (kg) | 64.4 ± 11.0 | | | | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.4 ± 3.2 | | | | |
| Duration of diabetes (year) | 11.3 ± 13.1 | | | | |
| Concomitant anti-diabetic medications | | | | | |
| Metformin (%) | 56.3 | | | | |
| DPP-4i (%) | 37.5 | | | | |
| SGLT2i (%) | 25 | | | | |
| GLP-1RA (%) | 12.5 | | | | |
| Sulfonylurea (%) | 12.5 | | | | |
| Glinide (%) | 6.3 | | | | |
| α-glucosidase inhibitor (%) | 0 | | | | |
| Complications | | | | | |
| Retinopathy (NDR/NPDR/PPDR/PDR) (%) | 87.5/12.5/0/0 | | | | |
| Nephropathy (stage 1/2/3/4/5) (%) | 68.5/26.3/5.2/0/0 | | | | |
| Coronary artery disease (%) | 12.5 | | | | |
| Body weight (kg) | 64.4 ± 11.0 | 63.4 ± 10.1 | | 0.80 | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.4 ± 3.2 | 25.0 ± 3.0 | | 0.74 | |
| Waist-hip ratio | 0.97 ± 0.04 | 0.96 ± 0.04 | | < 0.05 | |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.3 ± 0.7 | 7.0 ± 0.6 | 6.7 ± 0.4 | < 0.01 | < 0.001 |
