Comparison of the SeizCT Primer and Optimized Models for Predicting Positive Computed Tomography Findings in Patients With Non-Traumatic Seizures
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6375Keywords:
Seizures, Tomography, X-ray computed, Validation, Diagnosis, Mobile applicationsAbstract
Background: Previous studies developed the SeizCT primer and optimized models, both demonstrating similar values for the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AuROC). The optimized model incorporates Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) change from baseline instead of categorized GCS at emergency department (ED) presentation. This study aimed to validate these two models for predicting positive computed tomography (CT) findings in patients with non-traumatic seizures.
Methods: A retrospective cross-sectional study was conducted among adult patients (≥ 18 years) with non-traumatic seizures who underwent CT brain imaging in the ED at Lampang Hospital. Data were collected between December 2023 and July 2024 based on parameters from the SeizCT primer and optimized models. External validation compared model performance using AuROC, calibration, decision curve analysis (DCA), and confusion matrices.
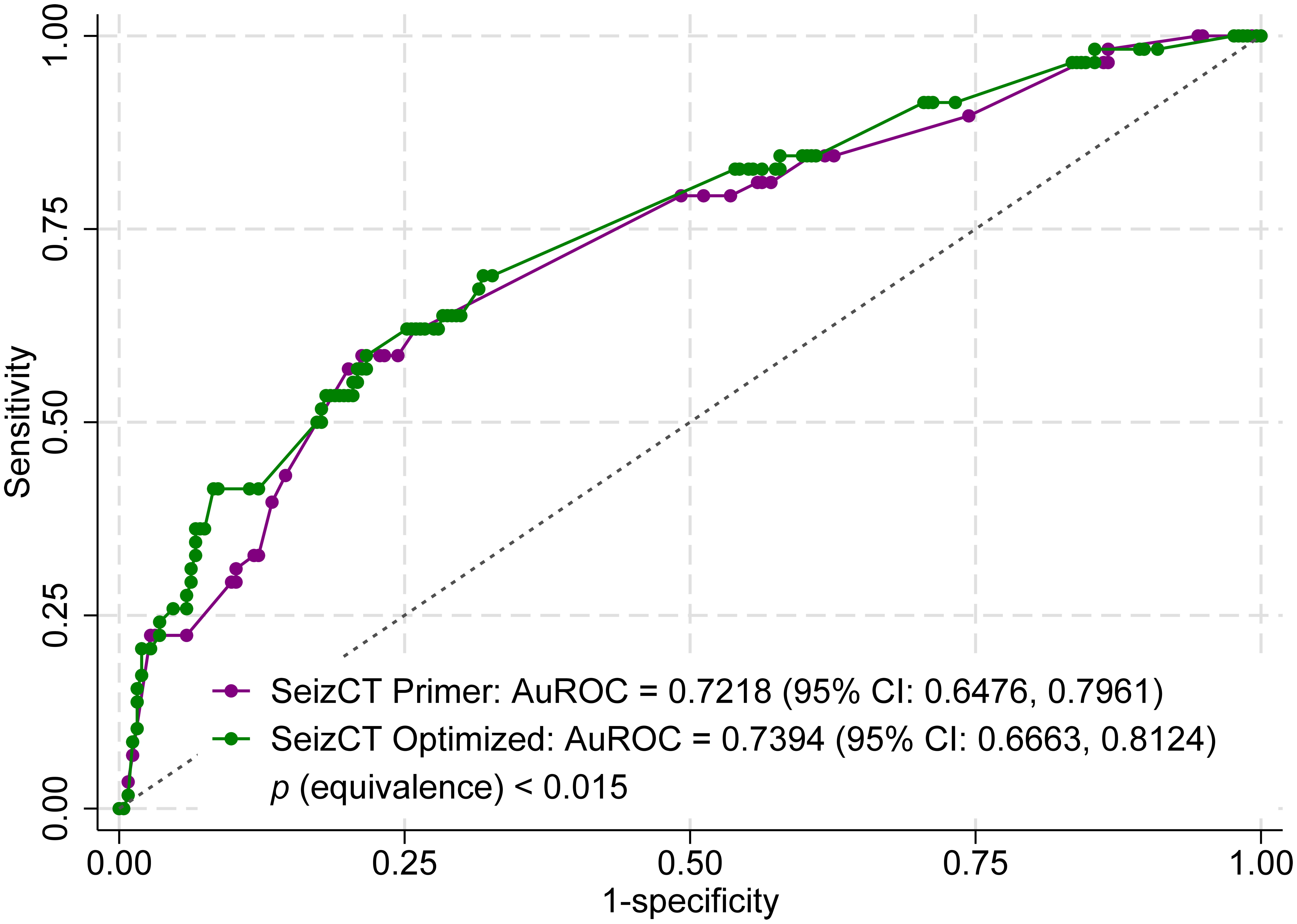
Results: The validation cohort included 312 patients (210 (67.3%) male; mean age 53 years). Positive CT findings were found in 58 patients (18.6%). The SeizCT primer model had an AuROC of 0.7218 (95% confidence interval (CI): 0.6476, 0.7961), while the SeizCT optimized model achieved 0.7394 (95% CI: 0.6663, 0.8124). An equivalence test showed statistically equivalent discrimination between the two models (P < 0.015), with the optimized model demonstrating better calibration (slope: 0.582 vs. 0.701; P = 0.002; observed-to-expected ratio: 0.934 vs. 0.971; P = 0.030).
Conclusions: Both models demonstrated fair to acceptable discrimination after external validation. The SeizCT optimized model is recommended, as it showed superior calibration and its incorporation of GCS change from baseline offers greater clinical applicability.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








