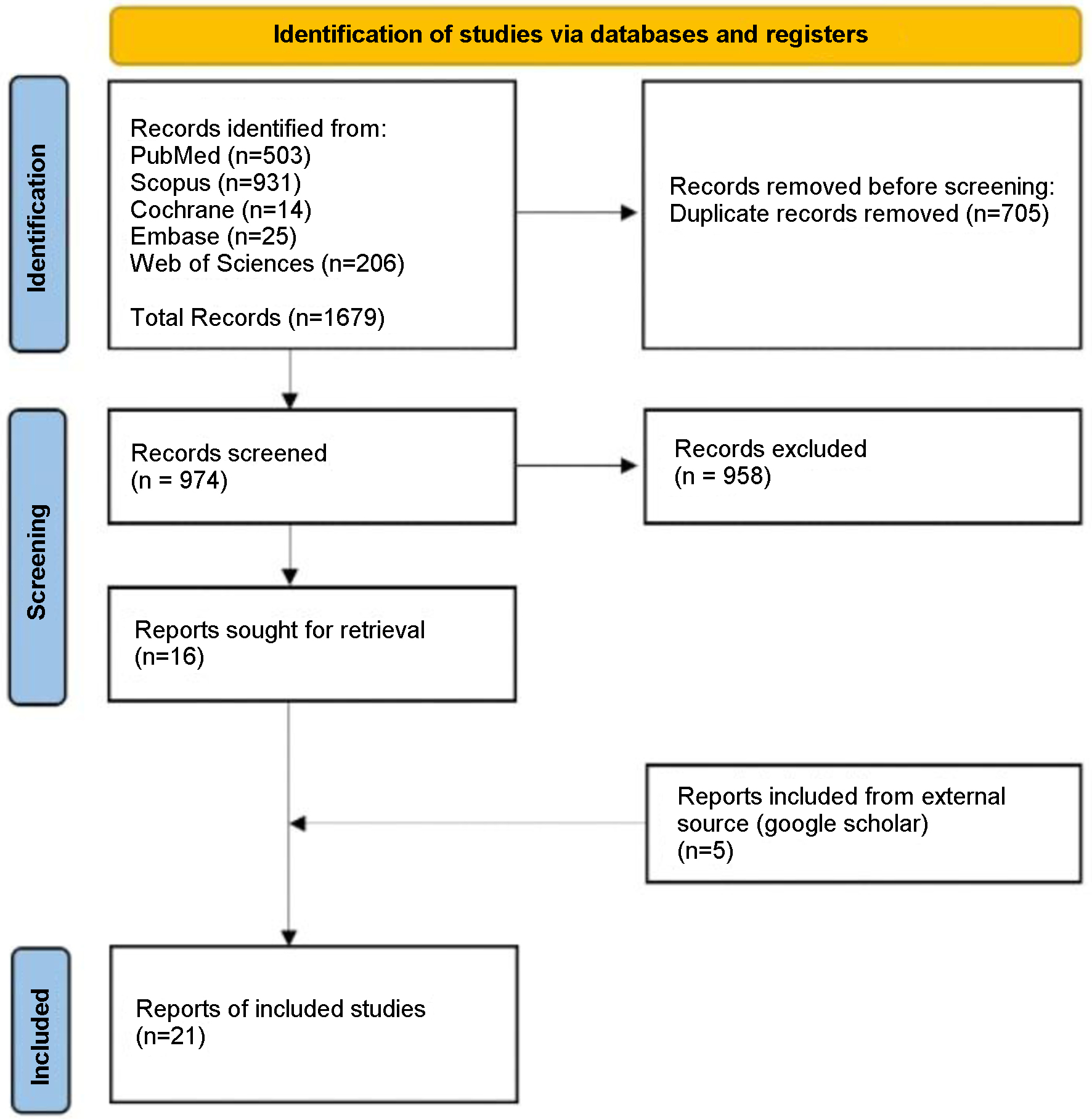
Figure 1. Article selection flow sheet per PRISMA 2020 guidelines [7].
