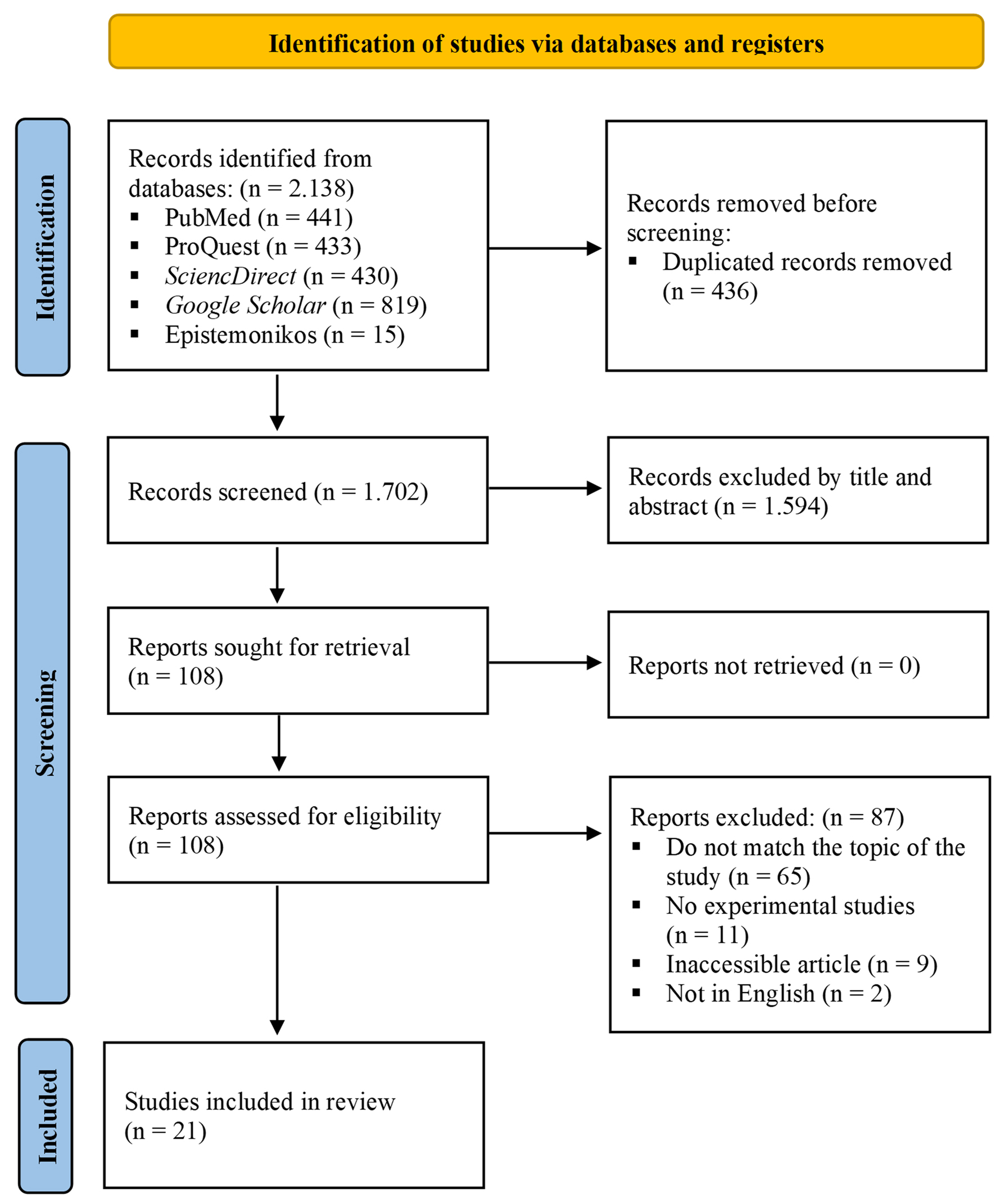
Figure 1. Flowchart illustrating the article selection procedure in accordance with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines for performing a systematic review.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jocmr.elmerjournals.com |
Original Article
Volume 17, Number 5, May 2025, pages 270-284
Anti-Breast Cancer Effects of Thymoquinone-Chemotherapeutic Combinations: A Systematic Review of the Latest In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Figure

Tables
| Author (years) | Country | Intervention group | Control group | Cellular type | Carrier | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACNP: aragonite calcium carbonate (CaCO3) nanoparticle; Bax: Bcl-2-associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; B-NE: borage nanoemulsion; Cis: cisplatin; CLNCs: chitosan-coated lipid nanocapsule; Cyclo: cyclophosphamide; DOX: doxorubicin; DTX: docetaxel; GCB: gemcitabine; 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; LLCNs: lyotropic liquid crystalline nanoassemblies; LNCs: lipid nanocapsules; NE: nanoemulsion; p-5473-Akt: phosphorylated Akt; PLGA: poly lactic-co-glycolic acid; PPAR: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PTEN: phosphatase and TENsin homolog; PTX: paclitaxel; TQ: thymoquinone; ULNCs: drug-loaded uncoated lipid nanocapsule. | |||||||
| Soni et al, 2015 [28] | India | TQ + PTX | PTX alone | MCF-7 breast cancer cell | PLGA nanoparticle | 24 h | 1) TQ + PTX significantly showed lower cell viability compared to PTX alone. P < 0.001. 2) TQ lowers the effective concentration (IC50) of PTX. 3) TQ + PTX showed 0.688 (synergistic effect). |
| Sakalar et al, 2016 [29] | Turkey | TQ + PTX | PTX alone, untreated embryonic fibroblasts cell (PMEFCFL-P1) | 4T1 (ATCC CRL-2539) breast cancer cells | - | 48 h | 1) TQ + PTX significantly showed lower cell viability compared to PTX alone. P < 0.0001. 2) Lower dose TQ showed higher apoptosis compared to untreated cells. P < 0.05. 3) TQ modulated apoptosis-related genes, cytokine, and p53 signaling pathway genes. |
| Bashmail et al, 2018 [40] | Saudi Arabia | TQ + GCB | GCB alone, untreated cell | MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cells | - | 24, 48, and 72 h | 1) TQ lowers the effective concentration (IC50) of GCB. 2) TQ + GCB showed 0.15 (strong synergistic effect). 3) TQ + GCB showed significantly higher apoptosis, increased cell death in the pre-G phase, and cell cycle arrest at S phase compared to GCB alone. P < 0.05. 4) TQ + GCB significantly increased autophagic cell death compared to control untreated cells. P < 0.05. |
| Zidan et al, 2018 [42] | Egypt | DOX + TQ + F2 gel, DOX + F2 gel, TQ + F2 gel | Free DOX, free TQ, untreated cell | MCF-7 breast cancer cells | F2 gel nanofibers | 24 h | 1) DOX + TQ + F2 gel showed lower cell viability compared to other treatments. P < 0.05. 2) DOX + TQ + F2 gel induced the highest apoptosis, 88.6%, compared to the control group. |
