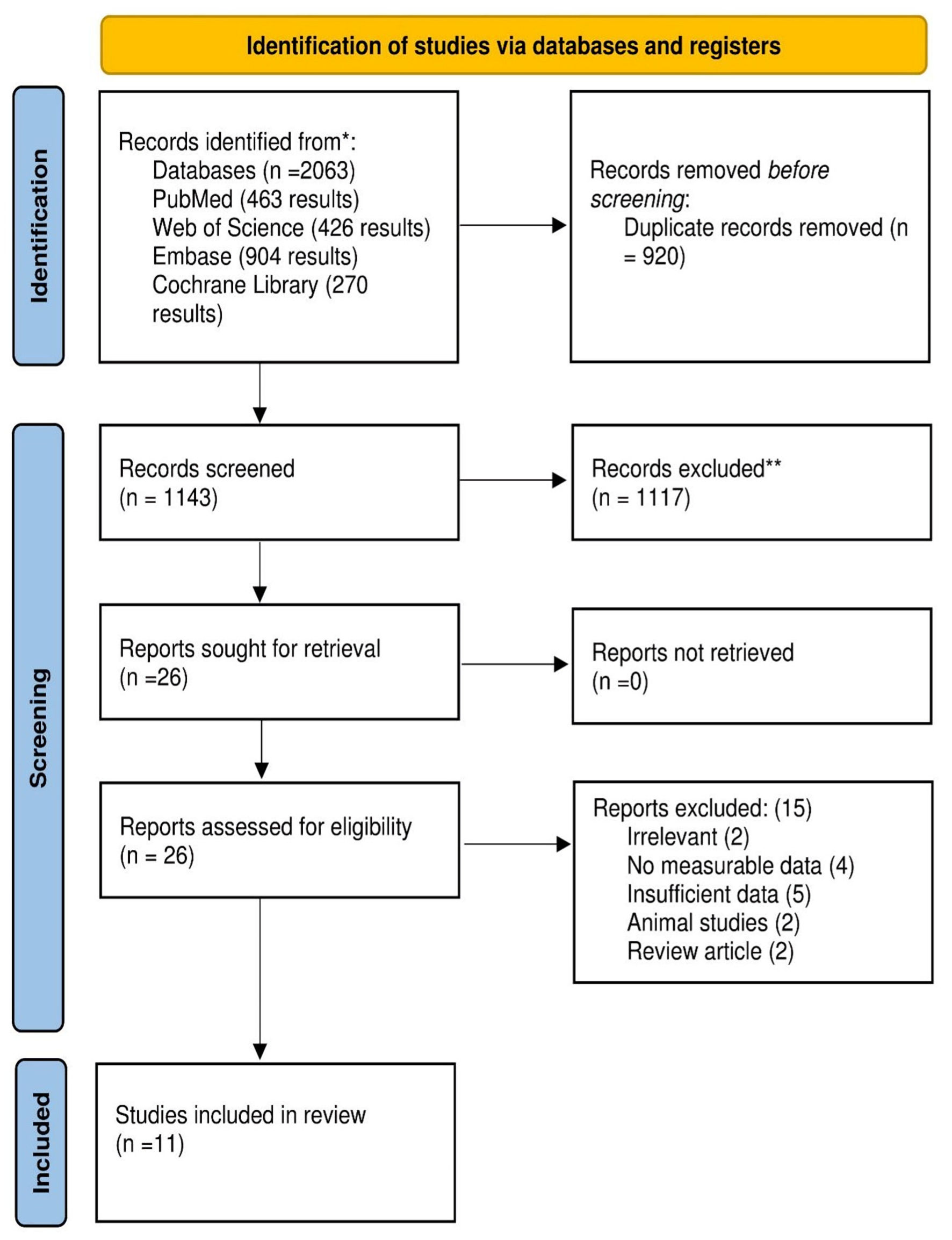
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jocmr.elmerjournals.com |
Original Article
Volume 17, Number 2, February 2025, pages 76-88
Impact of Prior Metformin Use on Stroke Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Updated Meta-Analysis
Figures


Tables
| Study | Study design | Country | Total participants | Time frame | Duration of follow-up | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | Results | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin | Non-metformin | ||||||||
| AIS: acute ischemic stroke; mRS: modified Rankin Scale; CT: computed tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage; SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage; ICD: International Classification of Diseases; IVT: intravenous thrombolysis; EVT: endovascular treatment; END: early neurological deterioration; END-prog: END as stroke progression; END-SHT: END as symptomatic hemorrhagic transformation; RT: reperfusion therapy; MT: mechanical thrombectomy; ASPECTS: Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; LAA: large-artery atherosclerosis; CES: cardioaortic embolic stroke; SVO: small-vessel occlusion; WHO: World Health Organization; NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; N/A: not available. | |||||||||
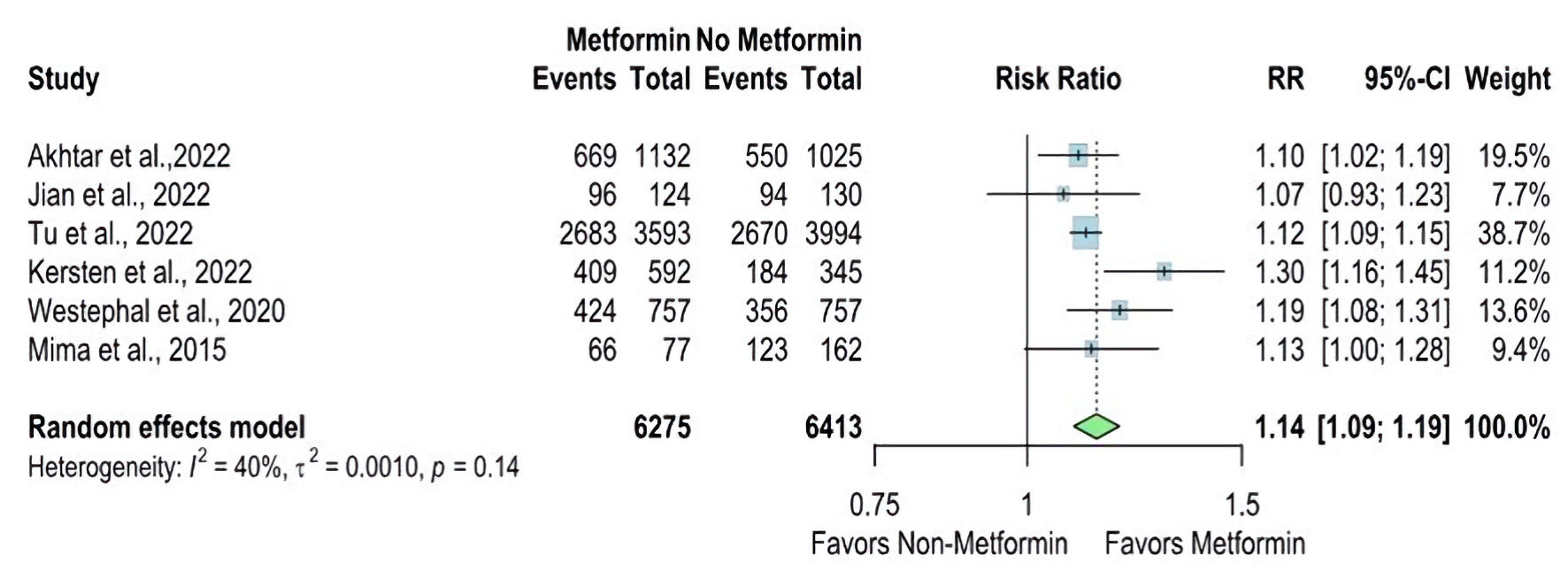
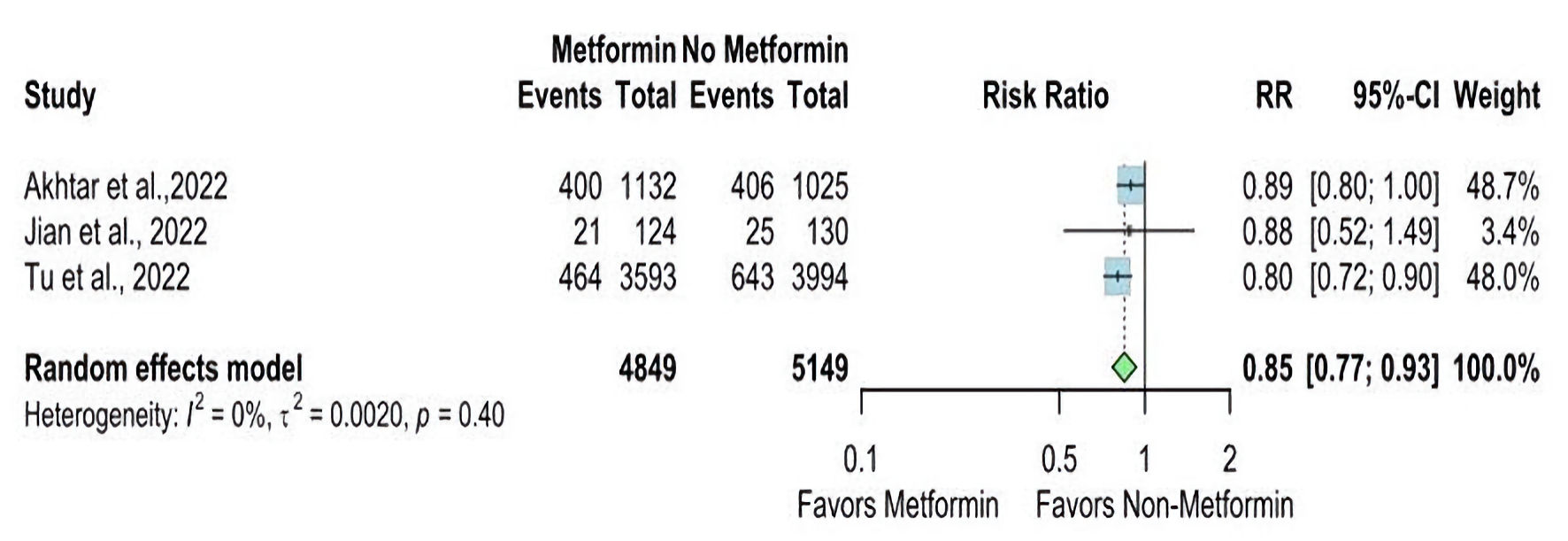
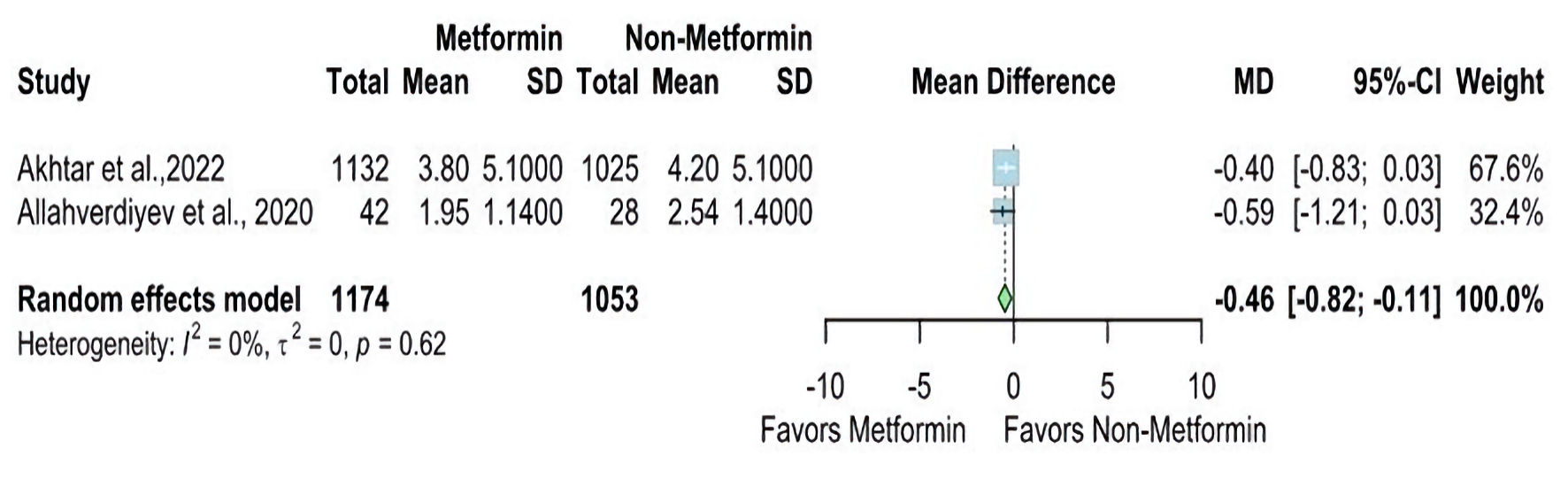
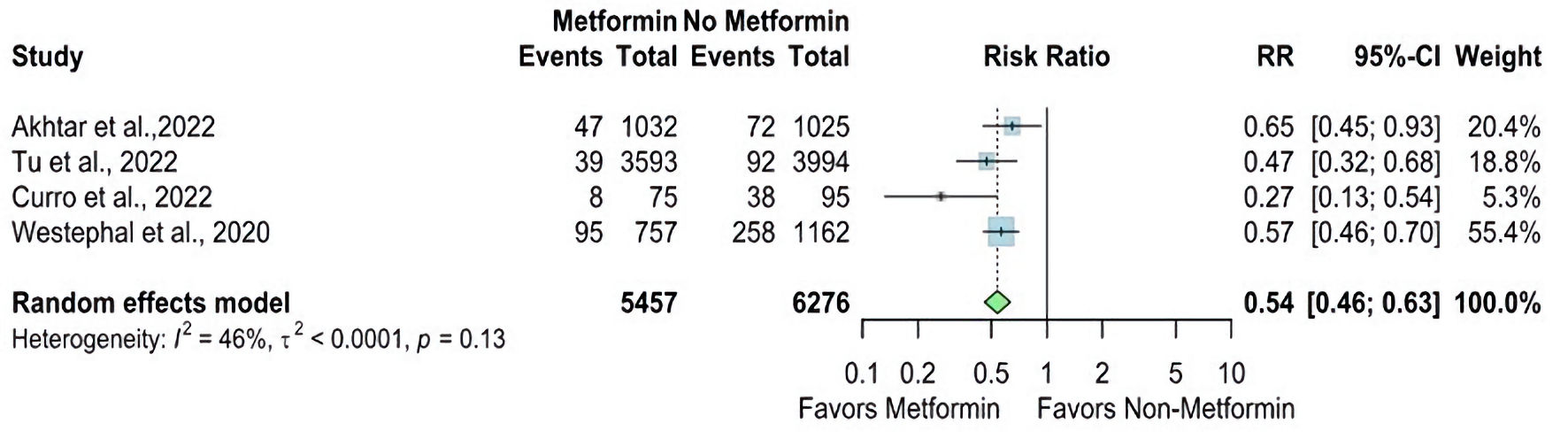
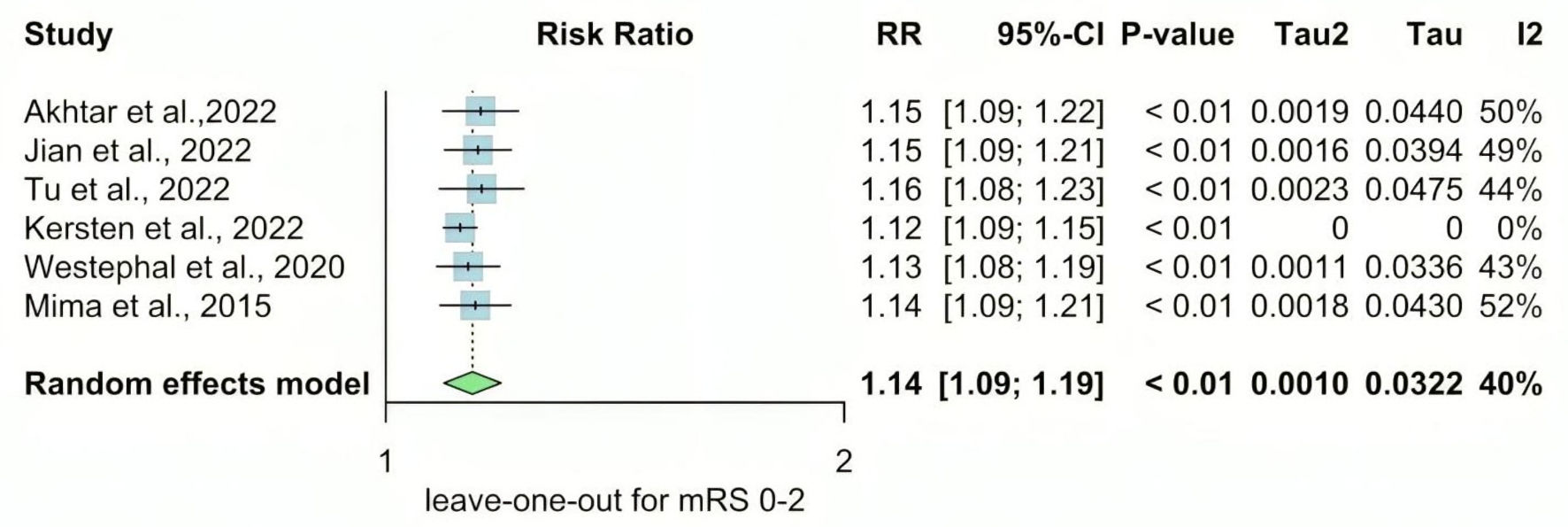
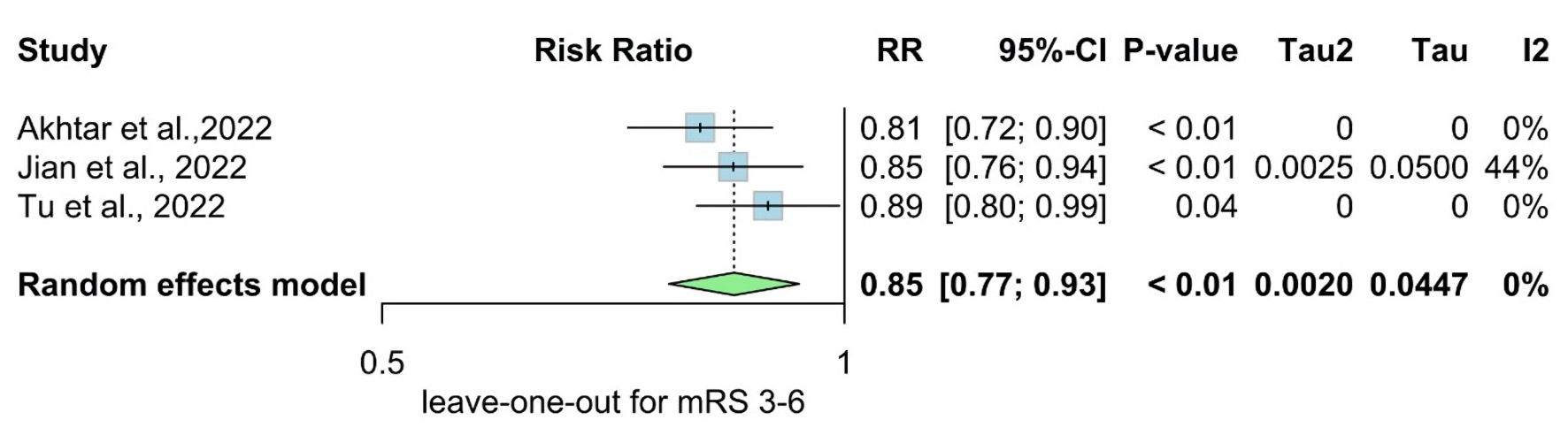
