Figures
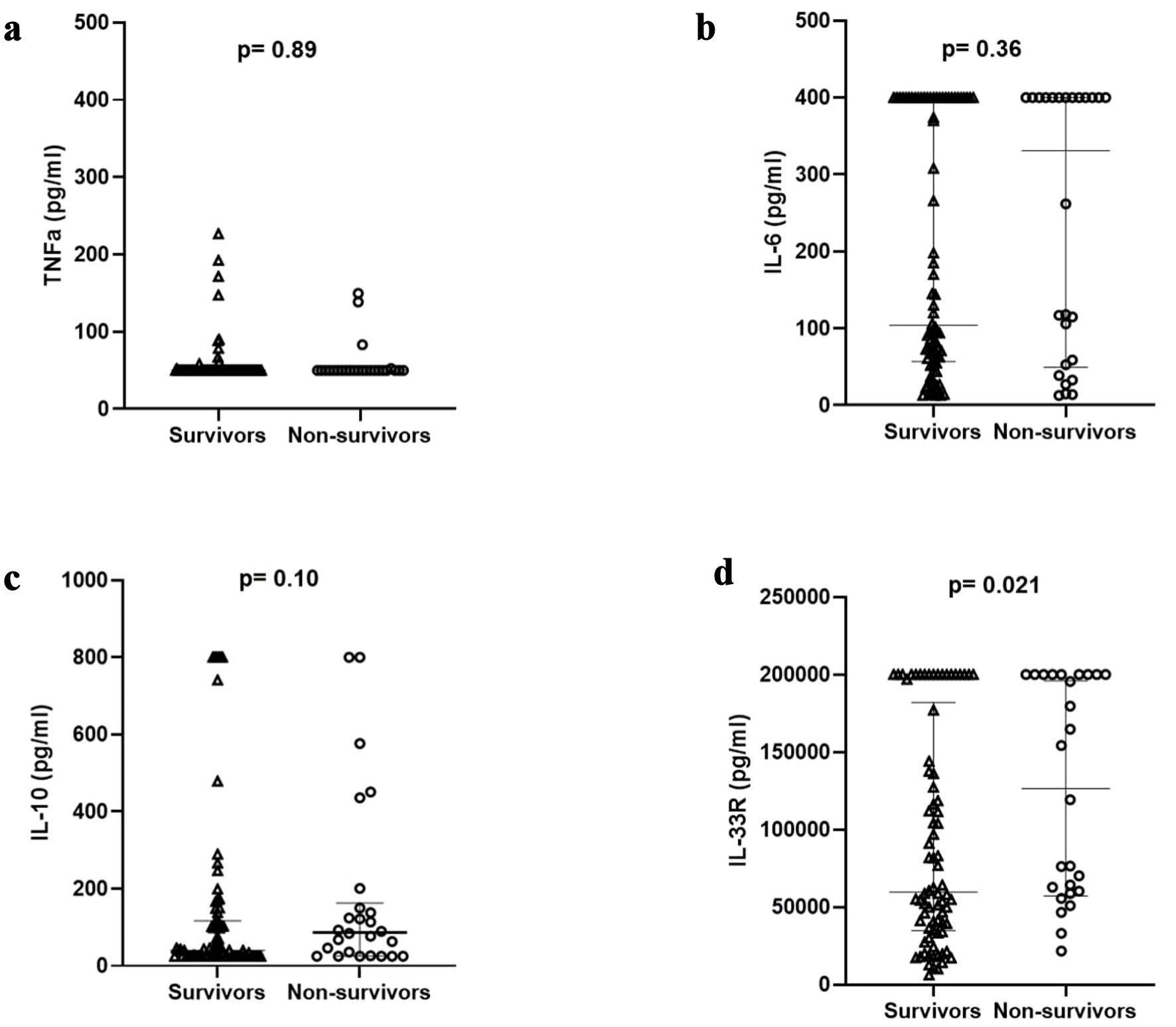
Figure 1. Cytokine differences regarding outcome in study population. TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL: interleukin; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
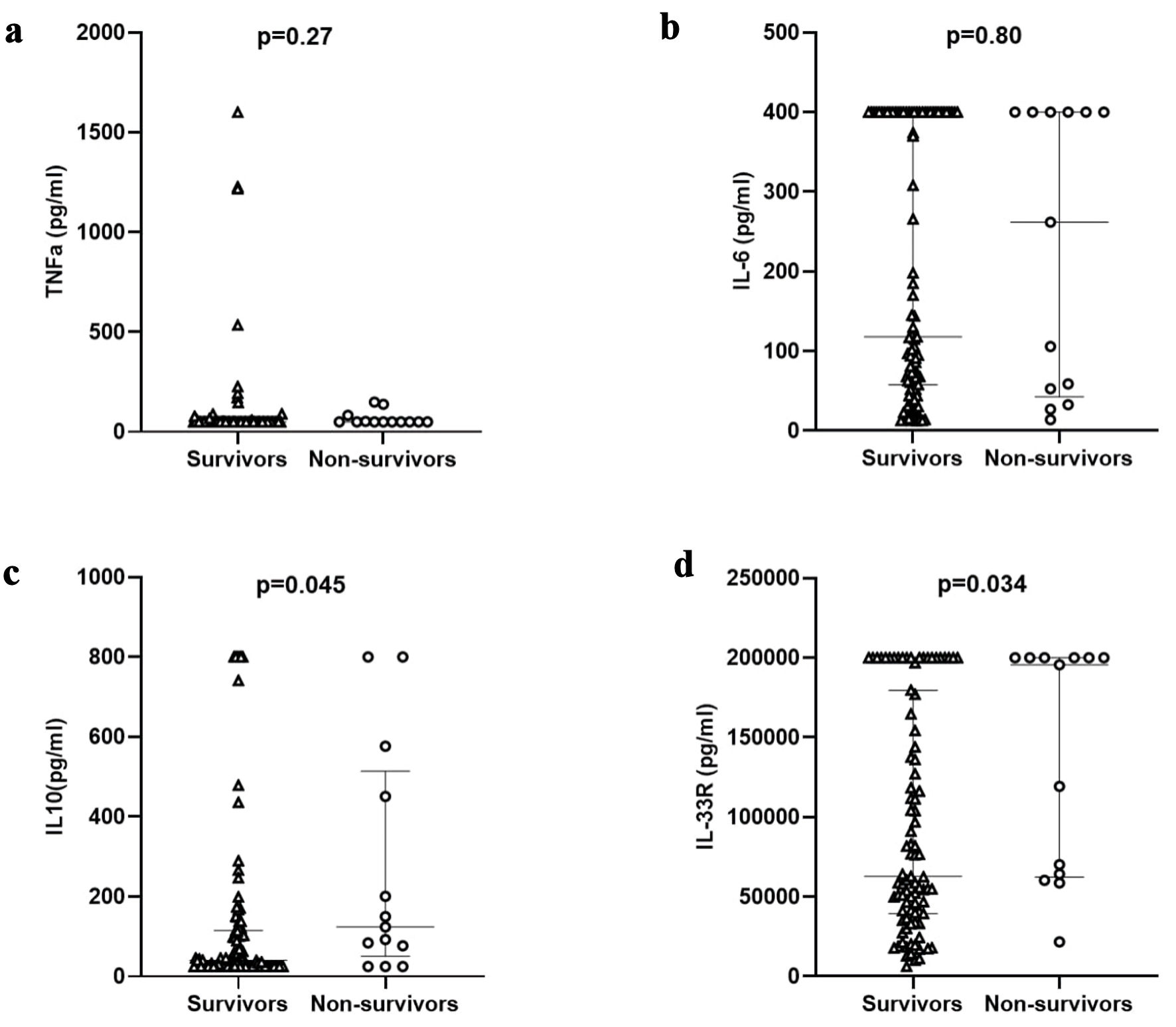
Figure 2. Cytokine differences regarding early outcome (in 72 h) in study population. TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL: interleukin; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
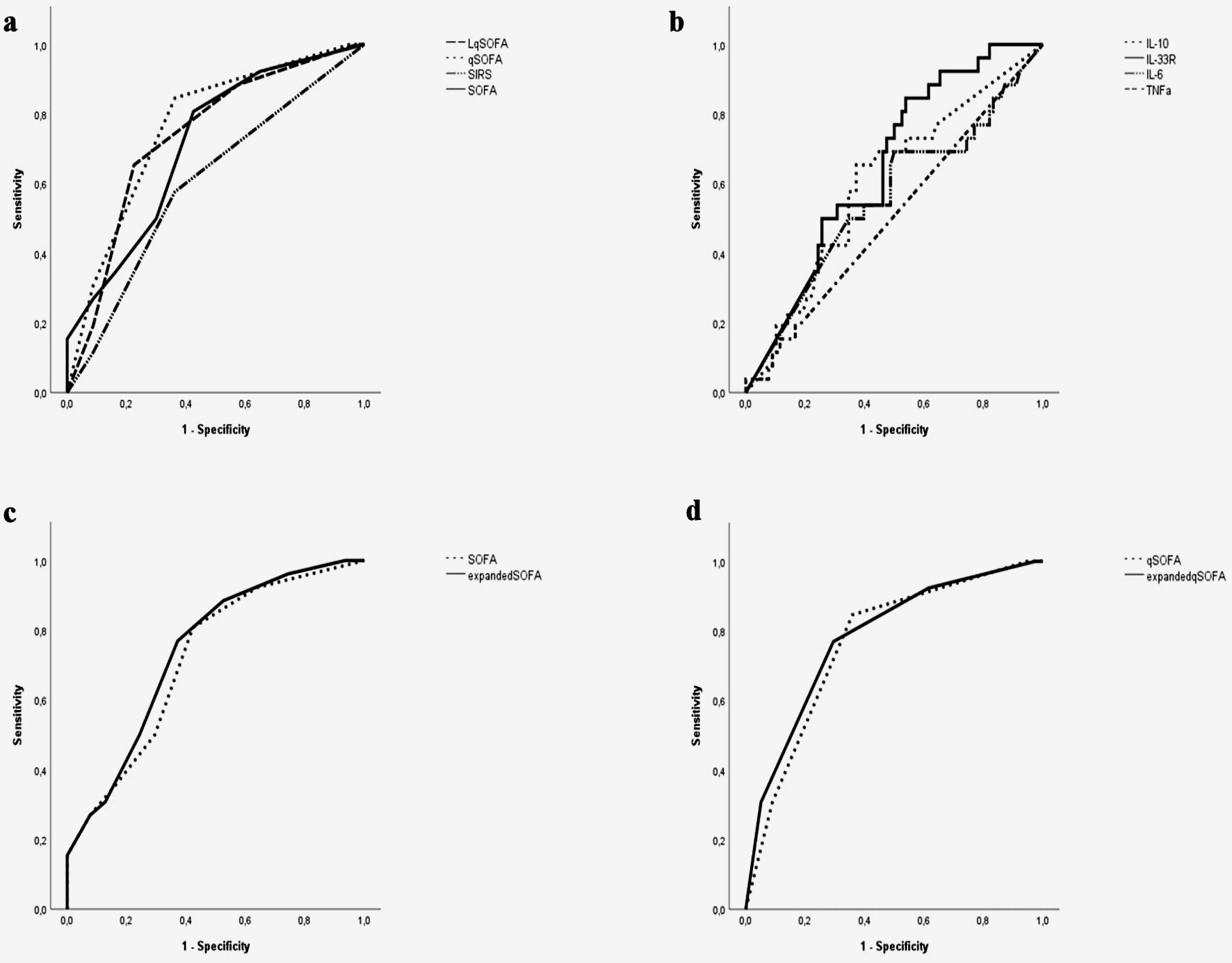
Figure 3. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of SIRS, SOFA, qSOFA, and LqSOFA (a), IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, IL-33R (b), expanded SOFA-IL-33R (SOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) and expanded qSOFA-IL-33R (qSOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) scores (c, d), respectively, in predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients. LqSOFA: lactate quick SOFA; qSOFA: quick SOFA; SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL: interleukin; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.

