Prevention of Chromium-Induced Radiation-Chemical Oncogenesis, Including in Offspring, in an Experimental Model: A Systematic Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6265Keywords:
Hexavalent chromium, Gamma-irradiation, Induced oncogenesis, Prevention, PhytopreparationsAbstract
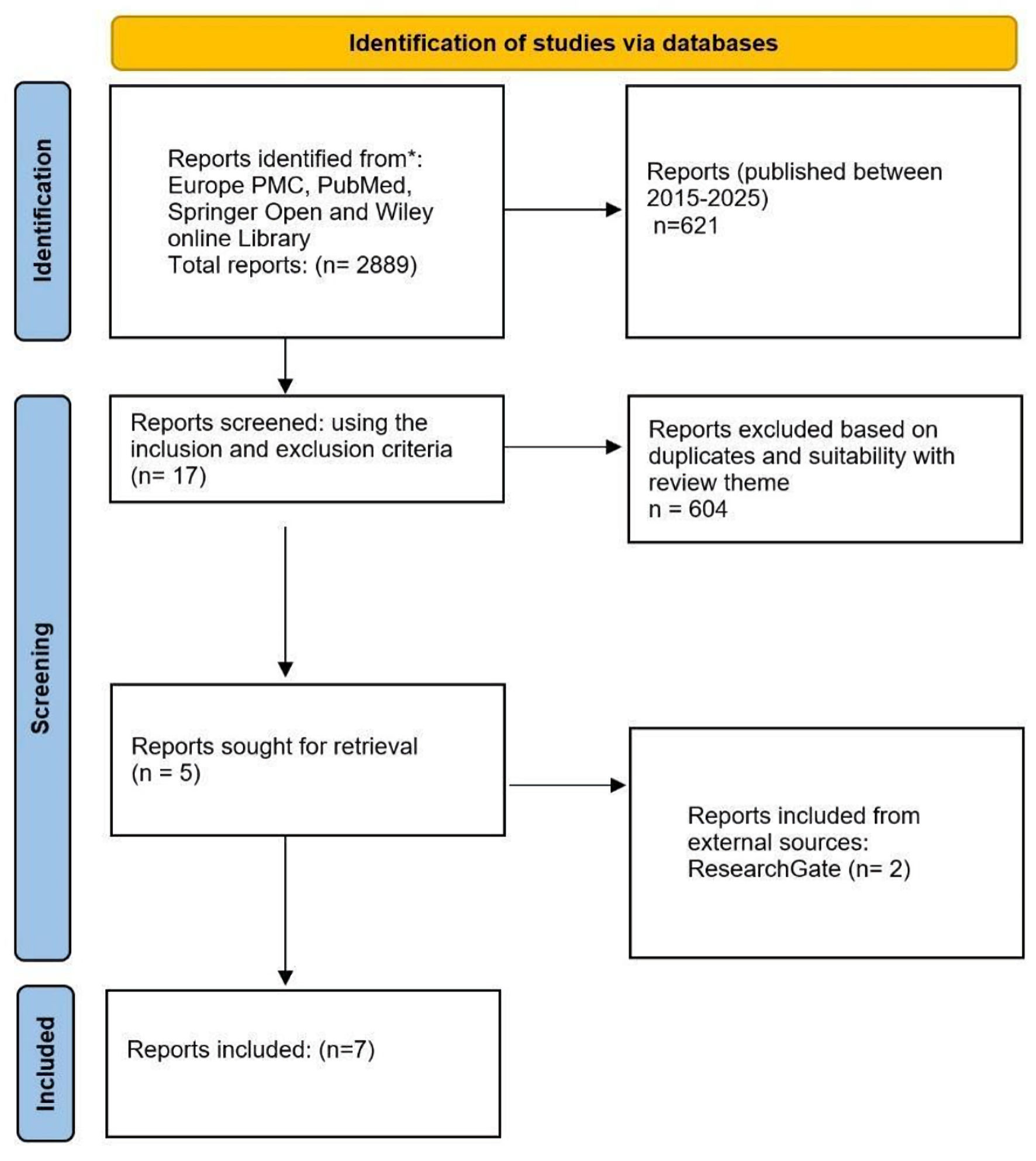
Radiation and chemical-induced cancer are of increasing concern as the various activities of humans continuously elevate the levels of radiation and toxic chemicals in the environment. The prevention of this incidence using alternative medicines-phytopreparations, therefore, becomes pertinent as conventional approaches tend to produce various unwanted side effects. To achieve this, there is a need to understand the various mechanisms of action through which phytopreparations exhibit their protective effects. This systematic review, therefore, aims to explore the mechanism of action of various phytopreparations in the prevention of induced radiation and chemical (chromium) cancer. A systematic review approach following the stipulated guidelines by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) was used to identify research papers published between 2015 and 2025. Four databases, namely Europe PubMed Central (PMC), PubMed, Springer Open, and Wiley Online Library were used to search for related open access papers. A total of 621 research papers were reviewed for suitability to the review objective; however, only five papers met the inclusion criteria, and an additional two papers were sourced from ResearchGate. Thus, a total of seven papers were finally included in the analysis. This review highlights the mechanisms of action of various phytopreparations in the prevention of radiation and chromium-induced cancer. The major mechanisms of phytopreparations’ action in the prevention of induced radiation and chromium oncogenesis majorly involve regulating pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines, improving cell-to-cell communication, and preventing damage to DNA structure.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