| Akhtar et al, 2022 [14] | Prospective cohort | Qatar | 1,132 | 1,025 | 2013 - 2020 | N/A | All patients with acute stroke admitted to the Hamad General Hospital (HGH) and prospectively entered the Qatar Stroke database | Patients with stroke mimics, transient ischemic attacks, ICH, cerebral venous thrombosis, and new-onset diabetes | Patients with diabetes on chronic pre-stroke treatment with metformin had improved recovery following the ischemic event. |
| Jian et al, 2023 [15] | Retrospective cohort | China | 124 | 130 | 2017 - March 2021 | N/A | Patients: 1) were diagnosed with AIS by cranial CT or MRI; 2) the time from onset to admission was < 7 days; 3) were diagnosed with T2DM, including self-reported diabetes and newly diagnosed diabetes at admission. | Patients with: 1) unclear hypoglycemic therapy before stroke onset or after admission; 2) a mRS > 1 before stroke onset; 3) an estimated glomerular filtration rate < 45 mL/min; 4) metformin withdrawal within 90 days; or 5) lost to follow-up. | Patients with diabetes who were treated with metformin continuously before stroke onset and after admission had a better 90-day functional outcome. |
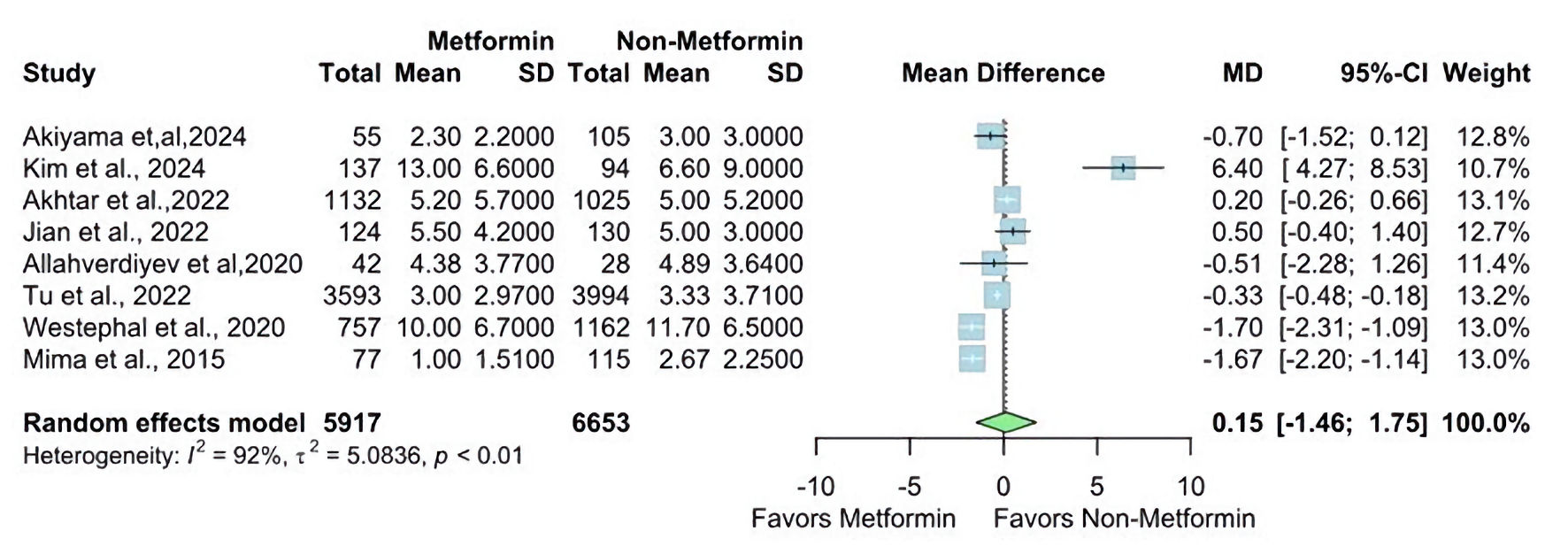
| Tu et al, 2022 [22] | Prospective cohort | China | 3,593 | 3,994 | August - September 2019 | 12 months | All patients with the first-ever stroke (ischemic stroke (ICD63), ICH (ICD61), and SAH (ICD60)) and T2DM were included. Patients were eligible for inclusion if admitted to the hospitals with a stroke defined according to the WHO criteria