Impact of the First Twenty-Four-Hour Area Under the Concentration-Time Curve/Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Vancomycin on Treatment Outcomes in Patients With Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr5238Keywords:
First 24-h AUC/MIC, Vancomycin, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, BacteremiaAbstract
Background: Vancomycin regimens are designed to achieve an area under the concentration-time curve/minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC/MIC) ratio ranging between 400 and 600 µg·h/mL in the steady state. However, in cases of critical infections such as bacteremia requiring an early treatment approach, the clinical course may be affected by the AUC/MIC before reaching the steady state, that is, the AUC/MIC values 24 h after the first dose (first 24-h AUC/MIC). This study evaluated the relationship between the first 24-h AUC/MIC and the clinical course of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the records of patients with MRSA bacteremia in a university hospital between 2015 and 2022. The first 24-h AUC/MIC cutoff was set at 300 µg·h/mL based on the results of early response, and eligible patients were divided into groups with a first 24-h AUC/MIC either < 300 µg·h/mL (< 300 group, n = 32) or ≥ 300 µg·h/mL (≥ 300 group, n = 38). The primary endpoint was the rate of treatment efficacy, and the secondary endpoints were time to clinical and bacteriological improvement and 30-day survival rate.
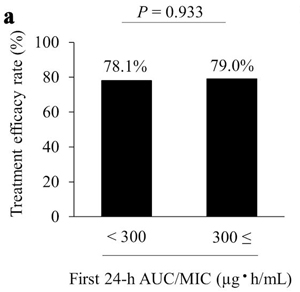
Results: Treatment efficacy and 30-day survival rates were not significantly different between the two groups (78.1% vs. 79.0%, P = 0.933 and 83.9% vs. 87.2%, P = 0.674, respectively). Among patients who showed treatment efficacy, the median time to clinical and bacteriological improvement was 11.5 days and 8.0 days in the < 300 and ≥ 300 groups, respectively; compared to the ≥ 300 group, the < 300 group had a significantly longer time to improvement (P = 0.001).
Conclusions: The first 24-h AUC/MIC had no effect on the treatment efficacy and 30-day survival rates. However, the time to clinical and bacteriological improvement was significantly prolonged in the < 300 group, indicating that the first 24-h AUC/MIC does not affect the rate of therapeutic efficacy but may affect the treatment period.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








