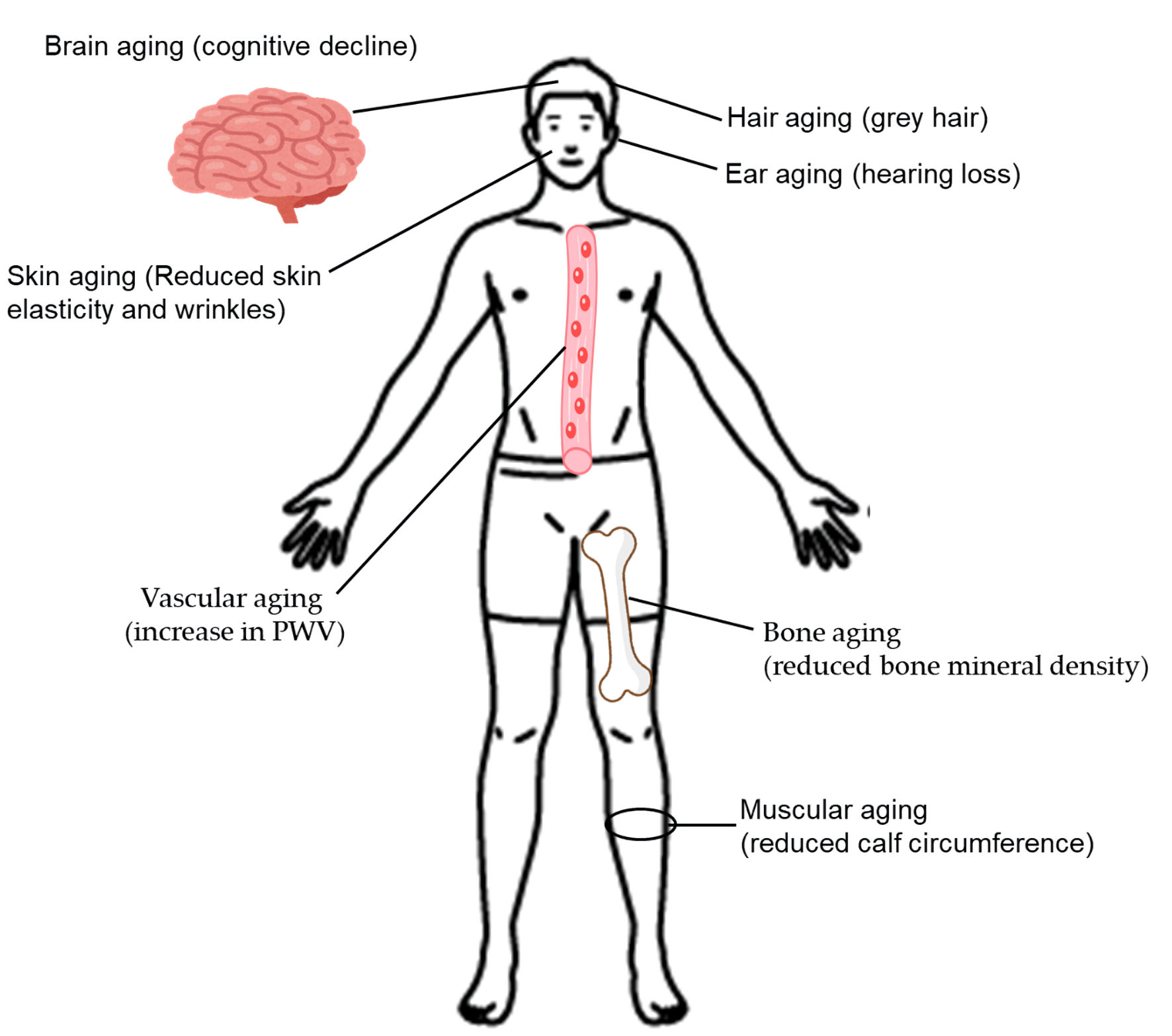
Figure 1. The clinical manifestations of aging. PWV, pulse wave velocity.
