Association Between the Development of Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Blood NAD+ Levels
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6083Keywords:
Sensorineural hearing loss, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, Sirtuin 1, Mitochondrion, AgingAbstract
Background: Hearing loss prevalence increases with age, affecting over 25% of the global population aged 60 years or older. The aim of the study was to investigate the association between the development of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and the blood levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
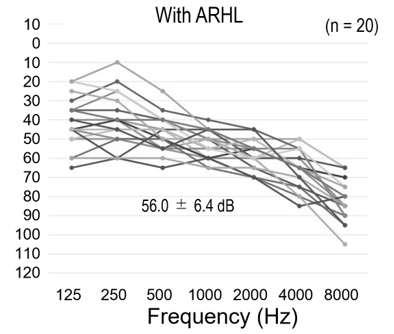
Methods: A single-center, observational study was conducted at Kawagoe Otology Institute in Japan. A total of 80 patients were included and allocated to four groups of 20 patients each: patients aged 50 - 79 years with or without unilateral sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL), and patients aged ≥ 80 years with or without bilateral age-related hearing loss (ARHL). The distribution of whole-blood NAD+ levels was investigated. We also measured oxidative stress markers (diacron-reactive oxygen metabolites (dROMs) and biological antioxidant potential (BAP)) and examined the relationship between the development of SNHL and whole-blood NAD+ levels, dROMs, and BAP.
Results: Comparison of NAD+ levels with and without hearing loss in the same age group by analysis of covariance showed a significantly lower NAD+ level in those with hearing loss than those without in the ≥ 80 age group (P = 0.047), whereas there was no difference between the two groups in the 50 - 79 age group (P = 0.232). All 80 patients, without consideration of age or type of hearing loss, were subjected to multivariate analysis to explore factors contributing to the development of hearing loss. With each 1 µM increase in the NAD+ level, the probability of developing SNHL decreased to 0.9-fold (P = 0.047), and each 1 U.CARR increase in dROMs was associated with a 1.01-fold increase in the risk of developing SNHL (P = 0.014). Whole-blood NAD+ levels in ARHL patients were significantly lower than those in non-ARHL patients. There was no association between whole-blood NAD+ and dROMs or BAP levels. This study has some limitations, including a sample size that was not large enough to detect a significant difference and an imbalance in the male-to-female ratio.
Conclusions: Decreased amount of NAD+ in the body and increased dROMs levels were associated with increased risk of developing SNHL, and the development of ARHL was especially highly associated with a decreased amount of NAD+ in the body.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