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jocmr.elmerjournals.com |
Review
Volume 17, Number 1, January 2025, pages 1-13
Strategies in Management of Pulmonary Embolism With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review
Figure

Tables
| Questions | Dada et al, 2018 [28] | Barros-Gomes et al, 2018 [24] | Delgado et al, 2012 [10] | Hattori et al, 2019 [29] | Christiansen et al, 2017 [17] | De Oliveira et al, 2016 [27] | Gunta and Kamath, 2012 [11] | Konala et al, 2019 [18] | Lio et al, 2019 [13] | Bagate et al, 2018 [12] | Pan et al, 2019 [20] | Pelletier et al, 2010 [9] | Saleh Velez and Ortiz Garcia, 2021 [19] | Duy et al, 2019 [25] | Ozsancak Ugurlu et al, 2015 [23] | Xie et al, 2014 [16] | Chakir et al, 2021 [21] | Naidoo and Hift, 2011 [15] | Nam et al, 2015 [26] | Omar et al, 2013 [22] | Jayalakshmi et al, 2021 [14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection 1. Does the patient(s) represent(s) the whole experience of the investigator (center) or is the selection method unclear to the extent that other patients with similar presentation may not have been reported? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ascertainment 2. Was the exposure adequately ascertained? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Ascertainment 3. Was the outcome adequately ascertained? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Causality 4. Were other alternative causes that may explain the observation ruled out? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Causality 5. Was there a challenge/rechallenge phenomenon? | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Causality 6. Was there a dose response effect? | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Causality 7. Was follow-up long enough for outcomes to occur? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Reporting 8. Is the case(s) described with sufficient details to allow other investigators to replicate the research or to allow practitioners make inferences related to their own practice? | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Study | Year | Study design | Risk of bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Publication bias | Quality of evidence | GRADE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dada et al [28] | 2018 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Barros-Gomes et al [24] | 2018 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Delgado et al [10] | 2012 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Hattori et al [29] | 2019 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Christiansen et al [17] | 2017 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| De Oliveira et al [27] | 2016 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Gunta and Kamath [11] | 2012 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Konala et al [18] | 2019 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Lio et al [13] | 2019 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Bagate et al [12] | 2018 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Pan et al [20] | 2019 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Pelletier et al [9] | 2010 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Saleh Velez and Ortiz Garcia [19] | 2021 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Duy et al [25] | 2019 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Ozsancak Ugurlu et al [23] | 2015 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Xie et al [16] | 2014 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Chakir et al [21] | 2021 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Naidoo et al [15] | 2011 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Nam et al [26] | 2015 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Omar et al [22] | 2013 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Jayalakshmi et al [14] | 2021 | Case report | High | None | Direct | None | Not significant | Low | Low |