Figure 4. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of expanded SOFA-IL-33R (SOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) (a), expanded qSOFA-IL-33R (qSOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) (b), expanded SOFA-IL-10 (SOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-10) (c) and expanded qSOFA-IL10 (qSOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-10) (d) in predicting early (within 72 h) in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients. qSOFA: quick SOFA; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
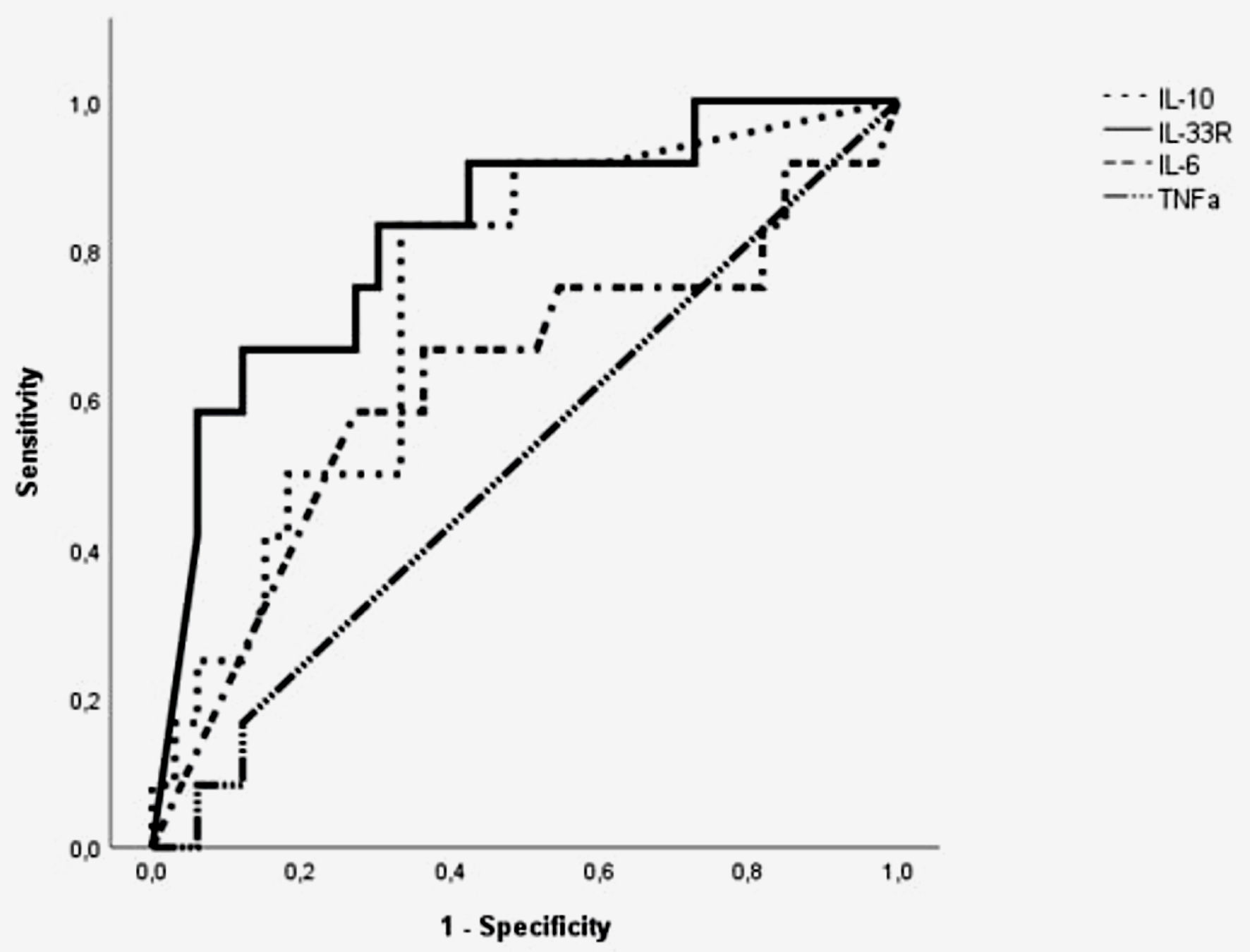
Figure 5. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, IL-33R in predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients with lower respiratory tract infections. TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IL: interleukin; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