| GA (%) | 17.4 ± 3.7 | 15.9 ± 2.8 | 15.1 ± 1.9 | < 0.001 | < 0.05 |
| Fasting CPI | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 2.3 ± 1.5 | | < 0.01 | |
| HOMA-β | 44.0 ± 35.6 | 66.9 ± 50.6 | | < 0.05 | |
| HOMA-IR | 2.4 ± 1.4 | 3.2 ± 4.2 | | 0.63 | |
| QUICKI | 0.35 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | | 0.56 | |
| AST (U/L) | 24.3 ± 9.4 | 24.8 ± 14.3 | | 0.30 | |
| ALT (U/L) | 30.6 ± 19.9 | 27.0 ± 16.1 | | 0.16 | |
| γGTP (U/L) | 28.4 ± 15.6 | 25.3 ± 14.0 | | 0.23 | |
| TG (mg/dL) | 143.8 ± 54.5 | 150.4 ± 66.2 | | 0.62 | |
| LDL-CHO (mg/dL) | 98.1 ± 27.1 | 101.2 ± 30.9 | | 0.49 | |
| HDL-CHO (mg/dL) | 57.7 ± 13.3 | 55.7 ± 12.6 | | 0.41 | |
| Cre (mg/dL) | 0.75 ± 0.13 | 0.79 ± 0.18 | | 0.17 | |
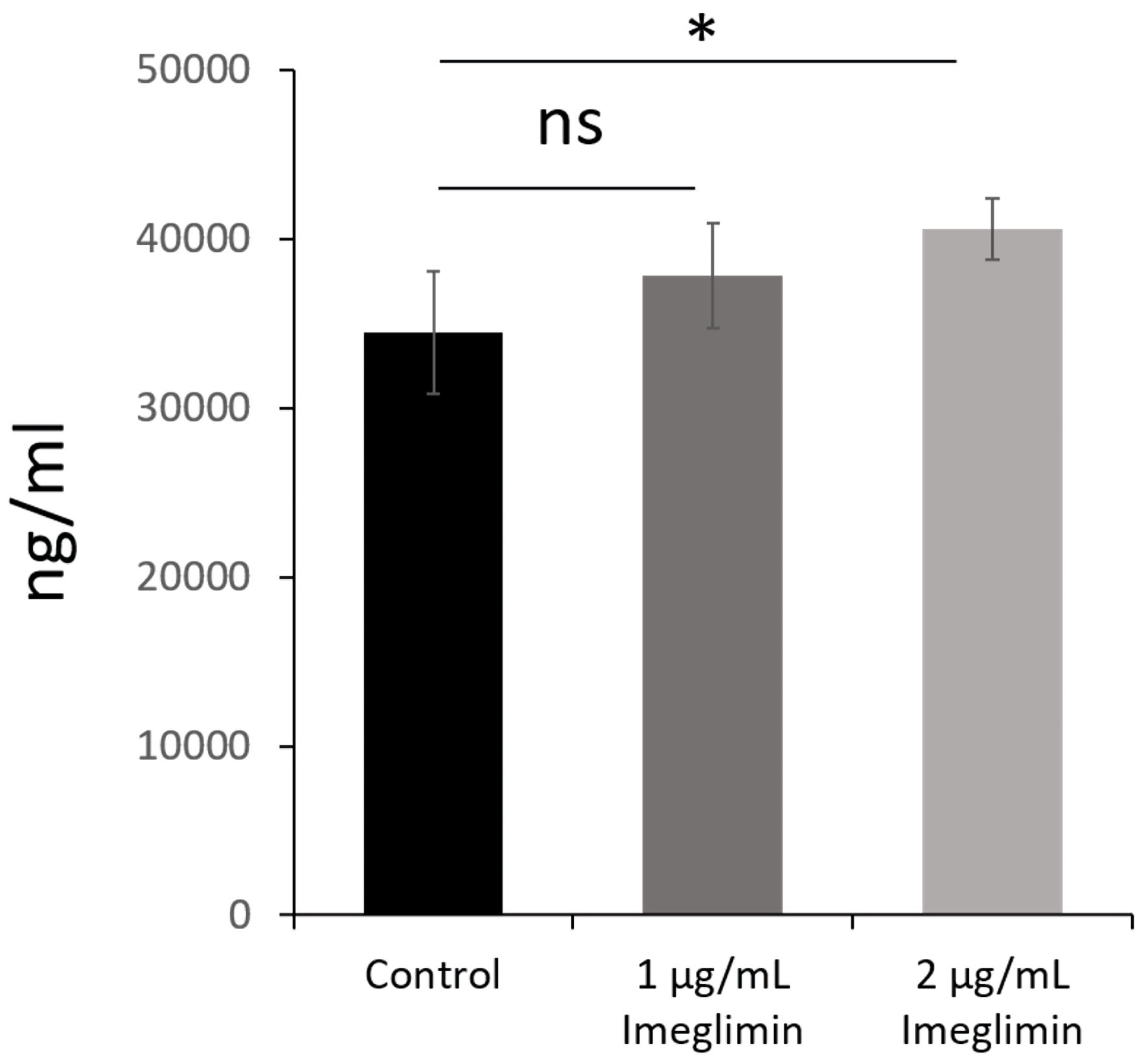
| Serum FGF21 (pg/mL) | 794.0 ± 1,236.2 | 483.1 ± 382.9 | | 0.11 | |
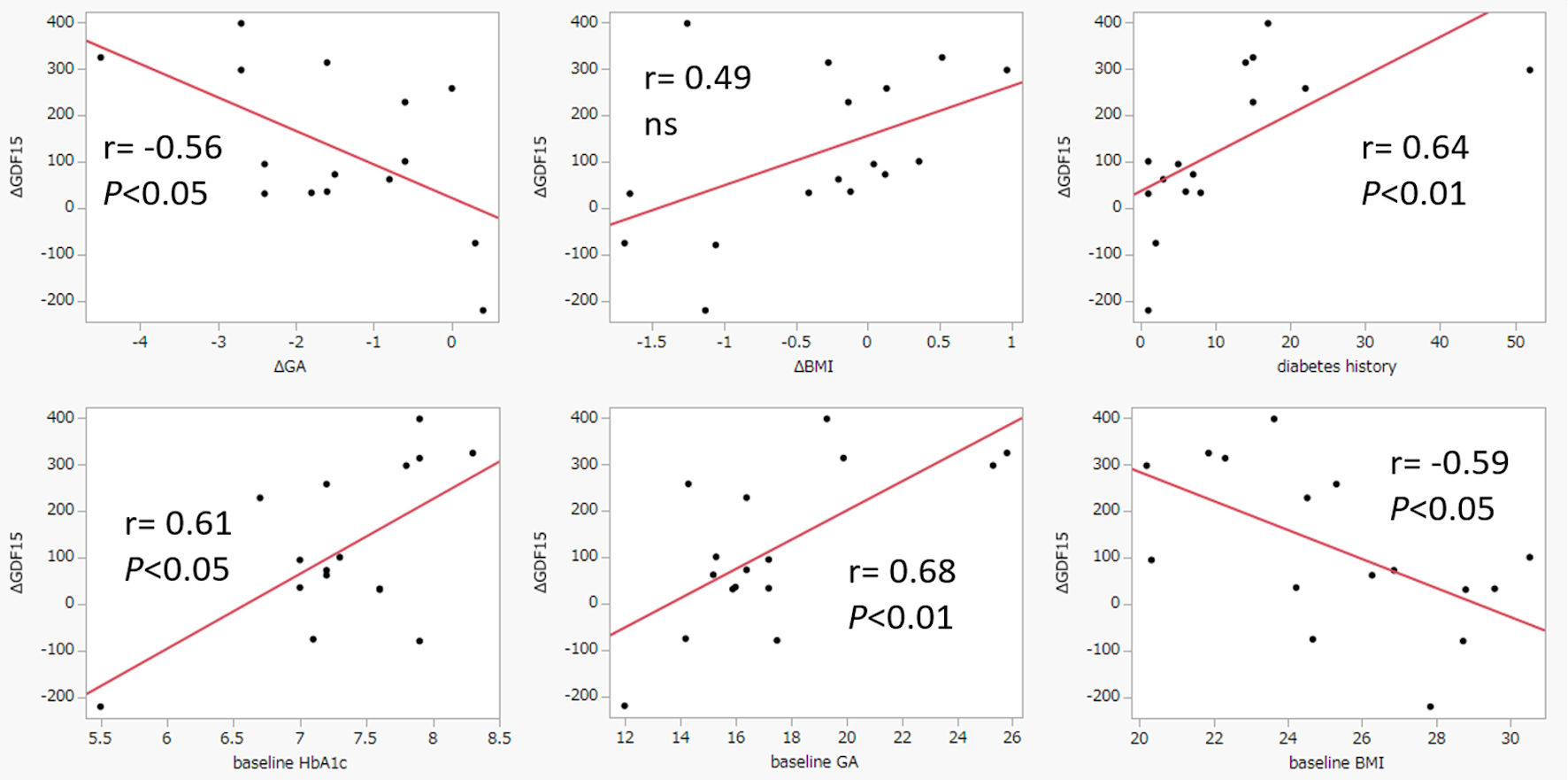
| Serum GDF15 (ng/mL) | 308.5 ± 134.0 | 425.7 ± 171.3 | | < 0.05 | |
| Urine 8-OHdG (ng/mL) | 7.2 ± 3.5 | 7.0 ± 2.5 | | 0.81 | |
| Type IV collagen (ng/mL) | 3.4 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | | 0.33 | |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 93.1 ± 57.7 | 89.5 ± 58.3 | | 0.32 | |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 0.17 ± 0.24 | 0.17 ± 0.25 | | 0.77 | |
| Skeletal muscle mass (kg) | 22.7 ± 5.4 | 22.7 ± 5.2 | | 0.99 | |
| Body fat percentage (%) | 31.5 ± 8.1 | 31.7 ± 9.6 | | 0.97 | |
| Resting metabolic rate (kcal) | 1,284.0 ± 319.9 | 1,198.0 ± 216.5 | | 0.45 | |
| Total energy expenditure (kcal) | 1,491.0 ± 371.4 | 1,391.3 ± 251.4 | | 0.44 | |
| Adverse effects of imeglimin during the study | |
| Metabolic and nutritional disorders | | Loss of appetite (6.3%, n = 1/16) |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | | Diarrhea (18.8%, n = 3/16), nausea (6.3%, n = 1/16), constipation (6.3%, n = 1/16), soft stool (6.3%, n = 1/16), abdominal bloating (6.3%, n = 1/16) |
| Laboratory abnormalities | | AST elevation (6.3%, n = 1/16) |