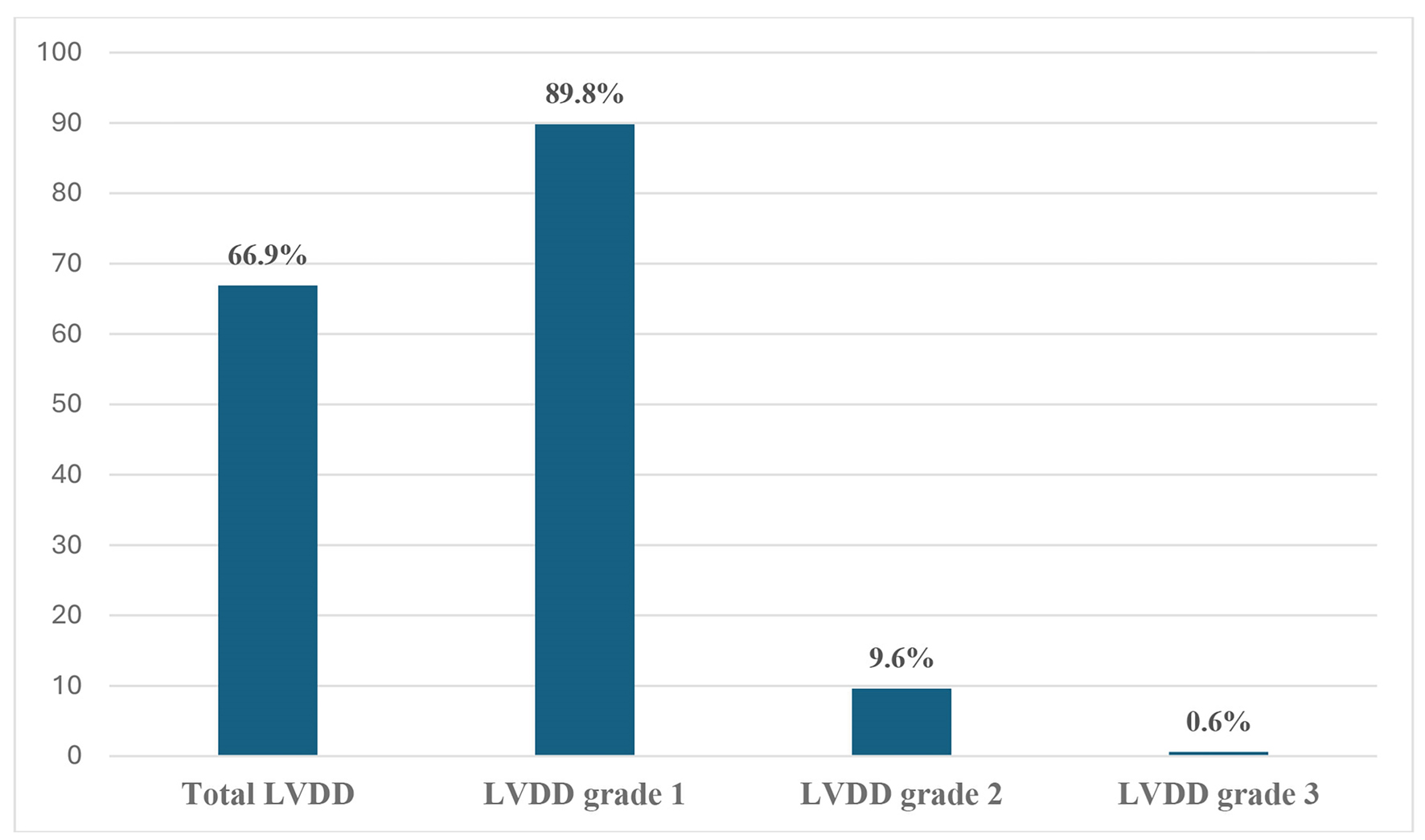
Figure 1. Prevalence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) and its grades.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jocmr.elmerjournals.com |
Original Article
Volume 17, Number 5, May 2025, pages 262-269
Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction and Its Predictive Factors Among Saudi Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Figure

Tables
| Parameter | Mean ± SD or n (%) |
|---|---|
| ACEi: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARBs: angiotensin II receptor blockers; BMI: body mass index; CVA: cerebral vascular accident; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; DM: diabetes mellitus; DPP4i: dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; FBS: fasting blood sugar; GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide 1; HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; HTN: hypertension; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; PVD: peripheral vascular disease; SBP: systolic blood pressure; TG: triglyceride. | |
| Age (years) | 59.47 ± 9.11 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 96 (38.2) |
| Female | 155 (61.8) |
| DM duration (years) | 20.28 ± 8.49 |
| HTN | 193 (76.9) |
| Dyslipidemia | 203 (81.2) |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 22 (8.8) |
| Diabetic neuropathy | 11 (4.4) |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 23 (9.2) |
| CVA | 33 (13.1) |
| PVD | 12 (4.8) |
| Height (cm) | 158.9 ± 9.06 |
| Weight (kg) | 83.26 ± 16.5 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.9 ± 6.6 |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 134.55 ± 23.88 |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 72.83 ± 12.55 |
| FBS (mmol/L) | 9.15 ± 4.85 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.76 ± 2.33 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 4.12 ± 1.06 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.27 ± 0.35 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.30 ± 0.8 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.64 ± 0.79 |
| Creatinine (mmol/L) | 73.88 ± 23.22 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 88.02 ± 21.06 |
| Metformin | 207 (82.5) |
| Sulfonylureas | 52 (20.7) |
| Insulin | 117 (46.6) |
| DPP4i | 105 (41.8) |
| Thiazolidinediones | 17 (6.8) |
| GLP-1 analogues | 13 (5.2) |
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | 1 (0.4) |
| ARBs/ACEi | 156 (62.2) |
| Beta-blockers | 88 (35.1) |
| Diuretics | 112 (44.6) |
| Calcium channel blocker | 92 (36.7) |
| Antiplatelet agent | 148 (69.2) |
| Lipid-lowering agent | 221 (88.0) |
| Patients’ characteristics | LVDD | P-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | ||||
| n | % | n | % | ||
| *P ≤ 0.05. ACEi: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARBs: angiotensin II receptor blockers; CVA: cerebral vascular accident; DPP4i: dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor; GLP-1: glucagon-like peptide 1; HTN: hypertension; LVDD: left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; PVD: peripheral vascular disease. | |||||
| Gender | 0.534 | ||||
| Male | 34 | 41.0% | 62 | 36.9% | |
| Female | 49 | 59.0% | 106 | 63.1% | |
| HTN | 50 | 60.2% | 143 | 85.1% | 0.000* |
| Dyslipidemia | 64 | 77.1% | 139 | 83.2% | 0.243 |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 5 | 6.0% | 17 | 10.1% | 0.280 |
