Phenotypic Variability and Hematological Characterization of β0- and β+-Thalassemia Carriers: A Comparative Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6213Keywords:
Hemoglobinopathies, β-thalassemia, Pathogenic variants, Phenotype, Hemoglobin variantsAbstract
Background: β-Thalassemia is a genetic disorder characterized by decreased or completely absent β-globin synthesis, leading to a spectrum of clinical manifestations. It is a major public health concern in Jordan, as in other Mediterranean countries. β-Thalassemia carriers are normally asymptomatic; nevertheless, laboratory examinations often reveal mild anemia characterized by microcytic hypochromic erythrocytes, with differences influenced by specific phenotypes. This study aimed to assess and correlate the variants among β0 and β+ phenotypes in the Jordanian population with hematological characteristics, as well as establish and determine reference values for distinguishing between the two phenotypes.
Methods: One hundred forty-five β-thalassemia carriers were recruited from various governorates in Jordan. Hematological parameters, including complete blood count (CBC) and capillary electrophoresis of hemoglobin (Hb), were evaluated in all participants. Molecular techniques, specifically polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with hybridization, were employed to identify β-thalassemia variants and classify the participants as having β0 and β+ phenotypes.
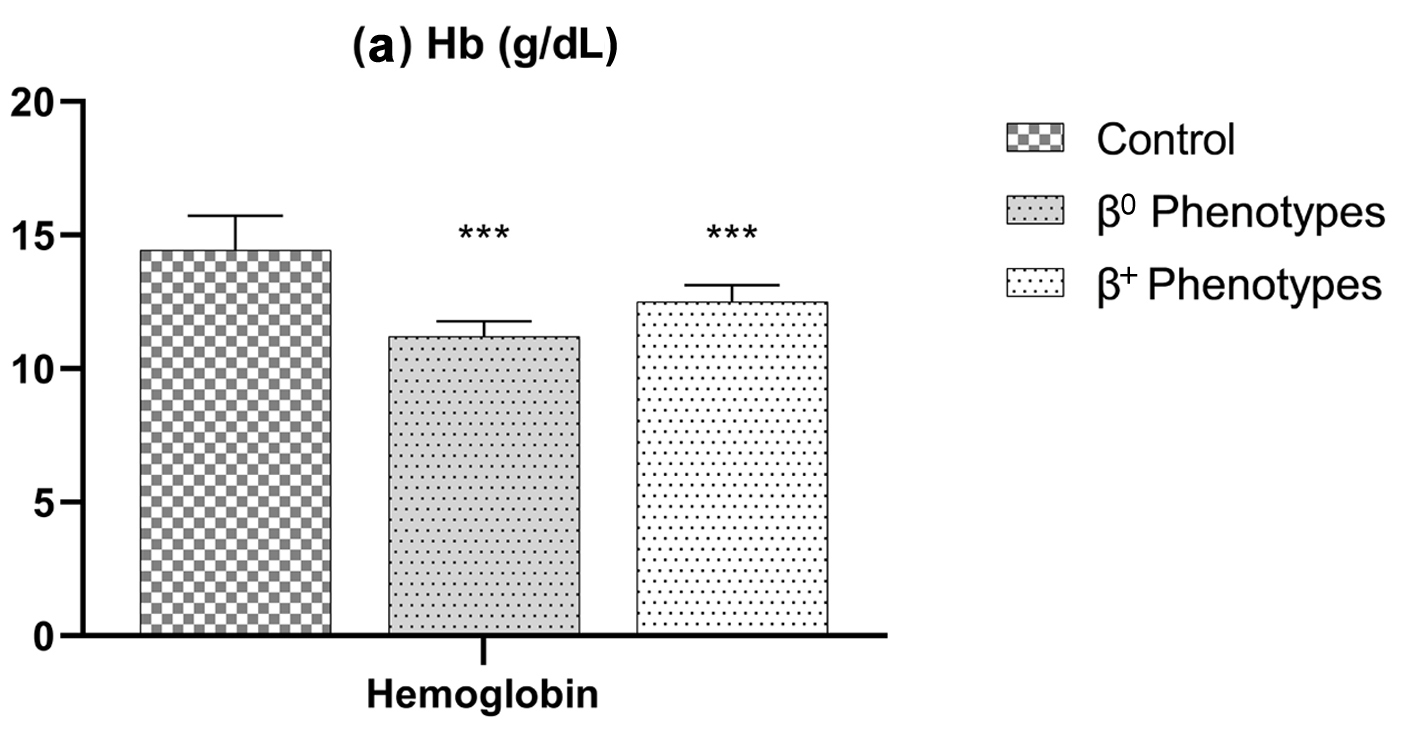
Results: Among the 145 β-thalassemia carriers, 64 (44.14%) and 81 (55.86%) had β0-thalassemia and β+-thalassemia, respectively. Participants exhibiting a cutoff value of Hb (≤ 11.0 g/dL), mean corpuscular volume (MCV) (≤ 64.0 fL), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) (≤ 19.0 pg), and hemoglobin A2 (Hb-A2) (≥ 5.00%) were classified as having the β0 phenotype. These participants demonstrated significantly lower mean Hb, MCV, MCH, and higher mean Hb-A2 than the participants with the β+ phenotype (P < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Hb, MCV, MCH, and Hb-A2 can serve as effective screening tools for predicting β0- and β+-thalassemia in the Jordanian population. These findings have important clinical implications for early diagnosis, genetic counseling, and prenatal screening of β-thalassemia.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