| Ibiyeye et al, 2019 [43] | Malaysia | DOX + TQ-ACNP, DOX-ACNP, TQ-ACNP | Free DOX + TQ, free TQ, free TQ | MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell, MCF10A normal breast cell, 3T3 normal fibroblast cell | ACNP | 24, 48, and 72 h | 1) TQ + DOX showed lower cell viability than other treatments. P < 0.05. 2) Free TQ + DOX showed 0.8 at 48 h (slight synergism), while TQ + DOX-ACNP showed 0.5 at 48 h (synergism). 3) Free TQ increased the late apoptosis in TQ + DOX compared to DOX alone. 4) DOX + TQ-ACNP has the highest percentage in SubG0 (dead cells) and S phase at 48 h. 5) TQ has been shown to significantly inhibit cancer cell invasion and migration in TQ + DOX compared to other treatments. P < 0.05. |
| Khan et al, 2019 [44] | Saudi Arabia | TQ + cyclo | Cyclo alone, untreated cell | SKBR-3 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | - | 48 h | 1) TQ enhanced the growth inhibition of Her2+ and Her2- breast cancer cells in combination with cyclo, inhibited p-5473-Akt, increased the expression of its inhibitor PTEN, and decreased cyclin D1 compared to cyclo alone. P < 0.001. 2) TQ + cyclo increased cells to arrest in sub-G1 and G1 compared to untreated cells. P < 0.05. |
| Odeh et al, 2019 [45] | Jordan | TQ + DTX | DTX alone | MCF-7 breast cancer cell | - | 72 h | 1) TQ lowers the effective concentration (IC50) of DTX. 2) TQ + DTX showed 0.552 - 0.803 (synergistic effect). |
| Alkhatib et al, 2020 [46] | Saudi Arabia | TQ + DTX + B-NE | Free TQ and DTX | MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | B-NE | 48 h | 1) TQ + DTX in B-NE exhibited a lower IC50 than free DTX and other treatments. 2) TQ + DTX in B-NE showed 0.6-0.9 (synergistic effect). 3) TQ + DTX in B-NE significantly showed higher apoptosis compared to DTX alone. P < 0.05. 4) TQ + DTX and free TQ or DTX significantly showed higher autophagy than untreated cell. P < 0.05. |
| Bashmail et al, 2020 [47] | Saudi Arabia | TQ + PTX | PTX alone, TQ alone | MCF-7 and T47D breast cancer cells | - | 24 and 48 h | 1) TQ did not enhance PTX potency but significantly eliminated tumor-associated resistant cell clones to PTX. P < 0.05. 2) TQ + PTX showed 1.6 - 4.6 (antagonistic effect). 3) TQ + PTX significantly increased apoptosis, pre-G phase population, autophagic cell death fluorescence, and reduced CD44+/CD24- compared to PTX alone. P < 0.05. |
| Bawadud et al, 2020 [48] | Saudi Arabia | NE-DTX + TQ, free DTX + TQ | Free DTX alone, free TQ alone, drug-free NEs | MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | NE | 48 h | 1) DTX + TQ-NE and free DTX alone significantly increased DNA fragmentation compared to free TQ alone and drug-free NEs. P < 0.05. 2) DTX + TQ-NE significantly reduced CD44+/CD24-, SNAIL-1, and TWIST-1 compared to other treatments. P < 0.05. 3) DTX + TQ-NE caused significant arrest at the G2/M phase (P < 0.0001) and the S phase (P < 0.0021) compared to untreated cells and free TQ alone. |