and with symptom onset within 14 days. | Hospitals with a sample size of less than 50 and a follow-up rate of less than 80% will be excluded. Also, patients with 1) lack of informed consent; 2) lost to follow-up; and 3) lack of crucial clinical information (such as MT information (yes or no) and functional scores during follow-up) would be excluded. | Metformin use in stroke patients with T2DM resulted in a less severe stroke and lower fatality and disability rates. |
| Kersten et al, 2022 [17] | Retrospective cohort | Netherlands | 592 | 345 | 2017 - June 2021 | N/A | All consecutive patients with AIS and known T2DM aged 18 years or older were included between 2017 and June 2021 | N/A | Pre-stroke metformin use was associated with favorable outcomes in a large group of patients with T2DM after AIS. |
| Mima et al, 2016 [7] | N/A | Japan | 77 | 163 | April 2010 - September 2014 | N/A | Only patients with brain infarction complicated by DM who were admitted to National Hospital Organization Kyushu Medical Center between April 2010 and September 2014 were included. | Mild stroke severity | Metformin use in stroke patients with T2DM resulted in a less severe stroke and lower fatality and disability rates. |
| Westphal et al, 2020 [19] | Multicenter retrospective analysis | Switzerland | 757 | 757 | N/A | N/A | Data from patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes before stroke or at the time of stroke based on admission HbA1c values ≥ 6.5% were included. | Either diagnosed with type-1 diabetes or diabetes type was not