Oral Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension-Targeted Therapy in Patients With Pulmonary Hypertension due to Interstitial Lung Disease
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6164Keywords:
Pulmonary hypertension, Interstitial lung disease, PAH-targeted therapyAbstract
Background: The aim of the study was to determine whether treatment with oral pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)-targeted therapy is associated with functional or hemodynamic improvement in patients with pulmonary hypertension due to interstitial lung disease (PH-ILD).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of 1,507 consented patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) from the University of Chicago PH Registry. Exclusion criteria included: enrollment in PH-related clinical trials, use of inhaled treprostinil or iloprost and prior PAH-targeted therapy initiated before consenting to registry enrollment, thus precluding baseline data. Data analyzed included demographics, interstitial lung disease (ILD) classification, PAH-targeted therapy, functional data, hemodynamics, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) before and after initiation of treatment. Data were analyzed using paired t-test, or related-samples Wilcoxon signed rank test.
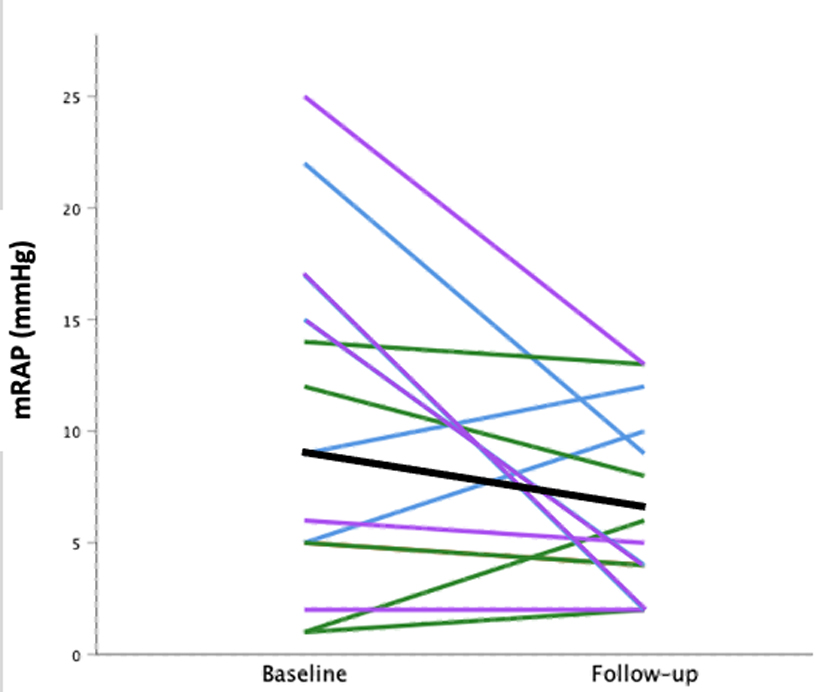
Results: Of 37 patients included, 27 (73%) received treatment with one PAH-targeted therapy and nine (24%) received dual therapy. At baseline, median NT-proBNP was 1,498 ng/dL (675 - 3,208), mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) was 45 ± 11 mm Hg, and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) of 9 ± 4 Wood units (WU). In patients with measurements both before and after treatment with PAH-targeted therapy, there was a decrease in PVR (n = 13, 8 vs. 5 WU, P < 0.001), an increase in cardiac output (n = 13, 4 vs. 5 L/min, P = 0.014), and a decrease in NT-proBNP levels (n = 26, 1,421 vs. 842 ng/dL, P = 0.045).
Conclusions: In this study, use of PAH-targeted therapy in patients with PH-ILD was associated with statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in NT-proBNP and pulmonary hemodynamics.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








