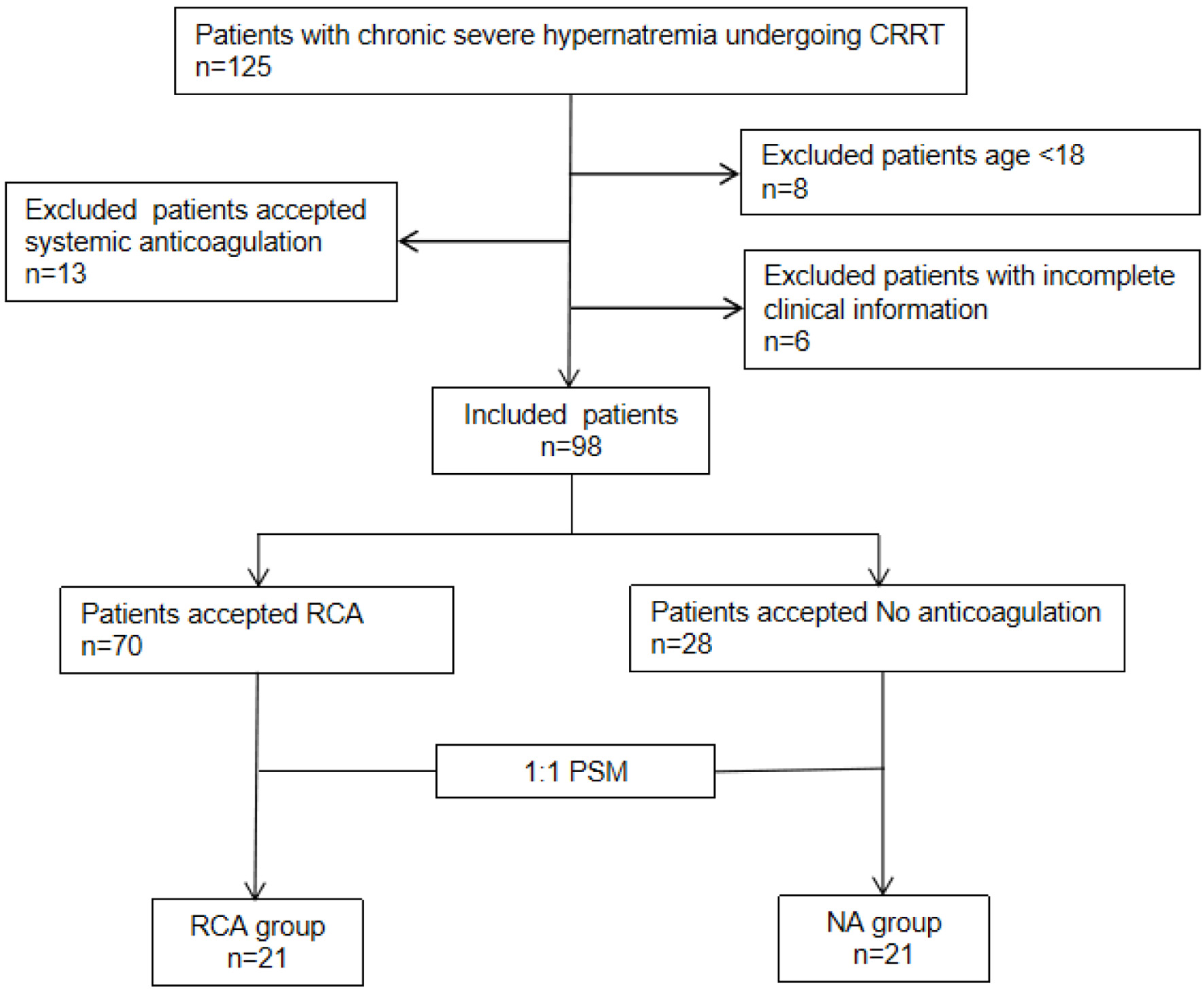
Figure 1. Flow chart of enrollment. Included patients (n = 98) were divided into two groups: regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) groups (n = 70) and no anticoagulation (NA) groups (n = 28). A 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to create two balanced groups: “NA group” and “RCA group,” each with n = 21 patients.