| Diabetic neuropathy | 3 | 3.6% | 8 | 4.8% | 0.676 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 11 | 13.3% | 12 | 7.1% | 0.114 |
| CVA | 8 | 9.6% | 25 | 14.9% | 0.248 |
| PVD | 2 | 2.4% | 10 | 6.0% | 0.213 |
| Metformin | 69 | 83.1% | 138 | 82.1% | 0.846 |
| Sulfonylureas | 18 | 21.7% | 34 | 20.2% | 0.790 |
| Insulin | 34 | 41.0% | 83 | 49.4% | 0.207 |
| DPP4i | 31 | 37.3% | 74 | 44.0% | 0.311 |
| Thiazolidinediones | 6 | 7.2% | 11 | 6.5% | 0.840 |
| GLP-1 analogues | 4 | 4.8% | 9 | 5.4% | 0.856 |
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors | 0 | 0.0% | 1 | 0.6% | 0.481 |
| ARBs/ACEi | 40 | 48.2% | 116 | 69% | 0.001* |
| Beta-blockers | 31 | 37.3% | 57 | 33.9% | 0.593 |
| Diuretics | 23 | 27.7% | 89 | 53.0% | 0.000* |
| Calcium channel blockers | 22 | 26.5% | 70 | 41.7% | 0.019* |
| Lipid-lowering agents | 15 | 50.0% | 153 | 69.2% | 0.036* |
| Antiplatelet agents | 44 | 62.9% | 104 | 72.2% | 0.164 |
| Clinical parameter | Mann-Whitney U test | Z | Effect size (r) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| *P ≤ 0.05. BMI: body mass index; DBP: diastolic blood pressure; DM: diabetes mellitus; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; FBS: fasting blood sugar; HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; LDL: low-density lipoprotein; LVDD: left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; SBP: systolic blood pressure; TG: triglyceride. | ||||
| Age | 3,814.5 | -5.84 | 0.369 | 0.000* |
| DM duration | 2,270.5 | -3.13 | 0.239 | 0.002* |
| Height | 6,645.5 | -0.6 | 0.038 | 0.546 |
| Weight | 6,017.5 | -1.76 | 0.111 | 0.078 |
| BMI | 5,336 | -2.76 | 0.175 | 0.006* |
| SBP level | 4,687.5 | -3.93 | 0.250 | 0.000* |
| DBP level | 5,987 | -1.75 | 0.111 | 0.080 |
| FBS | 5,824 | -2.12 | 0.134 | 0.034* |
| HbA1c level | 5,607 | -2.39 | 0.151 | 0.017* |
| Total cholesterol | 6,590 | -0.48 | 0.030 | 0.630 |
| HDL | 5,988.5 | -1.82 | 0.115 | 0.069 |
| LDL | 5,967.5 | -1.51 | 0.096 | 0.131 |
| TG | 5,973.5 | -1.57 | 0.100 | 0.116 |
| Creatinine | 6,170.5 | -1.48 | 0.093 | 0.138 |
| eGFR level | 4,841 | -3.94 | 0.249 | 0.000* |
| Predictor factor | B | SE | Exp(B)a | 95% CI for Exp(B) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| *P ≤ 0.05. aAdjusted for the effect of all other included predictor factors in the analysis. ACEi: angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARBs: angiotensin II receptor blockers; BMI: body mass index; CI: confidence interval; DM: diabetes mellitus; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; FBS: fasting blood sugar; HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin; HTN: hypertension; LVDD: left ventricular diastolic dysfunction; SBP: systolic blood pressure. | ||||||
| Age | 0.1 | 0.03 | 1.1 | 1.03 | 1.18 | 0.003* |
| DM duration | 0.03 | 0.03 | 1.03 | 0.98 | 1.08 | 0.244 |
| BMI | 0.13 | 0.04 | 1.14 | 1.05 | 1.23 | 0.002* |
| SBP | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.49 |
| FBS | -0.01 | 0.03 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 1.05 | 0.733 |
| HbA1c | 0.06 | 0.09 | 1.06 | 0.89 | 1.28 | 0.496 |
| eGFR | 0 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.98 | 1.03 | 0.967 |
| HTN | 0.14 | 0.61 | 1.15 | 0.35 | 3.79 | 0.816 |
| ARB/ACEi | -0.35 | 0.55 | 0.7 | 0.24 | 2.06 | 0.523 |
| Diuretics | -0.24 | 0.48 | 0.79 | 0.31 | 2.04 | 0.626 |
| Calcium channel blocker | 0.16 | 0.51 | 1.18 | 0.43 | 3.22 | 0.75 |
| Lipid-lowering medications | 1.02 | 0.6 | 2.77 | 0.85 | 9.07 | 0.091 |