| Journal of Clinical Medicine Research, ISSN 1918-3003 print, 1918-3011 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Clin Med Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://jocmr.elmerjournals.com |
Review
Volume 17, Number 9, October 2025, pages 469-489
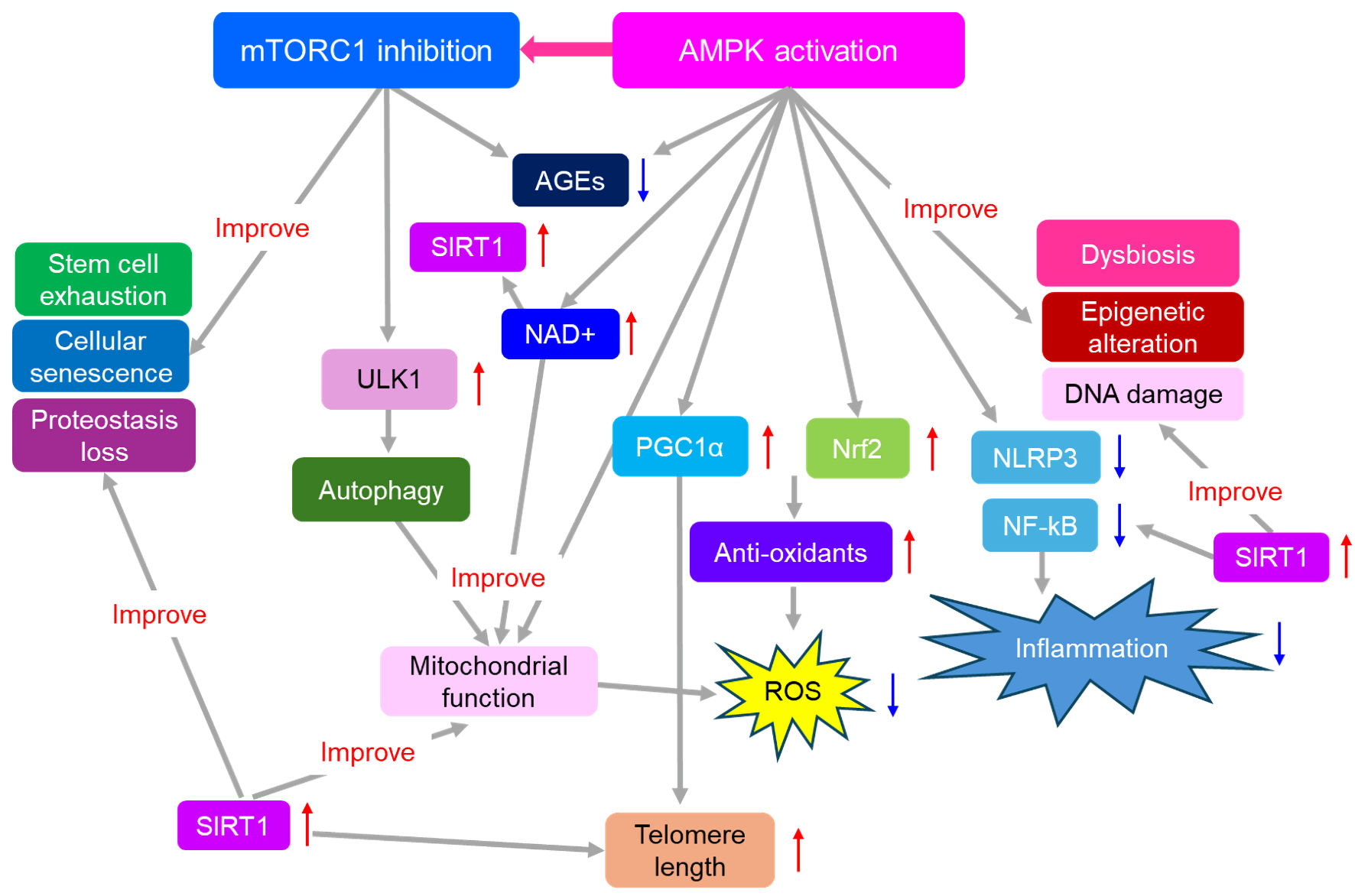
Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Activation and Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1 Inhibition: A Mechanistic Rationale for Anti-Aging Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
Figures

Tables
| Therapeutic interventions | AMPK activation | mTORC1 inhibition | Effects on type 2 diabetes |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acids; TG: triglyceride; HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin. | |||
| Calorie restriction | (+) [201] | (+) [202] | The meta-analysis showed that calorie-restricted diets were an effective intervention for type 2 diabetes remission in comparison to a usual diet or usual care [203]. |
| Vitamin E | (+) [204] | (+) [205] | The meta-analysis showed that vitamin E intake has a beneficial role in improving HbA1c and insulin resistance in a population with diabetes [206]. |
| Vitamin C | (+) [207] | (+) [208] | The meta-analysis showed that long-term (≥ 12 weeks) and high-dose vitamin C supplementation (≥ 1,000 mg/d) ameliorated glycemic profile in patients with type 2 diabetes [209]. |
| Resveratrol | (+) [210] | (+) [211] | In the meta-analysis, there was a significant effect on the reduction of insulin resistance and glycated hemoglobin. For fasting blood glucose, the results were significant for individuals with diabetes [212]. |
| Astaxanthin | (+) [213] | (+) [213] | Astaxanthin showed preventive effects against diabetes and atherosclerosis and may be a novel complementary treatment option for the prevention of diabetes in healthy volunteers, including subjects with prediabetes, without adverse effects [214]. |
| n3-PUFA | (+) [215] | (+) [216] | An individual participant-level pooling project of 20 prospective cohort studies showed that higher circulating biomarkers of seafood-derived n-3 PUFA were associated with lower risk of type 2 diabetes in a global consortium of prospective studies [217]. |
| Anti-diabetic drugs | Effects on CVD | Effects on AD |
|---|---|---|