| Study | Age/sex | Risk factors | Presenting symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DVT: deep vein thrombosis; GI: gastrointestinal; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; OCP: oral contraceptive pill; PE: pulmonary embolism; SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus. | |||
| Pelletier et al, 2010 [9] | 35/F | Recent leg varicosal stripping, one spontaneous abortion, OCP use | Collapsed, altered consciousness, expressive aphasia, subtle facial asymmetry |
| Delgado et al, 2012 [10] | 76/F | Hypertension, dyslipidemia | Sudden right leg paresis and hypoesthesia |
| Gunta and Kamath, 2012 [11] | 16/F | Long car ride, OCP, family history of venous thromboses and PE, MTHFR mutation, antithrombin III deficiency | Unresponsive, labored respirations, shortness of breath, cough, leg pain for 2 days |
| Bagate et al, 2018 [12] | 44/M | Psychiatric disorder | Non-shockable cardiac arrest, impaired consciousness |
| Lio et al, 2019 [13] | 69/M | Testicular carcinoma | Signs of cardiogenic shock, questionable GI bleeding |
| Jayalakshmi et al, 2021 [14] | 52/M | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Naidoo and Hift, 2011 [15] | 38/F | Immobility, dilated cardiomyopathy, HIV on antiretroviral therapy | Dyspnea, pleuritic chest pain, right-sided hemiplegia |
| Xie et al, 2014 [16] | 55/F | History of varicose veins of lower extremities | Chest distress, dyspnea, loss of consciousness, sudden non-fluent language, dyskinesis of right extremities |
| Christiansen et al, 2017 [17] | 59/F | Post-operative day 2 abdominoplasty and liposuction, OCP | Left-sided weakness, dysarthria, acute respiratory distress |
| Konala et al, 2019 [18] | 82/M | Type 2 diabetes mellitus, previous lower extremity DVT | Loss of consciousness while urinating, mild dyspnea before syncope |
| Saleh Velez and Ortiz Garcia, 2021 [19] | 72/F | Not mentioned | Collapsed, comatose state, flaccid quadriplegia, cardiac arrest |
| Saleh Velez and Ortiz Garcia, 2021 [19] | 75/F | Hypertension | Mild dysarthria, right arm paresis, severe pleuritic pain, shortness of breath |
| Pan et al, 2019 [20] | 27/F | Post-operative day 7 C-section, Glenn anastomosis 7 years prior for cor biloculare | Dizziness, chest tightness, dysarthria, facial asymmetry, right hemiparesis |
| Chakir et al, 2021 [21] | 60/M | Type II diabetes, COVID-19 infection | Left hemiplegia, typical anginal chest pain, hypotonia, left sensory deficit |
| Omar et al, 2013 [22] | 69/M | Post-operative day 1 right total hip replacement, hypertension, dyslipidemia, prior surgical repair of iliac artery aneurysm | Shortness of breath, wheezing, confusion, aphasia, right-sided weakness |
| Ozsancak Ugurlu et al, 2015 [23] | 64/F | Not mentioned | Shortness of breath, chest pain, recurrent syncope, convulsion |
| Barros-Gomes et al, 2018 [24] | 68/F | Hypertension, tobacco abuse, COPD | Facial droop, right arm weakness, aphasia |
| Duy et al, 2019 [25] | 53/F | Three prior ischemic strokes | Unconsciousness, dyspnea, right hemiplegia |
| Nam et al, 2015 [26] | 69/F | Not significant | Dyspnea, drowsy mental status, right-sided hemiplegia after surgery |
| De Oliveira et al, 2016 [27] | 41/F | Post-operative day 10 lap cholecystectomy | Dysarthria, acute respiratory distress, left calf tenderness |
| Dada et al, 2018 [28] | 55/M | Not mentioned | Left facial droop, left-sided weakness, garbled speech |
| Hattori et al, 2020 [29] | 68/F | History of multiple cerebral emboli, SLE on prednisolone | Dysarthria, dysphagia, left facial paralysis |
| SD: standard deviation. | |
| Patients, N | 22 |
| Case reports, N | 20 |
| Case series, N | 1 |
| Female, N (%) | 15 (68.18%) |
| Male, N (%) | 7 (31.82%) |
| Mean patient age, years | 56.68 (SD: 16.8) |
| Median patient age, years | 59.5 |
| Predisposing factors | N | % |
|---|---|---|
