Atrial Fibrillation in the Context of Thyrotoxicosis: Prevalence and Clinical Determinants
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6413Keywords:
Atrial fibrillation, Thyrotoxicosis, Hyperthyroidism, Risk factors, PrevalenceAbstract
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a frequent but variably reported complication of thyrotoxicosis, with mechanisms that extend beyond thyroid hormone excess. Clarifying its prevalence and determinants may guide early detection and management.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional study of adults with thyrotoxicosis. Clinical, biochemical, and electrocardiographic data were reviewed. Associations between variables and AF were assessed using generalized linear models with robust errors, and results expressed as adjusted odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
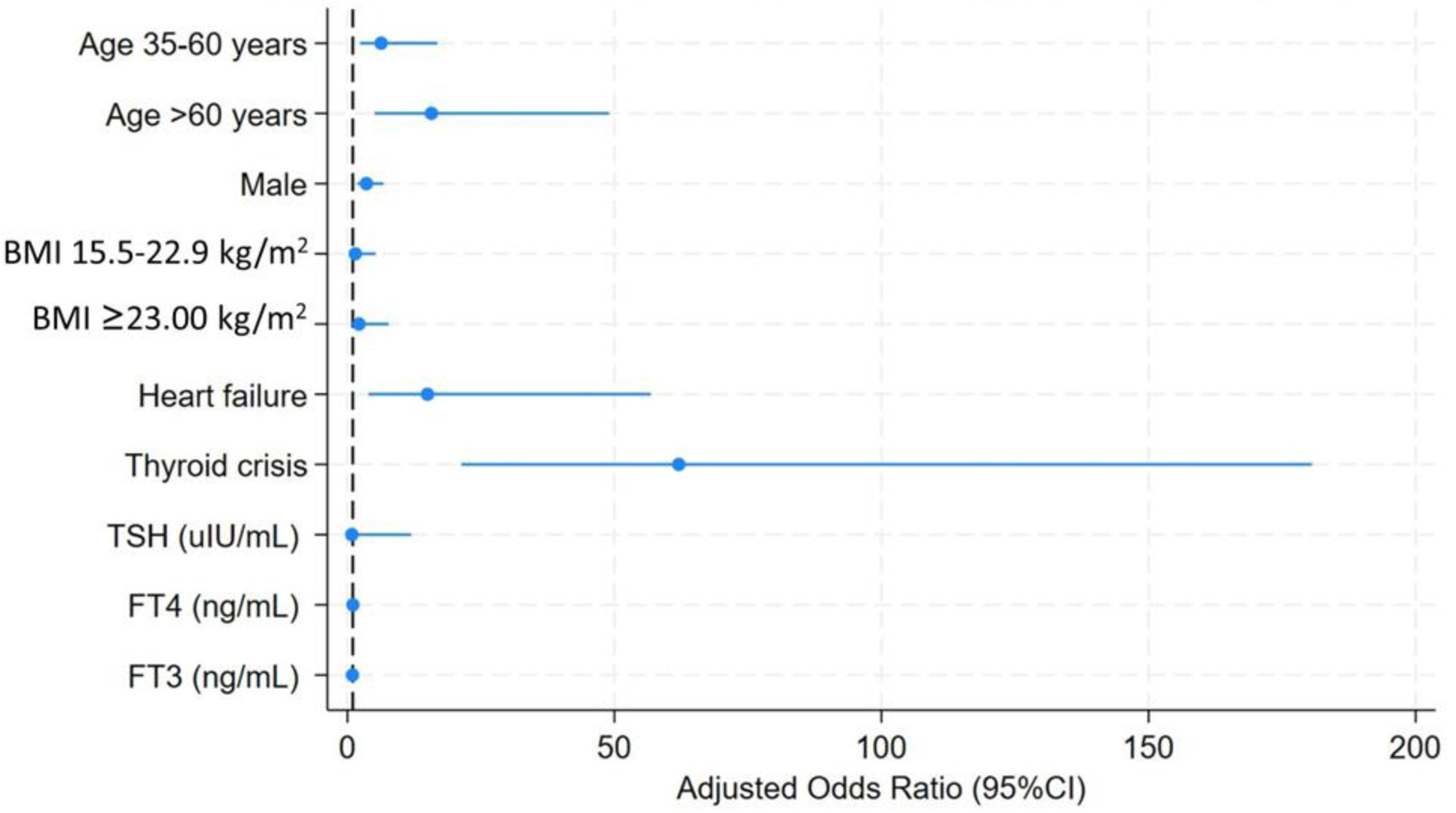
Results: Among 801 patients with thyrotoxicosis, 65 had AF, yielding a prevalence of 8.1% (95% CI: 6.3 - 10.2). Compared with non-AF patients, those with AF were older, more often male (48% vs. 20%), and more frequently had chronic kidney disease, dyslipidemia, diabetes, heart failure (HF), cerebrovascular disease, and thyroid crisis (all P < 0.01). In multivariable analysis, independent determinants included age 35 - 60 years (adjusted OR 5.48; 95% CI: 2.03 - 14.83), age > 60 years (adjusted OR 11.39; 95% CI: 3.43 - 37.76), male sex (adjusted OR 3.38; 95% CI: 1.70 - 6.30), HF (adjusted OR 11.25; 95% CI: 2.85 - 44.54), and thyroid crisis (adjusted OR 61.84; 95% CI: 21.89 - 181.32). Thyroid hormone levels were not independently associated with AF.
Conclusion: AF was observed in approximately 8% of patients with thyrotoxicosis. The findings suggested that clinical vulnerabilities - older age, male sex, HF, and thyroid crisis - were more strongly associated with AF than thyroid hormone levels. These results supported targeted AF screening in high-risk thyrotoxic patients and indicated that rhythm management should consider patient susceptibility alongside restoring euthyroidism.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








