Construction of a Clinical Prediction Model for Complications After Femoral Head Replacement Surgery
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr6047Keywords:
Femoral head replacement surgery, Complications, Logistic regression, Risk factor, Line graphAbstract
Background: While femoral head replacement is widely used with remarkable efficacy, the complexity and diversity of postoperative complications pose a serious prognostic challenge. There is an urgent need to develop a clinical prediction model that can integrate multiple factors and accurately predict the risk of postoperative complications to guide clinical practice and optimize patient management strategies. This study is dedicated to constructing a postoperative complication prediction model based on statistics and machine learning techniques, in order to provide patients with a safer and more effective treatment experience.
Methods: A total of 186 patients who underwent femoral head replacement in the Orthopedic Department of our hospital were collected in this study. Forty-two of the patients had at least one postoperative complication, and 144 had no complications. The preoperative and postoperative data of patients were collected separately and medical history was collected to study the correlation factors affecting the occurrence of postoperative complications in patients and to establish a prediction model.
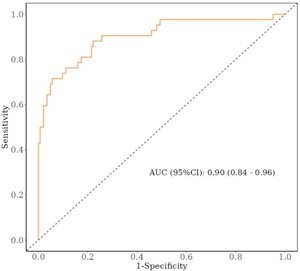
Results: Possibly relevant factors were included in a one-way logistic regression, which included the patient’s gender, age, body mass index, preoperative diagnosis of the mode of injury, osteoporosis or lack thereof, as well as medical history, surgical-related information, and laboratory indices. After analyzing the results, it was concluded that operation time, alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), white blood cell count, serum albumin, and osteoporosis, were the risk factors affecting the development of complications after femoral head replacement in patients (P < 0.2). The data obtained were further included in a multifactorial regression, and the results showed that operation time, AST, white blood cell count, serum albumin, and osteoporosis were independent risk factors for complications after the patients underwent femoral head replacement (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Based on the results of this study, five factors, including duration of surgery, AST, white blood cell count, serum albumin, and osteoporosis, were identified as independent risk factors for complications after patients underwent femoral head replacement. In addition, the prediction model developed in this study has a high scientific and clinical application value, providing clinicians and patients with an important tool for assessing the risk of complications after affected femoral head replacement.
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 The authors

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