| ART: antiretroviral therapy; AT: antithrombin; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; DVT: deep vein thrombosis; HIV: human immunodeficiency virus; OCP: oral contraceptive pill; PE: pulmonary embolism; SLE: systemic lupus erythematosus. | ||
| PE | ||
| OCP use | 4 | 18.18 |
| Post major surgical interventions | 4 | 18.18 |
| Immobility | 2 | 9.09 |
| Varicose veins | 2 | 9.09 |
| Prior lower extremity DVT | 1 | 4.55 |
| Family history of venous thromboses and PE | 1 | 4.55 |
| Homozygous for MTHFR mutation/ATIII deficiency | 1 | 4.55 |
| Tobacco abuse | 1 | 4.55 |
| COPD | 1 | 4.55 |
| HIV on ART | 1 | 4.55 |
| SLE | 1 | 4.55 |
| Pregnancy, especially first 6 weeks postpartum | 1 | 4.55 |
| Compression by mass (testicular carcinoma) | 1 | 4.55 |
| History of Glenn anastomosis | 1 | 4.55 |
| COVID-19 infection | 1 | 4.55 |
| Ischemic stroke | ||
| Hypertension | 5 | 22.73 |
| Dyslipidemia | 3 | 13.64 |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | 2 | 9.09 |
| Prior thromboembolic strokes | 2 | 9.09 |
| Tobacco abuse | 1 | 4.55 |
| Study | Location of PE | Treatment of PE | Location of stroke | Treatment of stroke | PFO and treatment | DVT | PFO with thrombus | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACA: anterior cerebral artery; DVT: deep vein thrombosis; LMWH: low molecular weight heparin; ICA: internal carotid artery; IV: intravenous; IVC: inferior vena cava; MCA: middle cerebral artery; MT: mechanical thrombectomy; PE: pulmonary embolism; PFO: patent foramen ovale; rt-PA: recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. | ||||||||
| Pelletier et al, 2010 [9] | Bilateral | Heparin infusion | Left tempoparietal | rt-PA, IVC filter | Present, closed | Negative | Marked improvement | |
| Naidoo and Hift, 2011 [15] | Bilateral | Streptokinase | Left frontoparietal | Not treated, since neuro improved | Absent | Positive, right | Marked improvement | |
| Delgado et al, 2012 [10] | Bilateral segmental, subsegmental | Heparin infusion | Left ACA | rt-PA | Present, not closed | Not mentioned | Marked improvement | |
| Gunta and Kamath, 2012 [11] | Bilateral main | Heparin infusion, LMWH IVC filter | Left striatocapsular and internal capsule | MT followed by aspirin | Present, planned closure at later date | positive | Marked improvement | |
| Omar et al, 2013 [22] | Descending trunk, right main segmental/subsegmental | IVC filter | Left MCA | MT | Present, not a candidate for PFO closure | Not mentioned | Bed-ridden and non-verbal | |
| Ozsancak Ugurlu et al, 2015 [23] | Bilateral main into lobar branches | Percutaneous embolectomy (MT), heparin infusion | Left occipital and bilateral cerebellar lobes | Not treated | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Marked improvement | |
| Xie et al, 2014 [16] | Bilateral | Urokinase, LMWH, aspirin and clopidogrel | Left temporal, parietal, insular lobes and basal ganglia | Increased aspirin and clopidogrel dose | Absent | Negative | Marked improvement, recurrence of PE 10 months later | |
| Nam et al, 2015 [26] | Bilateral | Surgical embolectomy | Left MCA and multifocal, embolic infarctions in right cerebrum | Decompressive craniectomy | Present, closed | Not mentioned | Biatrial thrombus across PFO | Long-term ventilatory support, no neuro improvement |
| De Oliveira et al, 2016 [27] | Not mentioned | Surgical thrombectomy | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Present, closed | Present, left | Right atrial thrombus straddling PFO | Marked improvement |
| Christiansen et al, 2017 [17] | Bilateral lobar and segmental | rt-PA, LMWH, aspirin | Right MCA | rt-PA, MT | Present, not closed | Negative | Abdominal hematoma post thrombolysis, marked improvement | |
| Barros-Gomes et al, 2018 [24] | Bilateral | MT | Left ICA | Not treated | Present, not closed | Not mentioned | Thrombus in PFO | Not reported |