specified | Stroke patients with diabetes on treatment with metformin receiving IVT had less severe strokes on admission and a better functional outcome at 3 months. This suggests that metformin has a protective effect, resulting in less severe strokes and beneficial thrombolysis outcomes. |
| Kim et al, 2024 [12] | Cohort | Korea | 137 | 94 | March 2015 - September 2023 | N/A | Patients with AIS with large artery occlusion of the anterior circulation who received EVT. Among these EVT-patients diagnosed as T2DM before stroke or who had an admission of HbA1c ≥ 6.5% at the time of stroke. | Patients with a mRS score ≥ 2 before stroke, patients without initial brain CT or MRI scan within 24 h of stroke onset, patients with an ASPECTS > 6, and patients without a 3-month mRS score | Subjects with prior metformin use, before EVT, the initial NIHSS and infarct volume were lower than those without prior metformin use. Prior metformin use could reduce the risk of END-prog and END-SHT after EVT and prior. Metformin use was associated with a 3-month mRS of 0 to 2 after EVT in patients with T2DM. |
| Akiyama et al, 2024 [13] | Retrospective cohort | Japan | 55 | 105 | 2010 - 2021 | N/A | Only patients with ischemic stroke subtypes defined as LAA, CES, or SVO were consecutively selected, and T2DM | Patients’ wide variety of etiologies of stroke, patients without antidiabetic agents before stroke, with only insulin, and with missing data on medication, and patients with a mRS score ≥ 3 before stroke onset were excluded. | Metformin treatment before stroke was associated with lower stroke severity and favorable functional outcome. |
