Ruxolitinib Plus Extracorporeal Photopheresis for Steroid-Refractory Acute and Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6385Keywords:
Steroid-refractory graft-versus-host disease, GvHD, Ruxolitinib, Extracorporeal photopheresis, Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantationAbstract
Background: Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a serious complication of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, and the major cause of post-transplant mortality and morbidity. If steroid treatment as first-line therapy fails, treatment options are limited. Ruxolitinib (Ruxo) as well as extracorporeal photopheresis (ECP) showed high efficacy in the treatment of steroid-refractory (SR) acute and chronic GvHD.
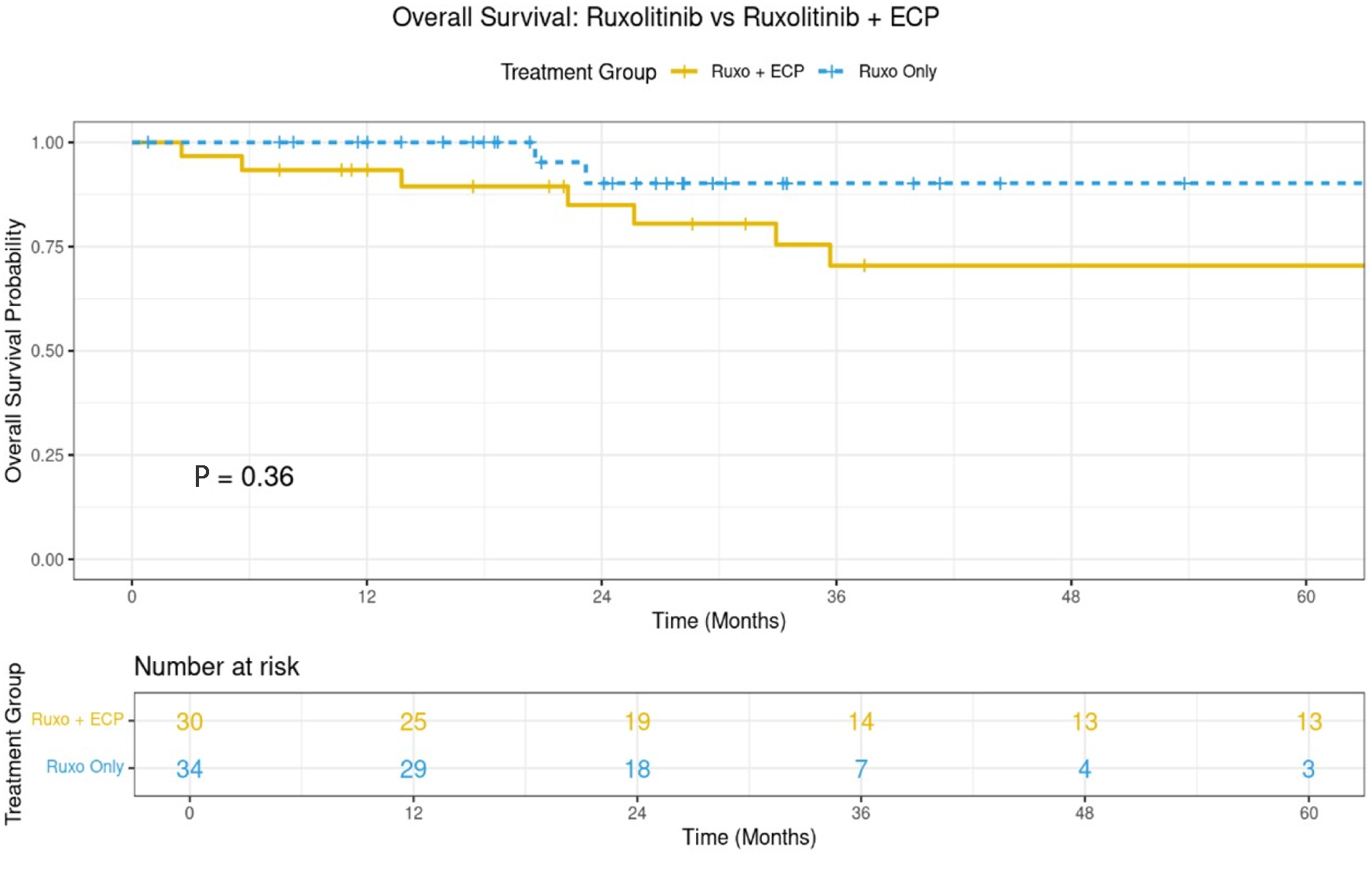
Methods: We interrogated data from 68 adult and pediatric patients with SR acute and chronic GvHD, between 2017 and 2024, who received either Ruxo plus ECP (Ruxo + ECP, n = 31) or Ruxo alone (Ruxo, n = 37). Endpoints were to compare the overall response rates (ORRs) including complete response (CR) and partial response (PR) of acute and chronic GvHD at last encounter, and the percentage of patients with history of acute GvHD, who progressed to chronic GvHD at 1 year, 1-year non-relapse mortality (NRM), graft-versus-host disease relapse-free survival (GRFS) and survival outcomes at 3 years.
Results: Patient, disease, and transplant characteristics were well balanced, except for more severe acute GvHD in Ruxo + ECP arm (66.6% vs. 18.5%, P = 0.007) and longer Ruxo treatment in Ruxo alone arm (11 vs. 7 months, P = 0.05). The ORRs were 58% for Ruxo + ECP arm compared to 49% in Ruxo alone arm (P = 0.002) at last encounter and the duration of response was 17.6 versus 9 months (P = 0.3171), respectively. In both arms, 87% and 93% of patients could taper steroids rapidly by 50% and 16%. At 1 year, cumulative incidence of chronic GvHD was higher after Ruxo versus Ruxo + ECP, being 55% (95% CI: 42-69%) vs. 26% (95% CI: 22-64%) (P = 0.018). No statistically significant difference in 1-year NRM, relapse, and GRFS and survival at 3 years was observed.
Conclusion: Our data suggest improved long-term control of acute and chronic GvHD by combining Ruxo plus ECP compared with Ruxo alone.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