| Zafar et al, 2020 [30] | India | DTX + TQ in ULNCs and CLNCs | Free DTX alone, free TQ alone, DTX-LNCs | MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | CLNCs and ULNCs | 24 and 48 h | 1) TQ + DTX in CLNCs and ULNCs significantly showed lower cell viability and higher cell inhibition than free DTX, free TQ, and DTX-LNCs. P < 0.05. |
| Zafar et al, 2020 [31] | India | DxTq-LNCs | DTX-LNCs, free DTX alone, free TQ alone | MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells | Long circulating sub-100 nm mPEG-DSPE- Vitamin E TPGS-LNCs | 24 and 48 h | 1) DxTq-LNCs significantly showed lower cell viability than free DTX alone and DTX-LNCs. P < 0.05. 2) TQ lowers the effective concentration (IC50) of DTX in LNCs. 3) DxTq-LNCs showed 0.53-0.79 (synergistic effect). |
| El-Far et al, 2021 [32] | Egypt | TQ + DOX | DOX alone, untreated cell | MCF-7 breast cancer cell | - | 5 days after DOX treatment and 24 h after TQ treatment | 1) TQ + DOX and TQ alone significantly increased apoptosis compared to untreated cell compared to untreated cells (P < 0.001 and P < 0.05, respectively). 2) TQ significantly increased the Bax/Bcl2 ratio and caspase-3 activity compared to DOX alone and untreated cells. P < 0.01. |
| Zheng et al, 2022 [33] | China | TQ + 5-FU | 5-FU alone | BT-549 and MDA-MD-231 breast cancer cells | - | 24 and 48 h | 1) 5-FU + TQ significantly showed lower cell viability, higher cell inhibition, and increased apoptosis than 5-FU or TQ alone. P < 0.01. 2) 5-FU + TQ was more effective in prolonging the S phase of the cell cycle than other treatments. |
| Anandan et al, 2023 [34] | India | TQ + PTX | PTX alone, TQ alone | MCF-7 breast cancer cells | - | 24 h | 1) TQ + PTX significantly showed lower cell viability than PTX and TQ alone. P < 0.05. 2) TQ lowers the effective concentration of PTX. |
| Bawadud et al, 2023 [35] | Saudi Arabia | NE-DTX + TQ, free DTX + TQ | Free DTX alone, free TQ alone, drug-free NEs | Human ductal carcinoma cells T47D | NEs | 48 h | 1) NE-DTX + TQ had a lower IC50 than free DTX alone and other treatments. 2) Free TQ + DTX showed 7.9 (antagonistic effect), while NE-DTX + TQ showed 0.75 (synergistic effect). 3) NE-DTX + TQ significantly increased apoptosis (P < 0.0001) and reduced CD44+/CD24- (P < 0.0002) compared to free DTX alone. 4) NE-DTX + TQ had the highest rate of autophagic vacuole formation compared to other treatments. P < 0.0001. |