| Bagate et al, 2018 [12] | Bilateral | Heparin infusion | Left parietal lobe | Not treated | Present, not closed | Not mentioned | Brain death | |
| Dada et al, 2018 [28] | Main | Surgical clot removal, heparin infusion | Left temporal occipital lobe | rt-PA not given, outside window | Present, closed | Positive, right | Biatrial thrombus straddling PFO | Marked improvement |
| Duy et al, 2019 [25] | Bilateral | Percutaneous thrombectomy (MT), heparin infusion | Left MCA | MT | Present, anticoagulant therapy only | Negative | Marked improvement | |
| Konala et al, 2019 [18] | Bilateral main | rt-PA, heparin infusion, IVC filter | Left caudate/putamen area | Not treated | Present, patient refused closure | Positive, bilateral | Biatrial thrombus straddling PFO | Marked improvement |
| Hattori et al, 2020 [29] | Bilateral main | Surg pulmonary embolectomy, IVC filter | Brain stem and left occipital lobe | Not treated | Present, closed | Positive | Thrombus straddling PFO | Marked improvement |
| Lio et al, 2019 [13] | Bilateral lobar | Heparin infusion | Basilar artery occlusion | MT | Present, not closed | Not mentioned | Dead | |
| Pan et al, 2019 [20] | Left inferior and right lobar | LMWH | Left basal ganglia | Not treated | Absent | Negative | Marked improvement | |
| Saleh Velez and Ortiz Garcia, 2021 [19] | Bilateral | Medical therapy | Right ICA | Medical therapy | Present | Negative | Dead | |
| Saleh Velez and Ortiz Garcia, 2021 [19] | Bilateral main | Catheter-directed thrombolysis, IV heparin | Left MCA | rt-PA deferred, unknown, last time well | Present | Positive, left | Marked improvement | |
| Jayalakshmi et al, 2021 [14] | Not mentioned | Heparin | Right MCA | Decompressive craniotomy | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Marked improvement | |
| Chakir et al, 2021 [21] | Bilateral | LMWH | Right MCA | Aspirin | Absent | Negative | Slight improvement in neuro | |
| Treatment approach for PE | Number of cases |
|---|---|
| AC: anticoagulation; LMWH: low molecular weight heparin; IVC: inferior vena cava; MT: mechanical thrombectomy; PE: pulmonary embolism; rt-PA: recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. | |
| Thrombolysis | 5 |
| rt-PA + AC | 2 |
| Streptokinase alone | 1 |
| Urokinase + AC | 1 |
| Catheter thrombolysis + AC | 1 |
| Heparin | 6 |
| Post rt-PA | 2 |
| Post MT | 2 |
| With craniotomy | 1 |
| Only | 1 |
| LMWH | 2 |
| Only | 1 |
| Aspirin | 1 |
| IVC filter only | 1 |
| Medical therapy only | 1 |
| Catheter-directed thrombectomy | 3 |
| MT | 1 |
| Percutaneous thrombectomy + heparin | 2 |
| Surgical approach | 4 |
| Surgical embolectomy/thrombectomy | 2 |
| Surgical pulmonary embolectomy + IVC | 1 |
| Surgical clot removal + heparin | 1 |
| Findings | Present | Absent | Not mentioned |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIS: acute ischemic stroke; DVT: deep vein thrombosis; PE: pulmonary embolism; PFO: patent foramen ovale. | |||
| PFO | 16 (72.72%) | 4 (18.18%) | 2 |
| PFO with thrombus | 6/16 (37.5%) | ||
| DVT | 7 (31.81%) | 7 (31.81%) | 8 |
| Treatment modality | Symptom improvement and survival | Deterioration in functional status | Mortality | Not reported | Total cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIS: acute ischemic stroke; PE: pulmonary embolism. | |||||
| Anticoagulation | 5 (62.5%) | 2 25.0%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0 (0.0%) | 8 |
| Thrombolysis | 5 (100.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 5 |
| Catheter-directed thrombectomy | 2 (66.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (33.3%) | 3 |
| Surgical thrombectomy | 3 (75.0%) | 1 (25.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 4 |
| Treatment without anticoagulation or thrombolytic therapy | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (50.0%) | 1 (50.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 |
| Total | 15 (68.2%) | 4 (18.2%) | 2 (9.1%) | 1 (4.5%) | 22 |