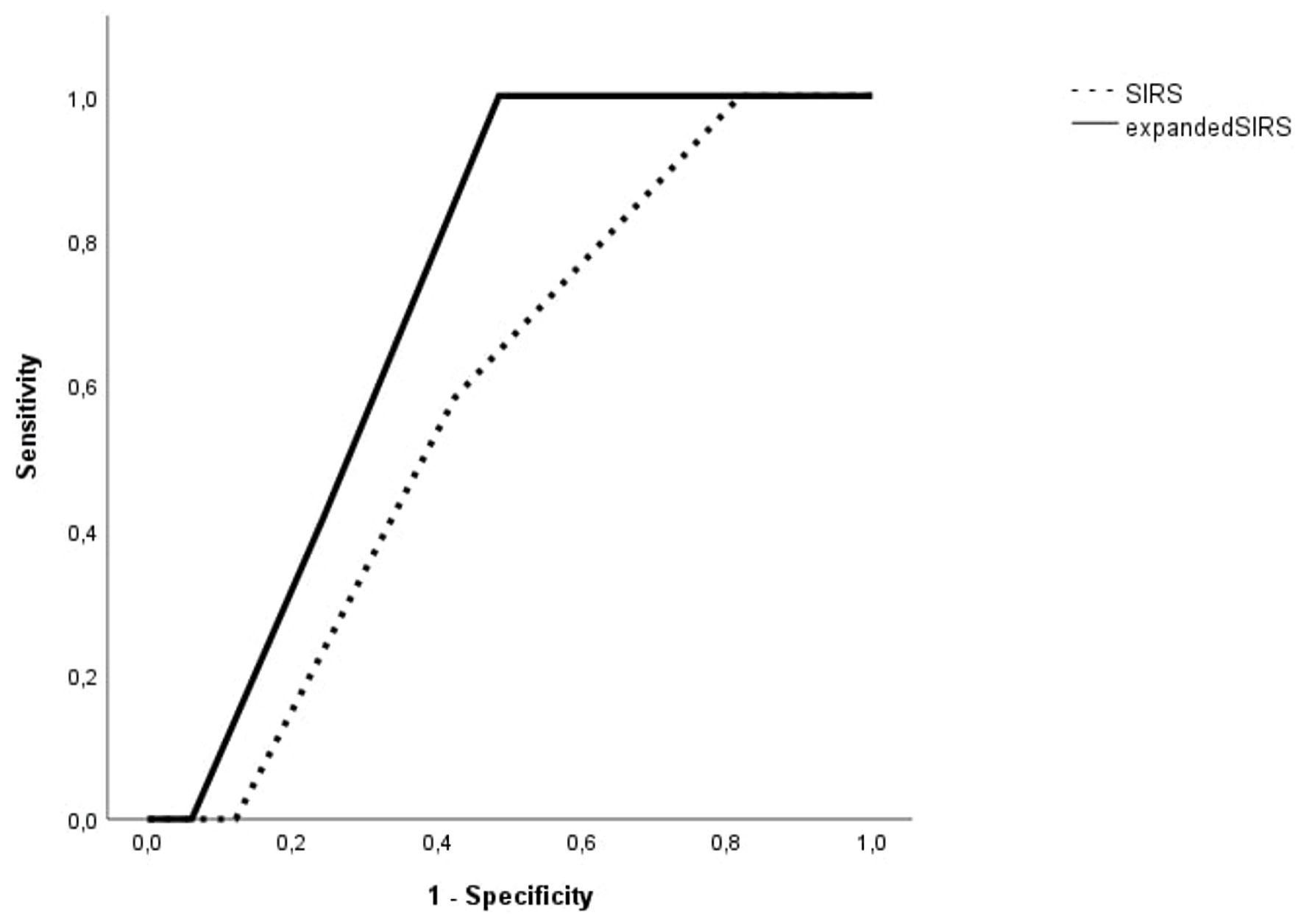
Figure 6. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of SIRS and expanded SIRS (SIRS combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) in predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients with lower respiratory tract infections. SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
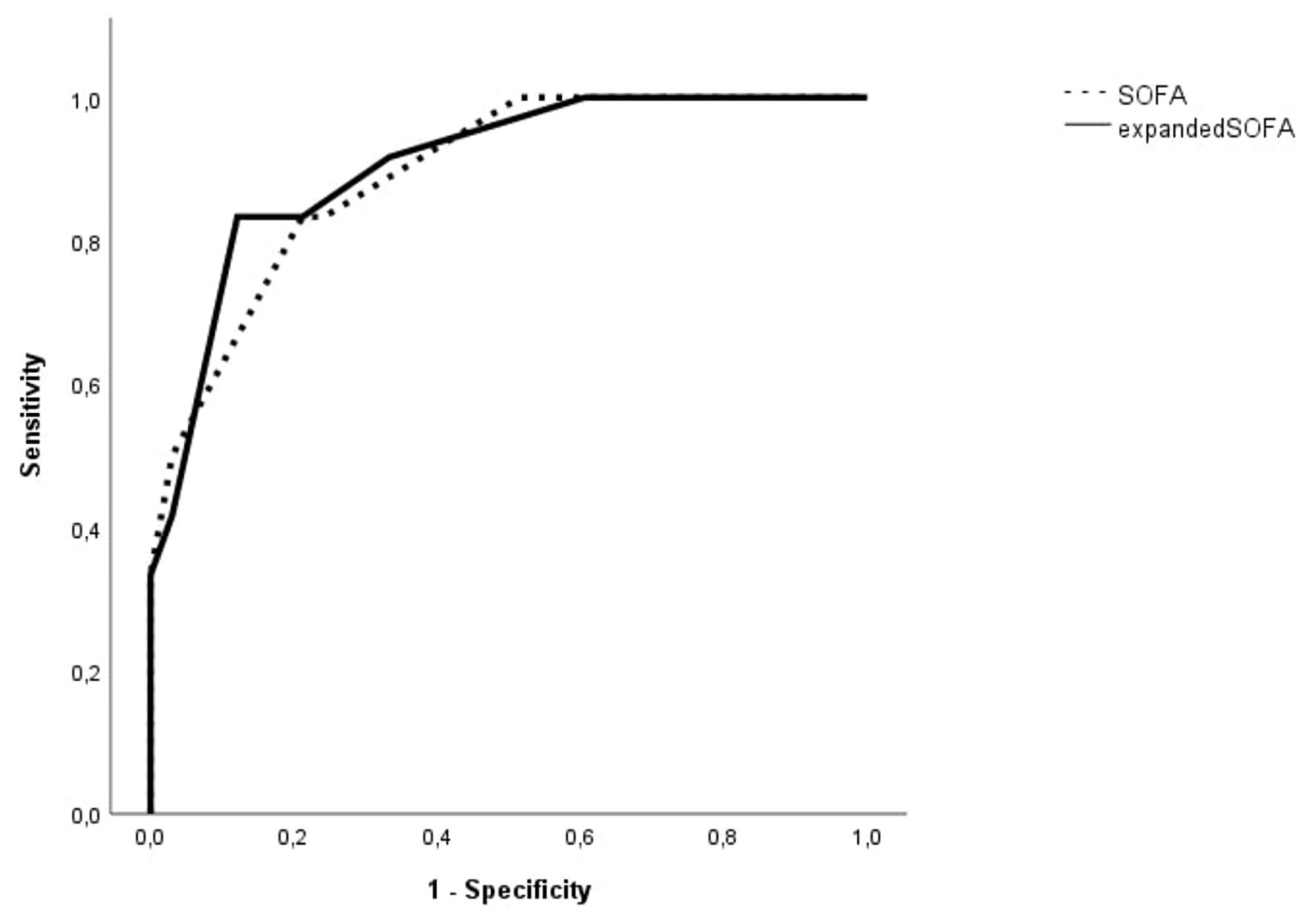
Figure 7. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of SOFA and expanded SOFA (SOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) in predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients with lower respiratory tract infections. SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
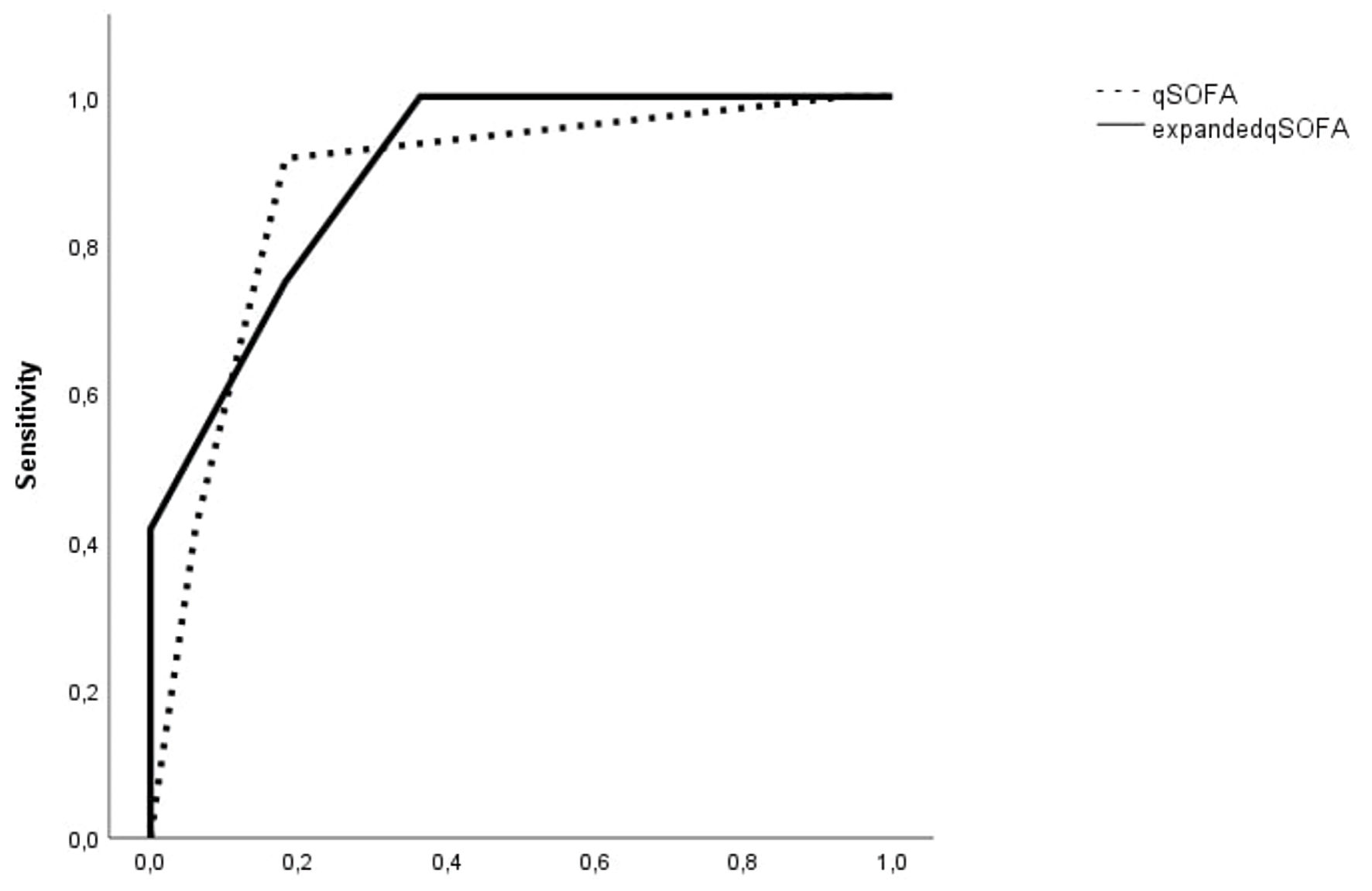
Figure 8. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of qSOFA and expanded qSOFA (qSOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) in predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients with lower respiratory tract infections. qSOFA: quick SOFA; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
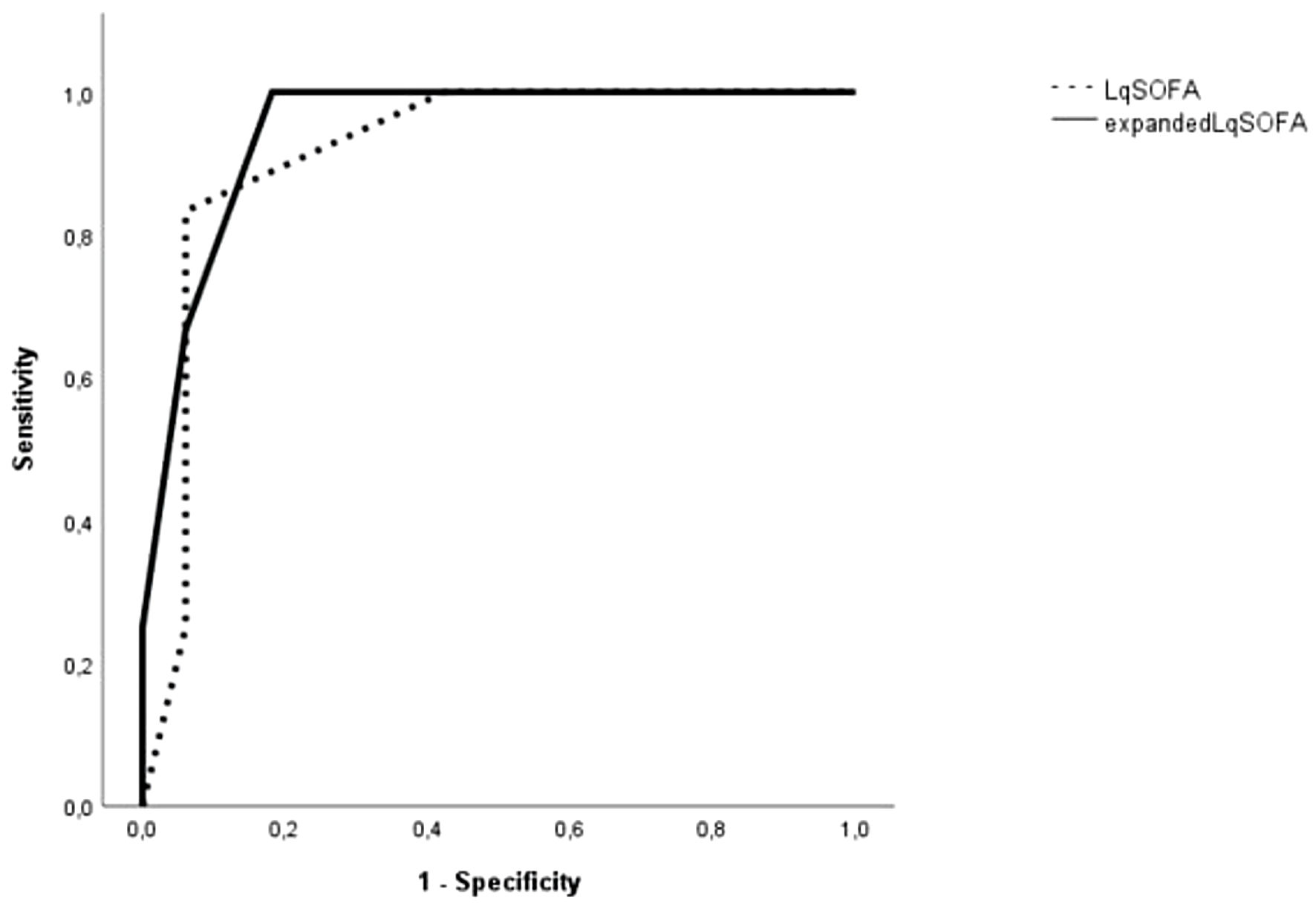
Figure 9. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of LqSOFA and expanded LqSOFA (LqSOFA combined with cutoff value of IL-33R) in predicting in-hospital mortality of sepsis patients with lower respiratory tract infections. LqSOFA: lactate quick SOFA; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; IL-33R: interleukin-33 receptor.
Table
Table 1. Study Population Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
| Survival | P |
|---|
| No | Yes |
|---|
| BTI: biliary tract infections; CKD: khronic kidney disease; CNS: central nervous system; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; CRP: C-reactive protein; CVD: cardiovascular disease; LqSOFA: lactate quick SOFA; NS: not