| Allahverdiyev et al, 2020 [20] | Cohort | Turkey | 42 | 28 | January 2017 - April 2019 | N/A | Patients with AIS and T2DM | Patients had a hemorrhagic stroke, T1DM, severe renal failure and severe deterioration in daily life activities before stroke (mRS score ≥ 3) | There was not any significant difference between the groups of severity and prognosis of AIS. |
| Abbasi et al, 2018 [21] | RCT | Iran | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3 months | Ischemic stroke patients and focal neurological symptoms | Patients with ICH, SAH, subdural hematoma (SDH), hypoglycemia, contraindications for metformin use, venous sinus thrombosis, and drug side effects and diabetic patients. | There was a significant difference in metformin taking in the reduction of NIHSS score in non-diabetic stroke patients. There was a significant association between metformin taking and a decrease in NIHSS scores in patients with cortical ischemic stroke. |
| Curro et al, 2022 [18] | Retrospective cohort | N/A | Overall = 170 | February 2014 - December 2019 | N/A | Patients underwent IVT within 4.5 h after ischemic stroke onset. Patients underwent MT within a time frame from symptom onset to treatment ≤ 6 h for anterior circulation and ≤ 24 h for posterior circulation. | Patients with large territorial infarction are defined as ASPECTS < 5, hospital arrival beyond the time window, and elevated bleeding risk for IVT. | A lower mRs was associated with lower glycemia and admission NIHSS (aNIHSS) in all RT and MT; lower aNIHSS and younger age in IVT. | |