| Loo et al, 2023 [36] | Malaysia | TQ + GCB, in LLCNs, free TQ + GCB | Free TQ alone, free GCB alone, drug-free LLCNs, untreated cell | MCF10A nonmalignant breast epithelial and MCF-7 breast cancer cell | LLCNs | 24, 48, and 72 h | 1) TQ + GCB in LLCNs had a lower IC50 compared to drug-free LLCNs. 2) Free TQ + GCB and TQ + GCB in LLCNs significantly showed the lowest cell viability compared to other treatments. P < 0.05. 3) TQ + GCB in LLCNs showed 0.87 (synergistic effect), while free TQ + GCB showed 0.92 to 1.40 (additive to antagonistic effect). |
| Mousavinasab et al, 2023 [37] | Iran | TQ + Cis | TQ alone, Cis alone | MCF-7 breast cancer cell | - | 24, 48, and 72 h | 1) TQ + Cis significantly showed lower cell viability compared to Cis alone. P < 0.05. 2) TQ lowers the effective concentration of Cis. 3) TQ + Cis significantly induced the highest caspase-9, caspase-3, PPAR, p53, Bax, and the lowest Bcl-2 compared to other treatments. P < 0.00001. |
| Author (years) | Country | Sample | Route | Intervention/dose | Control group | Animal (age) | Weight (g) | Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT: alanine transaminase; AST: aspartate transaminase; BUN: blood urea nitrogen; CK-MB: creatine kinase-MB; CLNCs: chitosan-coated lipid nanocapsule; DOX: doxorubicin; DTX: docetaxel; ECis: early cisplatin; GCB: gemcitabine; GSH: glutathione; LCis: late cisplatin; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; MDA: malondialdehyde; NS: normal saline; PBS: phosphate buffer saline; PTX: paclitaxel; RBC: red blood cell; SOD: superoxide dismutase; TQ: thymoquinone; WBC: white blood cell. | |||||||||
| Şakalar et al, 2016 [29] | Turkey | Total 20 (control = 6, low dose TQ = 6, high dose TQ = 8) | Intraperitoneal injection | 0.64 mg/kg TQ + 1.25 mg/kg PTX, 2.4 mg/kg TQ + 1.25 mg/kg PTX | PTX alone, DMSO and/or 50% ethanol in ddH2O | Female balb/c mice (8 - 12 weeks) | 26 - 28 | 8 days (low dose group), 11 days (high dose group) | 1) TQ significantly decreased tumor growth (weight) in PTX + TQ compared to PTX alone. P < 0.007 in lower dose and P < 0.001 in higher dose. |
| El-Ashmawy et al, 2017 [38] | Egypt | Ten/group (normal control, tumor control, F2 gel, free DOX, DOX + F2 gel, free TQ, TQ + F2 gel, and DOX + TQ + F2 gel) | Subcutaneous injection | DOX + F2 gel (200 µL with 100 µg of DOX), TQ + F2 gel (200 µL with 3 mg of TQ), and DOX + TQ + F2 gel (300 µL with 100 µg of DOX and 3 mg of TQ), free DOX (5 mg/kg), free TQ (3 mg/mouse) | Normal control, tumor control, F2 gel (100 µL/mouse) | Female albino mice (6 - 8 weeks) | 18 - 22 | 28 days | 1) TQ significantly decreased tumor growth (volume) and increased inhibition rate in DOX + TQ and TQ alone compared to DOX alone. P < 0.05. 2) DOX + TQ + F2 gel decreased Bcl-2 and P53 expression compared to other treatments. P < 0.05. 3) TQ reduces the side effects of DOX on the heart as evidenced by decreased cardiac markers when combined with DOX. P < 0.05. |