statistically significant; qSOFA: quick SOFA; RTI: respiratory tract infections; SIRS: systemic inflammatory response syndrome; SOFA: Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; UTI: urinary tract infections; WBC: white blood cells; IL: interleukin. |
| Number | 26 | 80 | |
| Age | 83.5(73.3 - 88.3) | 79 (66.5 - 85.8) | NS (0.09) |
| Male | 7 (27%) | 43 (53.8%) | 0.023 |
| Female | 19 (73%) | 37 (46.3%) | 0.023 |
| Type of infection | | | |
| RTI | 12 (46.2%) | 34 (42.5%) | |
| UTI | 2 (7.7%) | 22 (27.5%) | |
| Colitis | 1 (3.8%) | 4 (5%) | |
| Mixed infections | 9 (34.6%) | 9 (11.3%) | |
| BTI | 2 (7.7%) | 6 (7.5%) | |
| CNS infections | 0 | 3 (3.8%) | |
| Other | 0 | 2 (2.5%) | |
| Bacteremia | 5 (19.2%) | 13 (16.3%) | |
| Comorbidities | | | |
| CVD | 19 (73%) | 57 (71.3%) | NS (0.86) |
| Diabetes | 6 (23%) | 28 (35%) | NS (0.26) |
| CKD | 1 (4%) | 8 (10%) | NS (0.33) |