| AMPK: adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; mTORC1: mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; aHR: adjusted hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; CVD: cardiovascular disease; GLP-1RAs: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; OR: odds ratio; SGLT2is: sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors; 3P-MACE: 3-point major cardiovascular event. | ||
| Metformin | A meta-analysis showed that the risk of CVD mortality in metformin patients was lower than in the other two groups (placebo and other anti-diabetic drugs) (OR: 0.771; 95% CI: 0.688 to 0.853), and the risk of CVD in metformin users was also lower than in the other two groups (OR: 0.828; 95% CI: 0.781 to 0.785) [221]. | A meta-analysis of 10 clinical observational studies showed no significant association between AD incidence and metformin exposure (OR: 1.17; 95% CI: 0.88 to 1.56) [222]. Three relevant clinical trials, Metformin in Alzheimer’s Dementia Prevention (MAP), MET-FINGER, MET-MEMORY, are currently underway to understand the effect of metformin on the prevention of AD [223]. |
| SGLT2is | The EMPA-REG OUTCOME showed that empagliflozin reduced 3P-MACE by 14% as compared with placebo [224]. The CANVAS program showed that the rate of 3P-MACE was lower with canagliflozin as compared with placebo by 14% [225]. | A retrospective examination of data from a cohort of 1,348,362 participants with type 2 diabetes showed that SGLT2is use was associated with reduced risks of AD (aHR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.76 to 0.87) [226]. |
| GLP-1RAs | The LEADER showed that 3P-MACE occurred in significantly fewer patients in the liraglutide group than in the placebo group (HR: 0.87; 95% CI: 0.78 to 0.97) [227]. The SUSTAIN-6 trial showed that 3P-MACE occurred in 108 of 1,648 patients (6.6%) in the semaglutide group and in 146 of 1,649 patients (8.9%) in the placebo group (HR: 0.74; 95% CI: 0.58 to 0.95) [228]. | The meta-analysis of pre-clinical studies showed that GLP-1RAs improved the learning and memory abilities of AD rodents; GLP-1RAs reduced amyloid beta deposition and phosphorylated tau levels in the brains of AD rodents [229]. A meta-analysis of human studies also showed that GLP-1RAs effectively improved cognitive function in patients with AD [230]. |