The Effects of Preoperative Serum Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Cancer Antigen 15-3 and Cancer Antigen 125 on the Prognosis of Breast Cancer Patients With Different Molecular Subtypes
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr5237Keywords:
Breast cancer, Serum tumor markers, Molecular subtype, PrognosisAbstract
Background: The aim of the study was to investigate the relationship between serum carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), cancer antigen 15-3 (CA15-3), and cancer antigen 125 (CA125) levels and traditional clinicopathological factors in patients with early invasive breast cancer in Xinjiang, and the influence of those serum markers on the prognosis of patients with different molecular subtypes.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study based on the clinical data of 2,940 invasive breast cancer patients who were diagnosed and treated at the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University from 2015 to 2019. Firstly, in this study, preoperative serum CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 levels were divided into elevated and normal groups based on the optimal cut-off values. Secondly, Chi-square test was used to analyze the correlation between the elevated and normal groups of CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 and traditional clinicopathological factors. Finally, Cox regression model was also used to evaluate the effect of preoperative CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 elevated groups on the prognosis of patients with different molecular subtypes compared with normal groups.
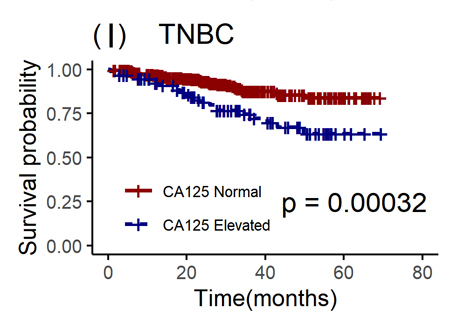
Results: The optimal cut-off values for preoperative CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 were 4.32 ng/mL, 23.10 U/mL and 29.80 U/mL, respectively. The elevated group of preoperative CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 patients usually had larger tumors (tumor size: T2-4), later clinical staging (TNM stage: II-III), and higher histological grading (histological grade: II-III). Univariate analysis showed that the overall survival (OS) of preoperative CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 patients in the elevated group was lower than that in the normal group (P < 0.0001), the 5-year OS was 76.63% vs. 95.35%, 74.34% vs. 95.60%, and 83.73% vs. 94.71%, respectively. Multivariate analysis revealed that for the luminal A, compared with the normal group, the hazard ratios (HRs) of preoperative CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 elevated groups were 6.475 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.850 - 22.66), 5.192 (95% CI: 1.153 - 23.38), and 7.294 (95% CI: 1.152 - 46.18), respectively. However, for the luminal B, elevated levels of CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 were not independent prognostic factors for OS. For the human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-enriched, the HR of preoperative CA15-3 elevated group was 3.155 (95% CI: 1.325 - 7.509). Additionally, for the triple-negative breast cancer, the HR of preoperative CEA elevated group was 2.390 (95% CI: 1.247 - 4.583).
Conclusions: High levels of CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 were positively correlated with increased tumor load. Preoperative CEA, CA15-3, and CA125 levels may have different prognostic effects on patients with different molecular subtypes. Particularly, preoperative elevated levels of CEA have a significant adverse impact on the prognosis of luminal A and triple-negative patients, while preoperative elevated levels of CA15-3 have an adverse effect on the prognosis of luminal A and HER-positive patients.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