| Country | Author, year | Study design | Group | Number of participants | Basic patient characteristics | Risk factors | On admission parameters | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | Sex (males), n | BMI, mean (SD) | HbA1c %, mean (SD) | DBP, mean (SD) | SBP, mean (SD) | Hypercholesterolemia, n | Hypertension, n | Atrial fibrillation, n | Current smoking, n | Stroke-to-needle-time (min), mean (SD) | CHD, n | Glucose (mg/dL), mean (SD) | Creatinine (mmol/L), mean (SD) | Platelets, mean (SD) | INR, mean (SD) | History of previous stroke, n | |||||
| BMI: body mass index; SD: standard deviation; CHD: coronary heart disease; INR: international normalized ratio; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; SBP: systolic blood pressure; MET: metformin; HbA1c: hemoglobin A1c. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Qatar | Akhtar et al, 2022 [14] | Prospective cohort | Met + | 1,132 | 54.4 (13.2) | 910 | - | 7.5 (2.5) | - | - | 623 | 848 | 48 | 350 | 59.9 (35.4) | 131 | - | 95.8 (64.4) | - | - | 134 |
| Met - | 1,025 | 54.6 (13.1) | 842 | - | 7.6 (4.3) | - | - | 537 | 766 | 42 | 276 | 59.8 (39.8) | 112 | - | 97.0 (66.6) | - | - | 137 | |||
| China | Jian et al, 2023 [15] | Retrospective cohort | Met + | 124 | 63.16 (12.33) | 87 | - | 8.1 (2) | 85.88 (13.93) | 152.39 (23.26) | 11 | 99 | 7 | 36 | - | 19 | 224.6 (40.5) | 57.43 (16.45) | 206.35 (70.06) | 0.93 (0.08) | 39 |
