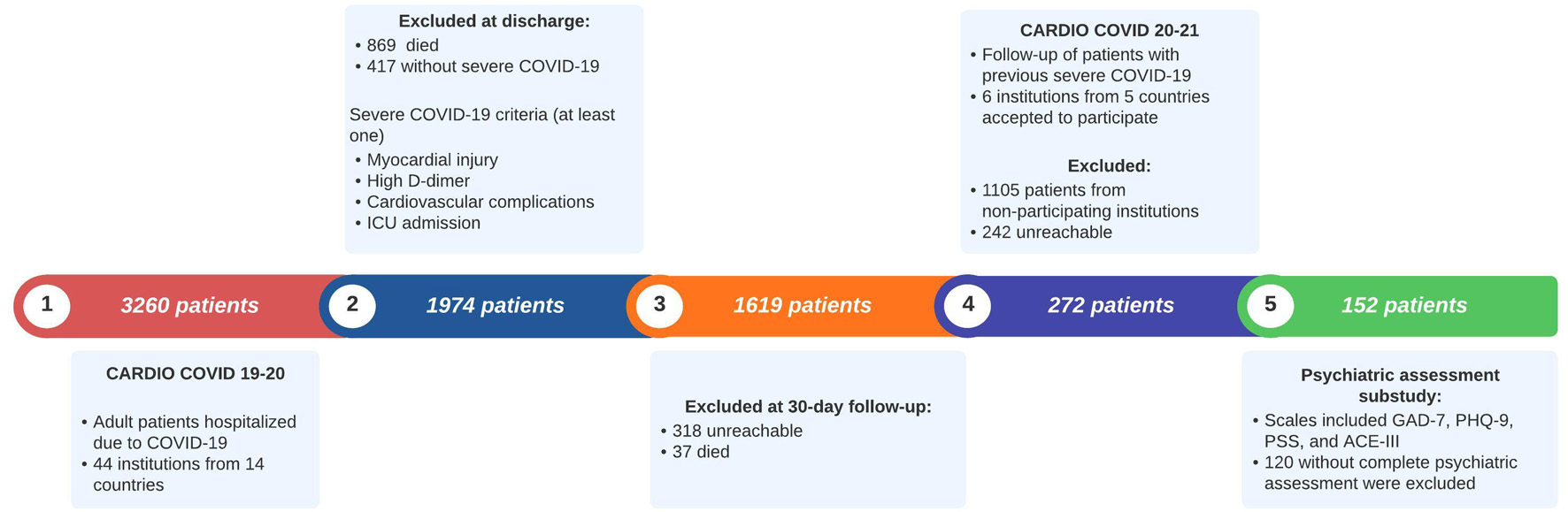
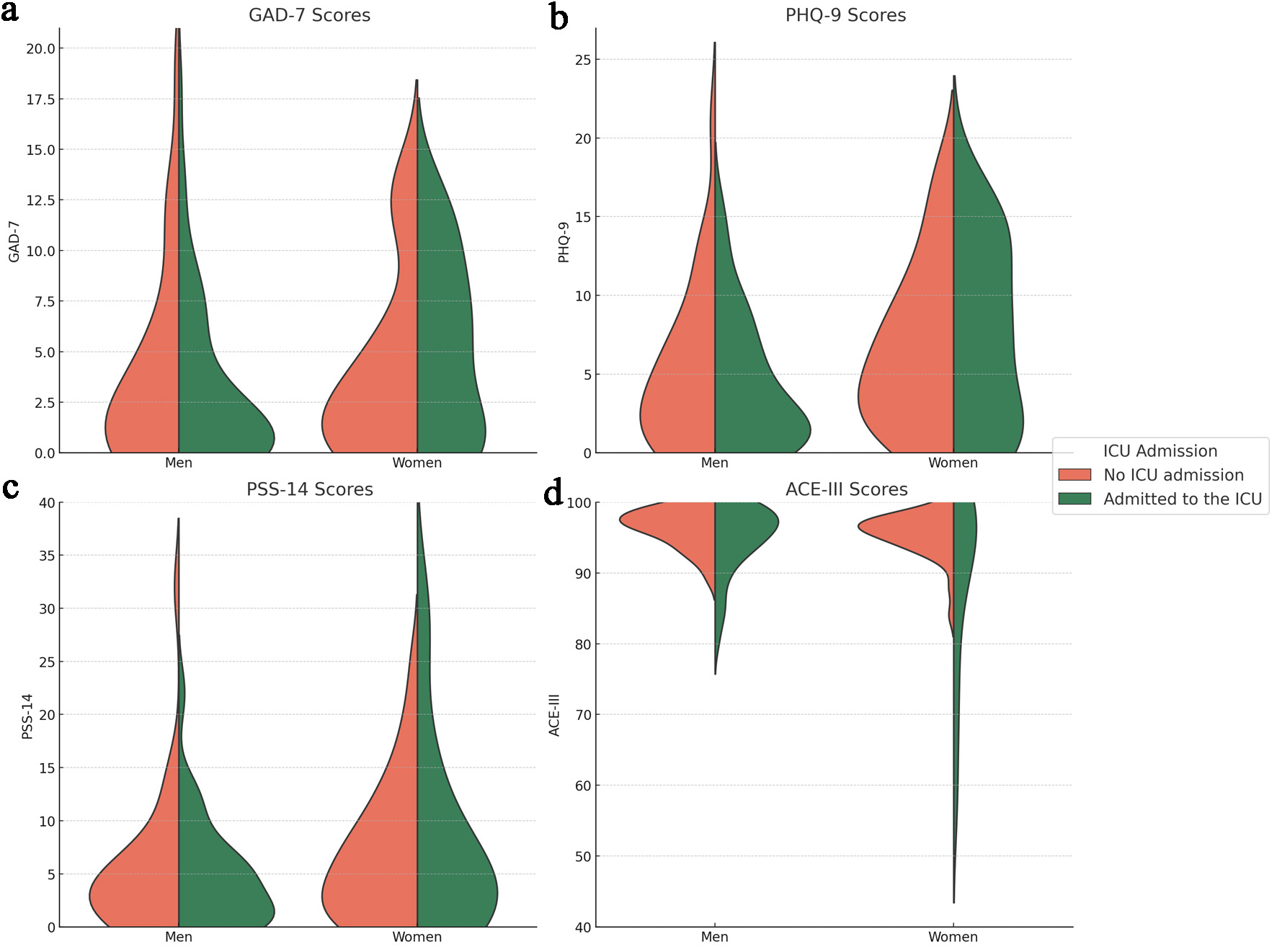
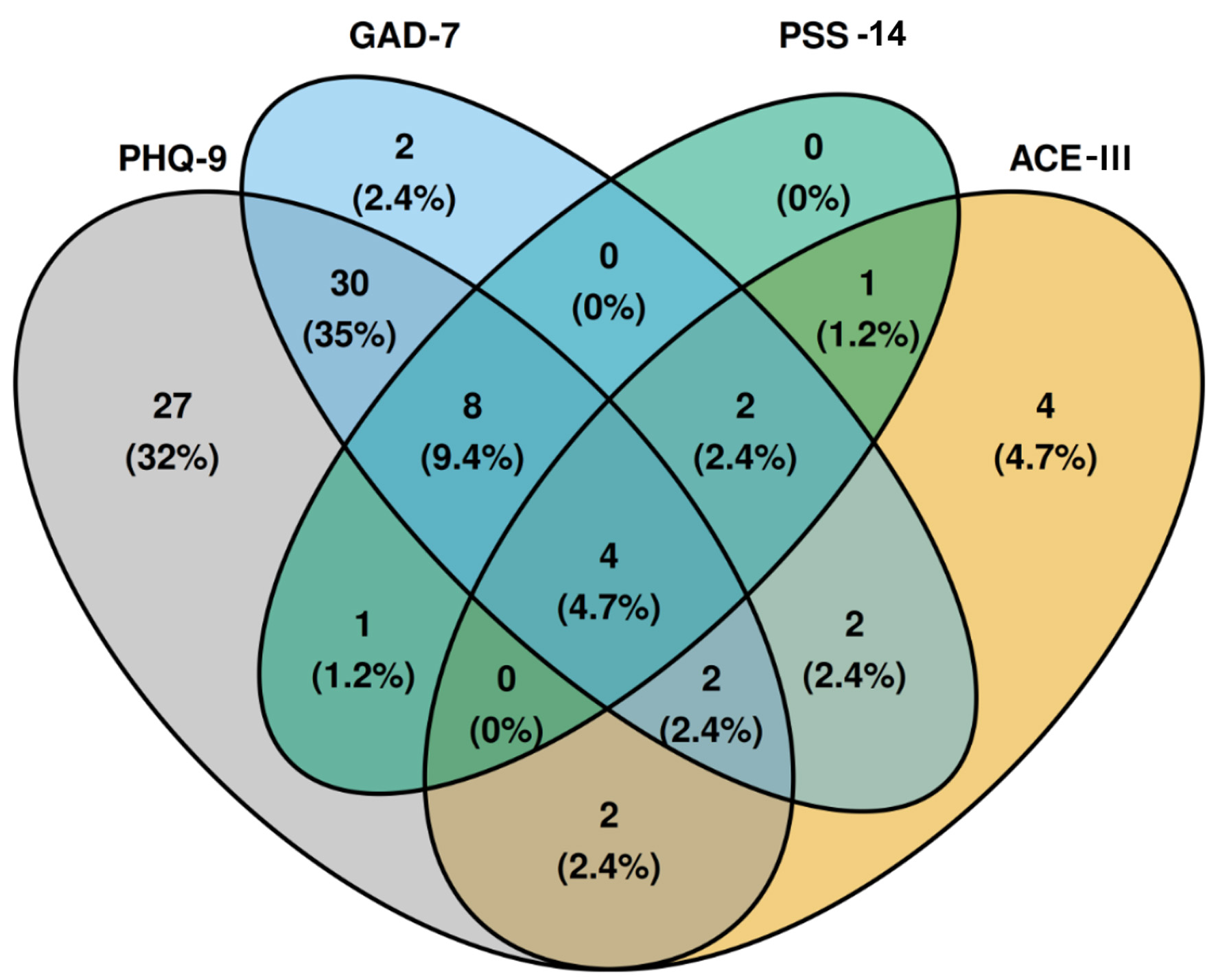
| GAD-7 | A 7-item scale to screen for general anxiety disorder [20]. A cutoff point of 5 has shown a sensitivity of 94% and a specificity of 65% [21]. The version of this scale in Spanish has been previously validated in Colombia [22]. | 0–4: none to minimal anxiety; 5–9: mild anxiety; 10–14: moderate anxiety; ≥ 15: severe anxiety |
| PHQ-9 | A 9-item scale validated for depression screening [23, 24]. A cutoff point of 5 has a sensitivity of 87% and a specificity of 80% [25]. The version of this scale in Spanish has been previously validated in Colombia [26]. | 0–4: none to minimal depression; 5–9: mild depression; 10–14: moderate depression; 15–19: fairly severe depression; ≥ 20: severe depression. |
| PSS-14 | A 14-item questionnaire used to measure psychological stress [27]. The Spanish version of this scale has been previously validated [28]. | 0–13: Low perceived stress; 14–26: moderate perceived stress; 27–40: high perceived stress. |
| ACE-III | An extended cognitive assessment to screen for cognitive dysfunction. A cutoff score of 88 has a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 93% [29]. The Spanish version has been previously validated [30]. | 100–88: No cognitive dysfunction; 88–82: possible mild cognitive dysfunction; < 82 possible dementia. |