| Gomaa et al, 2018 [39] | Egypt | Five/group (PB, gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), AuNPs/TQ conjugate, AuNPs/TQ + Cisplatin 10, and AuNPs/TQ + Cisplatin 40) | Intraperitoneal injection | AuNPs (21.4 µg/mouse) (AuNPs group), AuNPs/TQ conjugate (1 mg/mouse) (AuNPs/TQ group), AuNPs/TQ (1 mg/mouse) plus cisplatin (10 µg/mouse) (AuNPs/TQ + Cis10 group) or AuNPs/TQ (1 mg/mouse) plus cisplatin (40 µg/mouse) (AuNPs/TQ + Cis40 group) | PBS | Female Swiss albino mice (6 - 8 weeks) | 25 ± 2 | 6 days | 1) TQ significantly decreased tumor growth (weight) and increased CD4+, CD8+, granulocytic, and monocytic cell populations in AuNPs/TQ + Cis compared to untreated cells. P < 0.05. |
| Mosalam et al, 2020 [41] | Egypt | Ten/group (ECis, ECis + ETQ, ECis + ETQ + EPTX, LCis, LCis + LTQ, and LCis + LTQ + LPTX, tumor control) | Cis and TQ was given intraperitoneal injection, PTX was given subcutaneous injection | 7.5 mg/kg Cis (on 12th and 18th days for early groups, while on 19th and 25th days for late groups), 20 mg/kg TQ, 15 mg/kg PTX (TQ and PTX injected daily for 10 days) | ECis alone, LCis alone, tumor control PEG 200 µL/mouse/day | Female albino mice (6 - 8 weeks) | 20 - 22 | 28 days | 1) TQ significantly decreased tumor growth (weight), increased inhibition rate, CD4+, CD8+, and apoptosis rate in ECis + ETQ + EPTX and LCis + LTQ + LPTX compared to ECis or LCis alone and untreated cells. P < 0.05. |
| Zafar et al, 2020 [30] | India | Ten/group (control and TQ groups) | Direct contact | 3.3 µM DTX + 6.6 µM TQ in CLNCs carrier | DTX alone, TQ alone, NS | Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membran (CAM) (9 days) | - | 1 and 2 days | 1) TQ increased vascular inhibition (antiangiogenic effect) in TQ + DTX-CLNCs compared to DTX alone and untreated cells. |
| Zafar et al, 2020 [31] | India | Total 9 (NS = 3, 2 DTX = 3, DTX + TQ co-encapsulated lipid nanocapsules (DxTq-LNCs) = 3) | Intravenous tail vein injection | DTX + TQ - LNCs (equivalent to 0.3 mg DTX and 0.6 mg TQ) containing 2 mg/kg DTX | DTX alone, NS | Female balb/c mice | 20 - 25 | 14 days | 1) TQ significantly increased inhibition rate (volume) in DTX + TQ - LNCs compared to DTX alone. P < 0.05. 2) TQ significantly reduces liver, kidney, and blood toxicity of DTX as indicated by elevated SOD and GSH levels, reduced MDA, AST, and ALT, along with decreased BUN and creatinine, and increased WBC and RBC counts in DTX + TQ - LNCs. P < 0.05. |
| Benefit | Adverse effect |
|---|---|
| TQ itself has a direct anticancer effect and increases the immune response [29, 39-41]. | Potential drug interactions and toxicities depend on the concentration of TQ, drug carrier, and combination chosen [35, 36, 47, 54]. |
| Enhance the efficacy of various chemotherapeutic agents [28, 31, 34, 37, 40, 45]. | Possible variability in patient response [88]. |
| Reducing chemotherapy-induced toxicity [31, 38, 39]. | |
| Improve cost-effective adjunct chemotherapy by reducing the required doses of conventional treatments [28, 31, 34-37, 40, 43, 45, 46]. |