| Met - | 130 | 65 (13.49) | 78 | - | 8.5 (2.2) | 82.8 (12.9) | 148.5 (22.4) | 18 | 95 | 12 | 40 | - | 29 | 234.52 (74.16) | 59.73 (19.34) | 199.67 (74.22) | 0.93 (0.07) | 39 | |||
| China | Tu et al, 2022 [22] | Prospective cohort | Met + | 3,593 | 64.67 (11.12) | 2,015 | - | - | - | - | 867 | 2,789 | 167 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Met - | 3,994 | 65.67 (12.61) | 2,336 | - | - | - | - | 967 | 3,158 | 254 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Netherlands | Kersten et al, 2022 [17] | Retrospective cohort | Met + | 592 | 75 (10) | 332 | 28 (4.46) | - | - | - | 164 | 67 | - | 182 | - | - | 174.6 (48.2) | - | - | - | Excluded from the study |
| Met - | 345 | 76 (11) | 167 | 28 (4.47) | - | - | - | 108 | 41 | - | 87 | - | - | 166.86 (63) | - | - | - | Excluded from the study | |||
| Japan | Mima et al, 2016 [7] | Met + | 77 | 67.7 (10.3) | 56 | 25.7 (5.5) | 7.5 (1.2) | 83 (17) | 154 (25) | 52 | 64 | - | 20 | - | 9 | 175 (71) | - | - | - | - | |
| Met - | 163 | 73.2 (9.2) | 119 | 23.6 (3.2) | 7.3 (1.3) | 85 (17) | 160 (27) | 93 | 133 | - | 45 | - | 21 | 179 (70) | - | - | - | - | |||
| Switzerland | Westphal et al, 2020 [19] | Multicenter retrospective analysis | Met + | 757 | 71.4 (9.5) | 478 | 84.1 (16.8) | - | 83.2 (16.2) | 159.6 (24.8) | 481 | 673 | 176 | 135 | 161.4 (96.8) | 183 | 169.2 (63) | 87.0 (47.7) | 232.5 (71.3) | 1.0 (0.2) | 145 |
| Met - | 757 | 71.8 (10.9) | 458 | - | - | - | 158.8 (25.9) | 450 | 656 | 187 | 139 | 158.4 (120.2) | 182 | 169.2 (70.2) | 92.0 (51.7) | 238.3 (79.8) | 1.0 (0.1) | 271 | |||
