Effect of Comorbidities on the Incidence of Surgical Site Infection in Patients Undergoing Emergency Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr5222Keywords:
Comorbidity, Surgical site infection, Emergency, SurgeryAbstract
Background: Surgical site infection (SSI) is a significant concern in patients undergoing emergency surgery, particularly in those with underlying comorbidities. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effect of comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus, hypertension, obesity, pulmonary disease, cardiac disease, liver disease, and renal disease, on the incidence of SSI in patients undergoing emergency surgery.
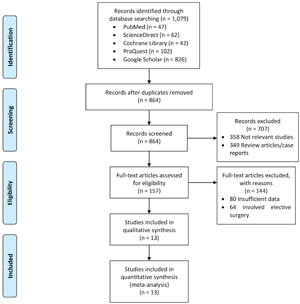
Methods: We performed a systematic literature search across electronic databases including PubMed, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, ProQuest, and Google Scholar to identify studies examining the effect of comorbidities on the incidence of SSI in patients undergoing emergency surgery. To determine the effect size, pooled odds ratios (ORs) were calculated. Statistical analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.3 software.
Results: Thirteen studies involving 8,952 patients undergoing emergency surgery were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled analysis showed that the following comorbidities significantly increased the risk of SSI following emergency surgery: diabetes mellitus (OR = 2.22; 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.52 - 3.25; P < 0.0001), obesity (OR = 1.43; 95% CI = 1.19 - 1.72; P = 0.0001), and liver disease (OR = 1.66; 95% CI = 1.37 - 2.00; P < 0.00001). However, hypertension, pulmonary disease, cardiac disease, and renal disease showed no significant association with SSI.
Conclusions: In patients undergoing emergency surgery, the presence of comorbidities including diabetes mellitus, obesity, and liver disease increases the incidence of developing SSI.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