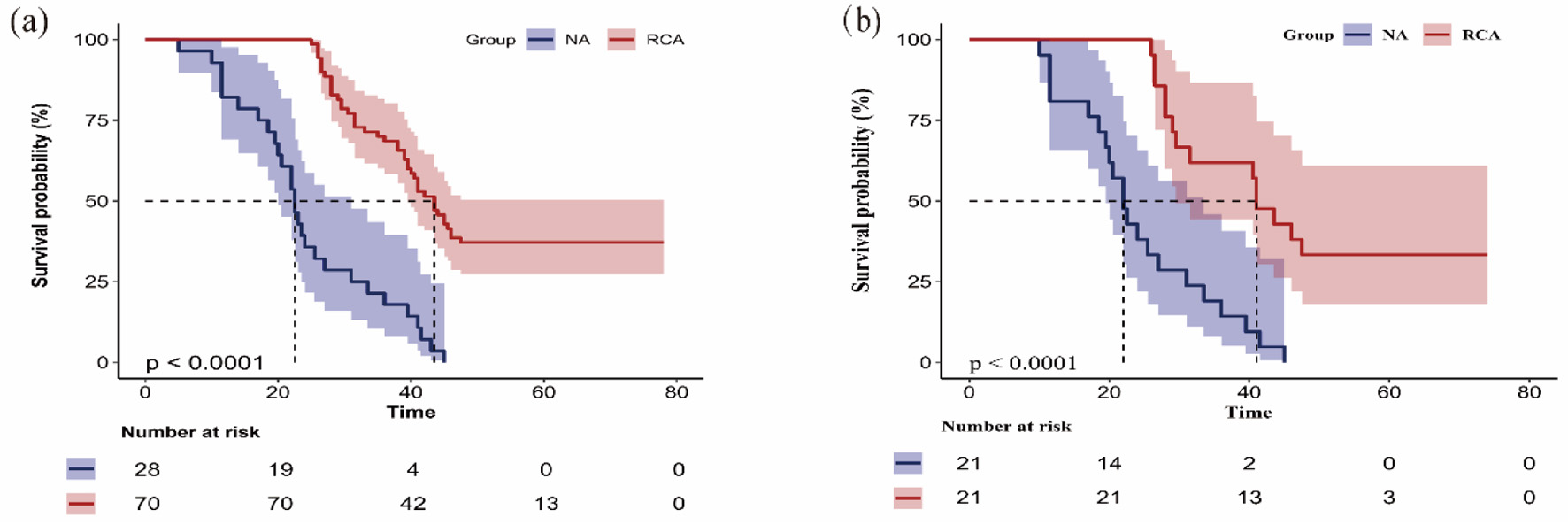
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier curve shows the filter lifespan of the first filter of the regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) group and no anticoagulation (NA) group in the original cohort (a) and the matched cohort (b). The Kaplan-Meier survival curves demonstrated significant differences in first filter lifespan between the two anticoagulation groups. The overall median filter survival time was 39.0 h (95% CI, 34.1–43.9). Median filter lifespan was 22.5 h in NA group (95% CI 19.9–25.1). Median lifespan was significantly longer at 43.5 h in RCA group (95% CI, 39.8–47.2) (a). Kaplan-Meier survival curves after matching. The first filter lifespan was considerably longer in the RCA group compared to the NA group (P < 0.001) (b). 95% CI: 95% confidence interval.
