Anti-Breast Cancer Effects of Thymoquinone-Chemotherapeutic Combinations: A Systematic Review of the Latest In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/0.14740/jocmr6230Keywords:
Anti-cancer effect, Breast cancer, Thymoquinone, Nigella sativa, Systematic reviewAbstract
Background: Breast cancer is a leading malignancy among women globally, with chemotherapy as a cornerstone of treatment. However, the side effects and toxicity associated with chemotherapy necessitate the exploration of adjunctive therapies to improve efficacy and reduce adverse effects. Thymoquinone (TQ) has shown potential anti-cancer properties. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of TQ in combination with chemotherapeutic agents in treating breast cancer.
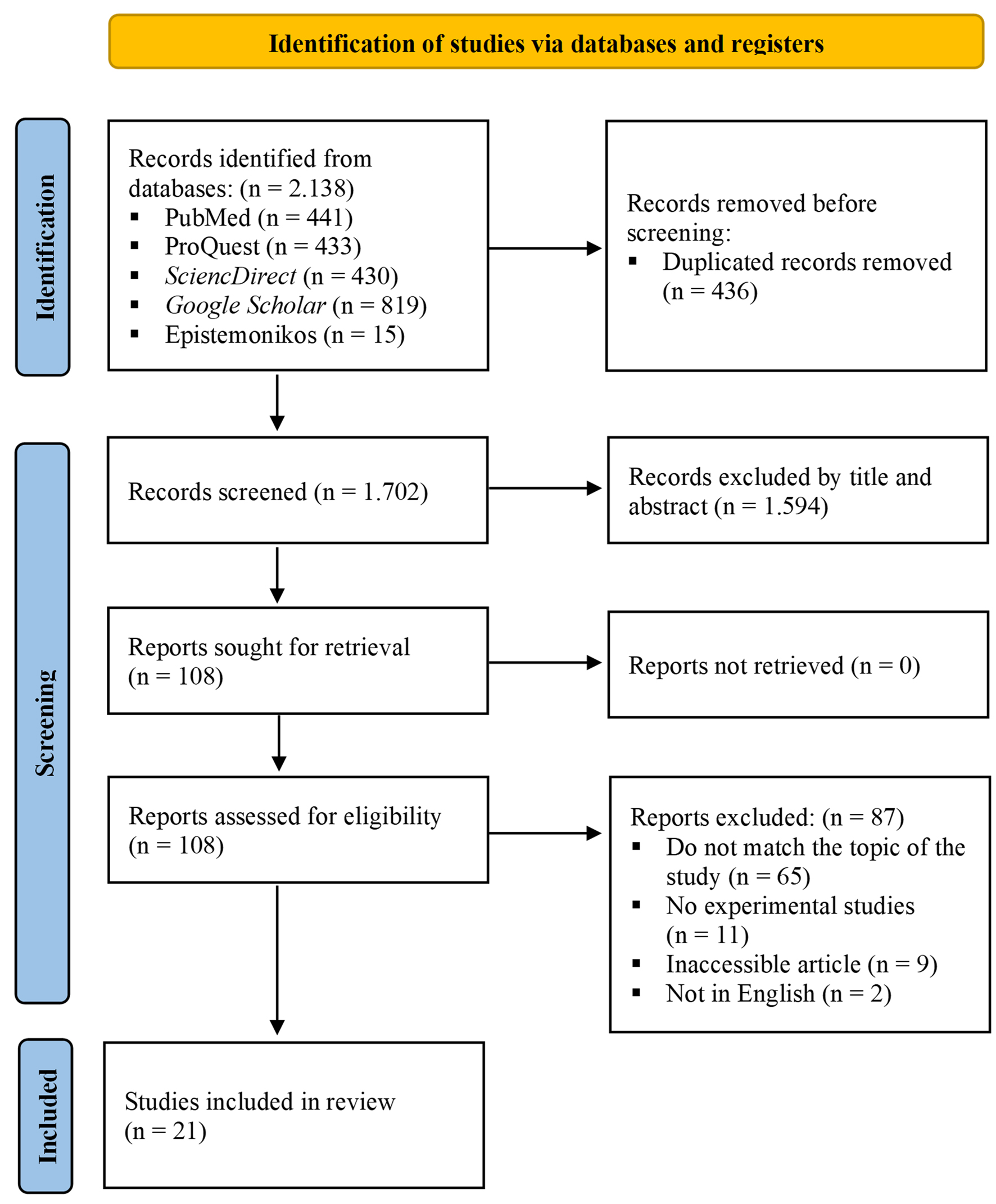
Methods: This study thoroughly reviewed and synthesized existing research following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) 2020 guidelines. The selected databases, including PubMed, ProQuest, ScienceDirect, Epistemonikos, and Google Scholar, were searched over the past 10 years. Eligibility criteria were based on the PICOS framework, focusing on experimental studies involving TQ-chemotherapy combinations. Data extraction and quality assessment were performed using SYRCLE and SCIRAP tools. This review included 18 in vitro and six in vivo studies.
Results: Findings revealed that TQ enhances the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents by inducing apoptosis, enhancing autophagy, inhibiting tumor growth, and regulating cancer cell signaling pathways as well as multiple phases of the cell cycle. Additionally, TQ reduced chemotherapy-related toxicity, such as heart, blood, liver, and kidney damage, and also improved patient tolerance. Nanoparticle-based delivery systems further amplified these synergistic effects.
Conclusions: The TQ-chemotherapy combination shows significant potential as a therapy for breast cancer, enhancing treatment efficacy while mitigating side effects. Future clinical studies are needed to establish its safety and therapeutic applicability.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








