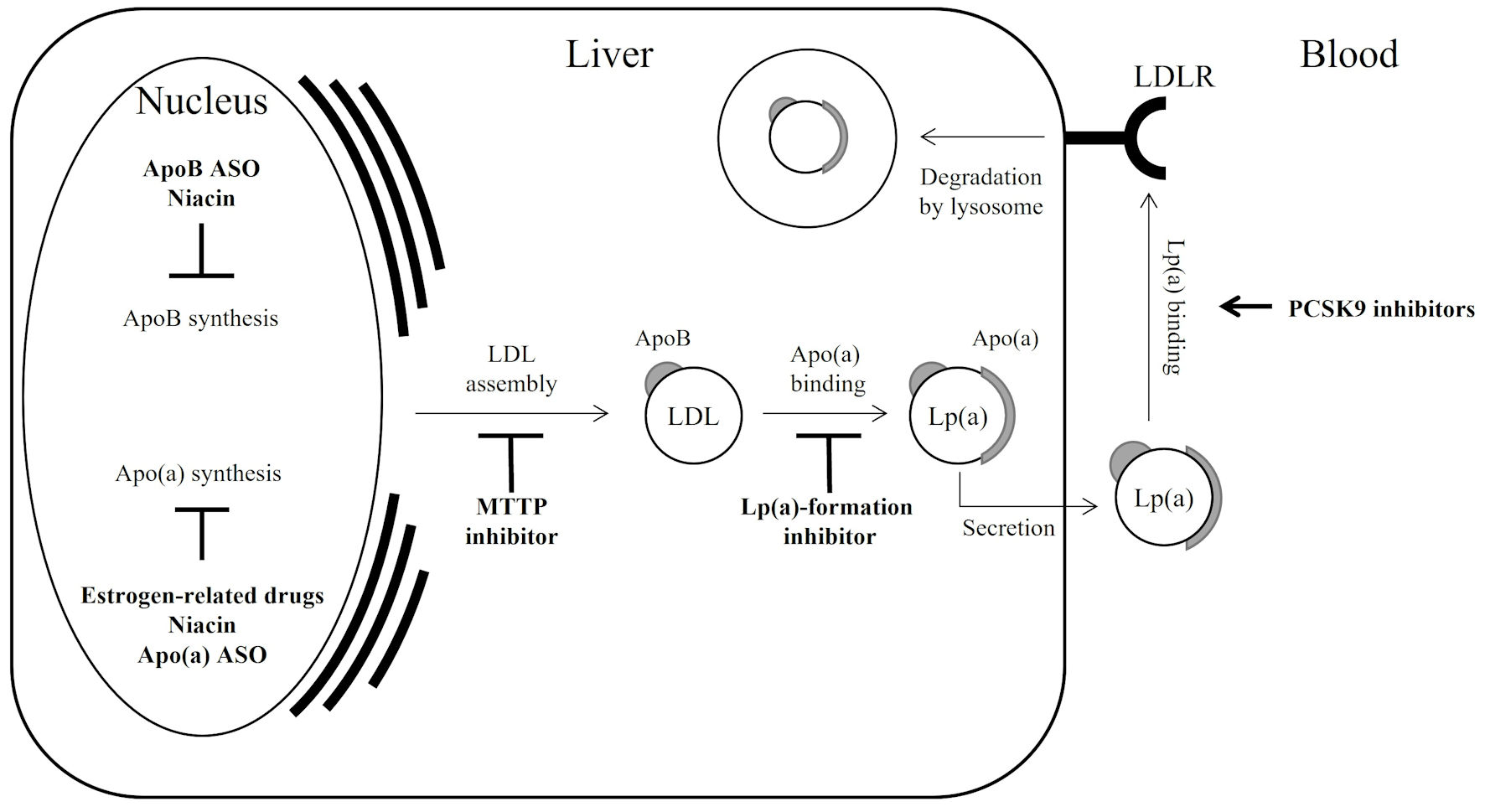
Figure 1. Lp(a) regulation by drugs; a simple schematic illustration. Bold arrow indicates acceleration; bold T-bar indicates inhibition. Since statins modulate both apoB synthesis and LDLR activation, resulting in a varied effect on Lp(a), they are not described in the figure. Apo(a): apolipoprotein(a); apoB: apolipoprotein B; ASO: antisense oligonucleotide; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; LDLR: low-density lipoprotein receptor; MTTP: microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; PCSK9: proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; Lp(a): lipoprotein(a).