Comparative Evaluation of Risk of Death in Mechanically Ventilated Patients With COVID-19 and Influenza: A Population-Based Cohort Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6189Keywords:
COVID-19, Influenza, Mechanical ventilation, MortalityAbstract
Background: Reports on the comparative mortality among mechanically ventilated patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and influenza show conflicting findings, but studies focused largely on the early phase of the pandemic, using historical influenza comparators. We sought to examine the population-level comparative mortality among mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 during the latter pandemic years using contemporaneous influenza comparators.
Methods: We used a statewide dataset to identify mechanically ventilated hospitalizations aged ≥ 18 years with COVID-19 or influenza in Texas between October 2021 and March 2023. Their comparative short-term mortality (in-hospital death or discharge to hospice) was estimated using overlap propensity score weighting (primary model), entropy balance, and hierarchical logistic models.
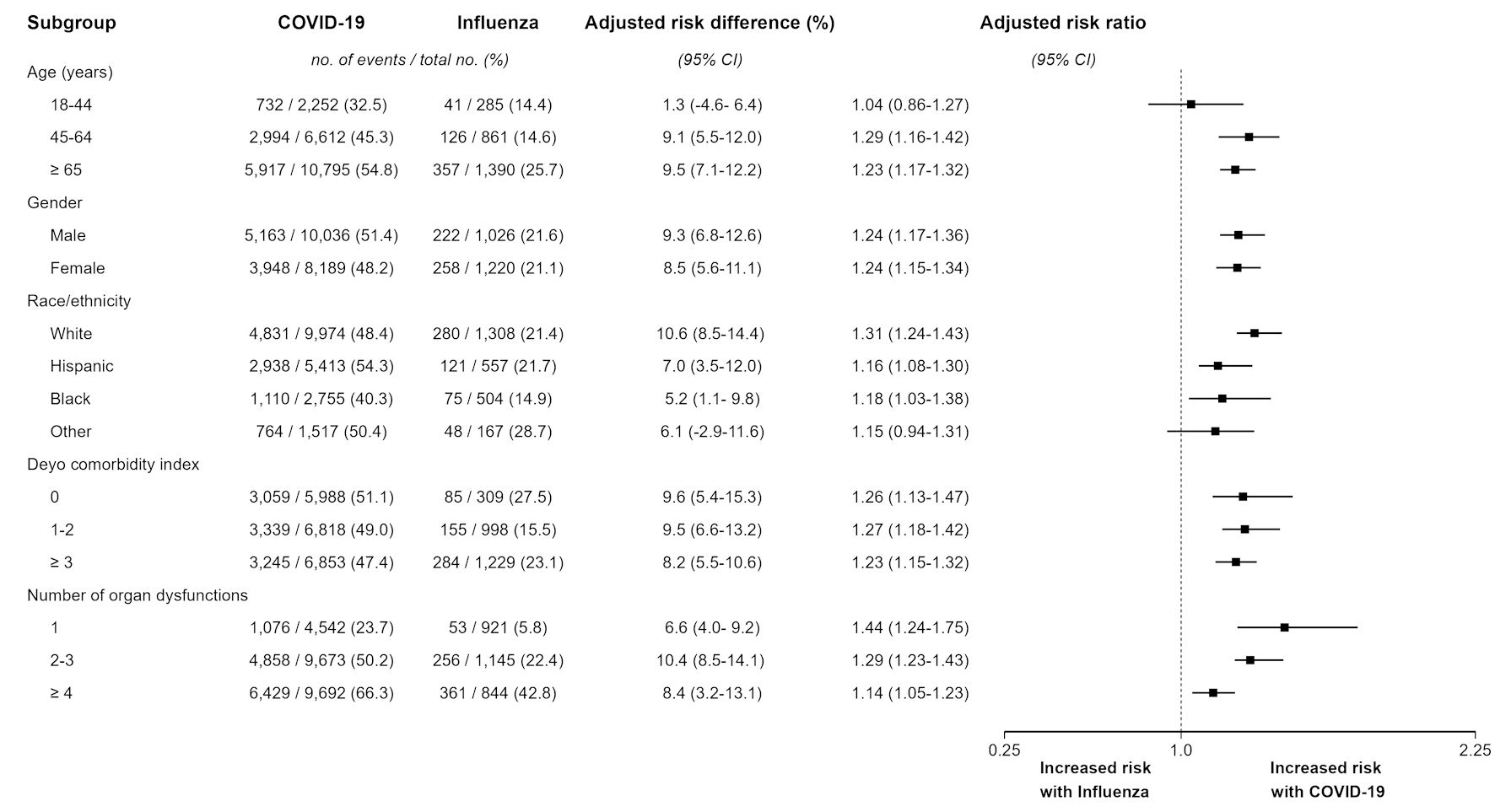
Results: Among 22,195 mechanically ventilated hospitalizations, 19,659 (88.6%) had COVID-19 and 2,536 (11.4%) had influenza. Compared to mechanically ventilated hospitalizations with influenza, those with COVID-19 were more commonly racial or ethnic minority (49.3% vs. 48.4%) and had lower mean (standard deviation (SD)) Deyo comorbidity index (2.04 (2.03) vs. 2.53 (1.91)), but higher number of organ dysfunctions (2.60 (1.37) vs. 2.13 (1.27)), respectively. Short-term mortality among mechanically ventilated hospitalizations with COVID-19 and influenza was 49.1% vs. 20.7%. The risk of short-term mortality was attenuated but remained higher among hospitalizations with COVID-19 in the primary model (adjusted risk ratio: 1.24 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.18 - 1.30); adjusted risk difference 8.8% (95% CI: 6.7 - 10.4)), with consistent findings in alternative models, subgroups, and sensitivity analyses.
Conclusions: Population-level short-term mortality among mechanically ventilated hospitalizations with COVID-19 has been higher than that among those with influenza during the latter years of the pandemic.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