| Korea | Kim et al, 2024 [12] | Cohort | Met + | 137 | 71.2 (11.5) | 76 | - | 7.5 (1.4) | - | 151.7 (26.5) | 32 | 94 | 73 | 18 | 123 (48.9) | - | 180.8 (70.1) | 97.26 (53.05) | - | 1.06 (0.29) | 34 |
| Met - | 94 | 72.5 (13.1) | 49 | - | 7.2 (1.6) | - | 151.9 (28.3) | 26 | 68 | 50 | 13 | 121 (56.3) | - | 175.6 (86.7) | 106.1 (106.1) | - | 1.03 (0.18) | 32 | |||
| Japan | Akiyama et al, 2024 [13] | Retrospective cohort | Met + | 55 | 73.3 (11.4) | 44 | 22.9 (2.7) | 7.37 (0.99) | 84.7 (17.5) | 161.7 (31.2) | 35 | 44 | - | 33 | - | 8 | 175.3 (73) | 75.16 (17.68) | - | - | 15 |
| Met - | 105 | 73.3 (8.3) | 78 | 23 (3.4) | 7 (0.98) | 84.7 (16.5) | 160 (26.3) | 70 | 89 | - | 59 | - | 20 | 158.3 (57.1) | 85.77 (43.33) | - | - | 28 | |||
| Turkey | Allahverdiyev et al, 2020 [20] | Cohort | Met + | 42 | 70.02 (10.92) | 18 | - | 8.11 (1.78) | 80.71 (14.69) | 145.33 (27.86) | 10 | 34 | 4 | 10 | - | 17 | 144.94 (60.74) | - | - | - | 7 |
| Met - | 28 | 68.43 (11.09) | 16 | - | 8.84 (3.16) | 81.32 (17.83) | 155.8 (33.24) | 8 | 26 | 2 | 13 | - | 11 | 159.23 (87.31) | - | - | - | 4 | |||
| Iran | Abbasi et al, 2018 [21] | RCT | Met + | Overall 100 | 68.9 (10.6) | Overall 50 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Met - | 67 (11.63) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Italy | Curro et al, 2022 [18] | Retrospective cohort | Met + | Overall 170 | 76.72 (8.72) | 84 | - | - | 81.88 (15.52) | 154.81 (25.53) | 56 | 140 | - | 26 | 251.88 (107.26) | 47 | 185.33 (69.52) | 96.38 (49.52) | 237.73 (91.96) | - | 31 |
| Met - | |||||||||||||||||||||