| COPD | 2 (7.7%) | 18 (22.5%) | NS (0.09) |
| Neoplasm | 1 (4%) | 9 (11.3%) | NS (0.26) |
| SOFA | 4.5 (4 - 7) | 3 (2 - 5) | 0.001 |
| SIRS | 3 (2 - 3) | 2 (2 - 3) | NS (0.09) |
| qSOFA | 2 (2 - 3) | 1 (1 - 2) | < 0.001 |
| LqSOFA | 3 (2 - 3) | 2 (1 - 2) | < 0.001 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) | 2.6 (1.6 - 4.8) | 2 (1.5 - 3.3) | NS (0.17) |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 14.6 (11.6 - 19) | 12.4 (4 - 22.3) | NS (0.29) |
| WBC (cells/µL) | 14,495 (7,440 - 17,490) | 13,685 (8,660 - 18,380) | NS (0.69) |
| Cytokines | | | |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 331 (49.5 - 400) | 104 (57.3 - 400) | NS (0.36) |
| IL-10 (pg/mL) | 87 (25.8 - 162.8) | 40 (25 - 116.8) | NS (0.11) |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 50 (50 - 50) | 50 (50 - 50) | NS (0.89) |
| IL-33R (pg/mL) | 136,800 (59,932 - 200,000) | 59,693 (34,920 - 182,035) | 0.021 |