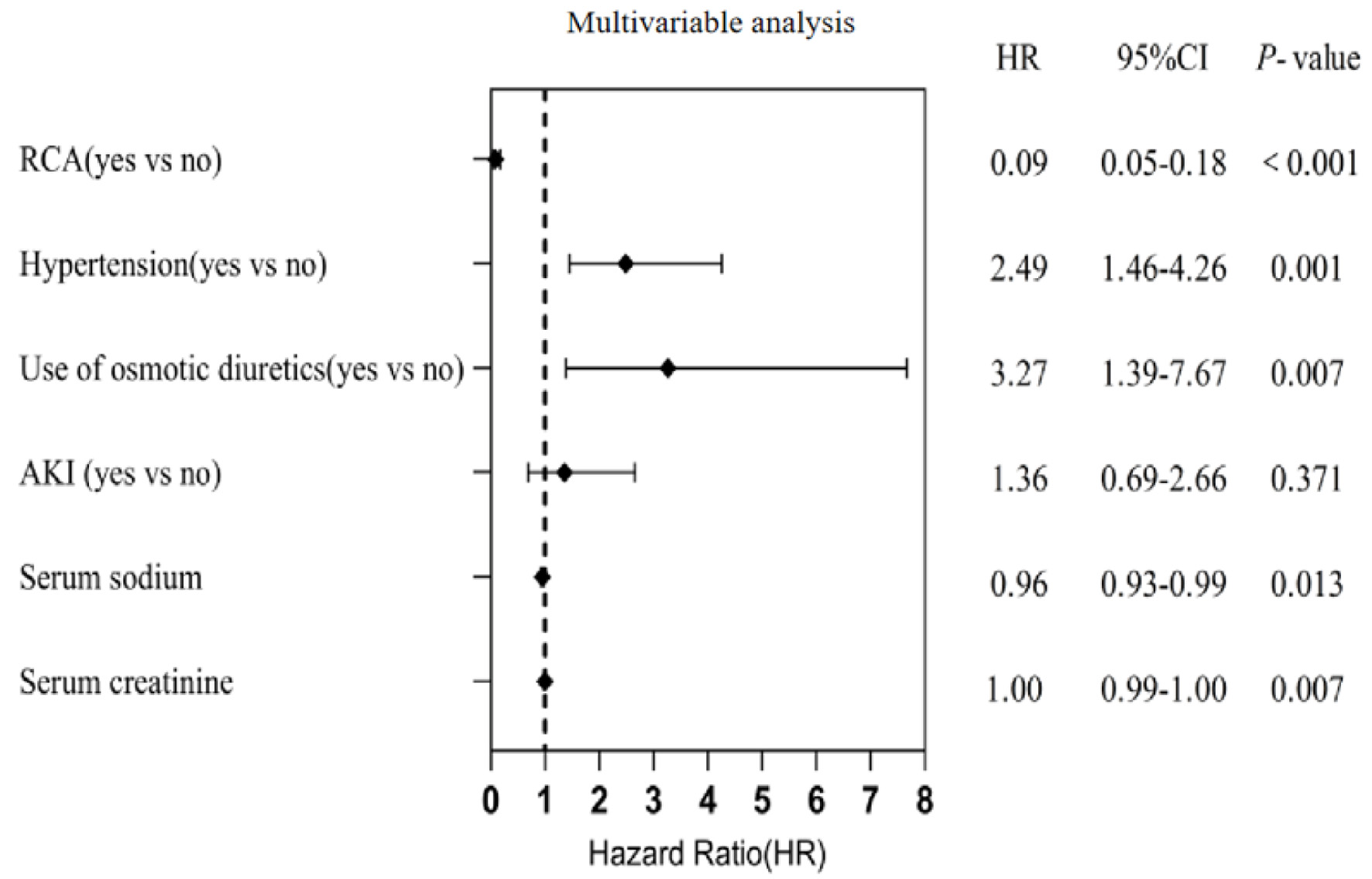
Figure 3. Multivariable Cox proportional risk model regression analysis affecting the lifespan of the first filter. Regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) remained a significant independent predictor of prolonged first filter lifespan after adjustment for covariates (HR = 0.09, 95% CI, 0.05−0.18). 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; HR: hazard ratio.


